Home / Design of external sewerage
Sewage networks for any facility are as important a necessity as the respiratory or excretory system for the human body. The entire history of mankind is connected with fresh water bodies close to the place of residence, which provided the settlement with clean water.
But, unfortunately, human residence near a water source inevitably creates dangers of pollution for this source.
Contaminated water, in turn, is a source of danger to human health. That is why, after some time, people realized that in order to live comfortably near a water source, it is necessary to build special structures that would isolate and drain water contaminated during life.
Today, the design of sewerage networks is almost a scientific branch, which uses the most modern equipment to ensure maximum comfort for people living in the area, as well as to carry out maximum purification of water used in everyday life.
Modern external sewer network -
it is one of the key components in the construction of any modern building.
According to the modern classification, there are three types of sewerage systems:
- household and industrial;
- partial and complete;
- autonomous and centralized.
Partial sewerage assumes that when creating an external system, it is planned to implement exclusively a scheme for draining wastewater into a tank specially designated for these purposes with a sump function. A full sewer project also includes a septic tank, an additional treatment mechanism.
Industrial sewerage is a system for the disposal of industrial waste. Often, when designing such a sewer system, mechanisms are provided for cleaning wastewater from fats, organic waste, and other types of pollutants. The process of industrial wastewater treatment occurs using powerful modern treatment facilities.
The process of designing an autonomous sewerage system involves the use of various technological solutions: it is possible here to either implement a septic tank or a dry closet treatment system, or design modern powerful aeration units that allow for deep purification of wastewater from various types of pollution
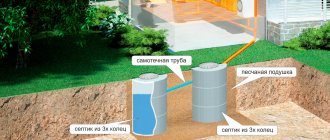
A septic tank is a special treatment device that has a tank design with three treatment chambers. Solid waste settles inside the first chamber. In the second and third chambers, procedures are carried out to purify wastewater from chemical or biological pollutants. After the third chamber - the last stage of purification, the water moves further through the system and ends up either in a special drainage well or in a specially designated filtration area.
The volume of the septic tank is determined for each specific case. The main factor influencing the required volume is the number of people living in a given family.
In addition to the above systems, there is another specialized type - storm sewers. This type of sewer system is designed to purify gravity drains formed as a result of water precipitation from the atmosphere.
Project for external sewerage networks
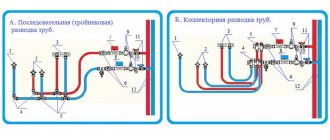
The process of designing an external sewerage system takes place in several stages, during which the identification of places for laying pipe communications, the correct calculation of places for creating ventilation structures, as well as places for installing plumbing are carried out.
Developing an external sewer system is a very complex process, as it requires attention to a whole range of important nuances. For accuracy and to ensure maximum quality of design when making calculations, it is important to rely on such indicators as: volumes of wastewater, the level of slope of the pipe structures used within the sewer system, the type of pipes that were chosen for the project.
It is important that a rational approach and accuracy in the design process guarantee significant savings in the customer’s budget: everything depends on the volume, and in some cases, correct design guarantees you savings of up to 30%.
Another important point is that the system, which was designed based on the world's leading industry requirements for modern sewerage, guarantees you a multifold improvement in the quality of water resources used in the building.
Taking into account all the difficulties and the huge number of important nuances that must be taken into account during the development of the project, such work can only be entrusted to highly qualified specialists.
Turnkey design and installation of external sewerage networks!
We guarantee you top quality when developing an external sewer system; our project will save you from the danger of unnecessary costs for repairs or reconstruction in the future. In our work we use advanced international standards of quality and comfort at affordable prices.
You can order a full range of services for the design, coordination and installation of sewer systems: we install any types of modern systems, regardless of their complexity, and also provide services for the correct installation of internal and external systems. We work in Moscow, Odintsovo and the entire Moscow region.
Cost of design work for external sewerage
The price for a project for connecting sewer networks in a private house ranges from 35 thousand rubles, and depends on the amount of work performed, the more and more complex, the more expensive.
All sewerage projects are carried out by highly qualified specialists.
| No./item | Sections | price, rub. |
| 1. | Development of an external sewerage project for a private house | from 45 000 |
| 2. | Development of an external sewerage project for a village, SNT, DNP | individually |
We undertake both small volumes and lengths of several thousand meters!
The importance of making correct calculations when designing a sewer system
Wastewater is not just a flowing liquid of a homogeneous structure. Sewage includes impurities of various fractions and weights. The polydisperse substance, which is wastewater, also contains colloids and suspensions. The speed of movement of sewage may change periodically. If liquid inclusions move faster, then heavy impurities in the form of sand, slag, etc. more often settle on the walls of the pipes, forming growths and blockages. As a result, the collector becomes clogged. To prevent this from happening, hydraulic calculations of sewer networks are carried out at the system design stage.
To calculate all parameters, the estimated volume of wastewater is taken as the initial data.
Calculation according to the Lukin table for a diameter of 150 mm
In the case under consideration, we are talking about intra-block sewerage, so we will try to select a pipe with a diameter of 150 mm.
Open the Lukin tables for this type of pipe:
Fragment of Lukin tables for diameter D=150 mm
We are trying to find the minimum slope, because... this will contribute to a minimum pipe laying depth and reduce the amount of excavation work.
Main types of payments
When performing calculations, data from SNiP 2.04.03-85 “Sewerage. External networks and structures”, as well as recommendations from SP 40-102-2000 “Design and installation of pipelines for water supply and sewerage systems made of polymer materials. General requirements".
Slope of sewerage pipeline
Recommended slope
The slope is responsible for the free-flow operation of the system and the unhindered discharge of wastewater into the receiver. The SNiP tables show the recommended minimum slopes for each pipe diameter:
- cross section 110 mm - 1 cm for each linear meter of the collector;
- diameter 160 mm - 0.8 cm per meter;
- cross section 220 mm - 0.7 cm per meter of collector length.
For the internal part of the communication, a slope of 1.5-2 cm is maintained for each linear meter.
If there is a need to calculate the slope of the collector using the formula, use the following: d x coefficient, where d is the cross-section of the pipeline, and the coefficient corresponds to the following values:
- 160 — 0,6;
- 220 — 0,7;
- 500 mm - 1;
- 600-800 — 1,1;
- 1000-1200 mm - 1.3.
The slope is made towards the central highway or yard septic tank/cesspool.
Calculation of pipe cross-sections
To lay pipes of the required diameter, you can use the SNiP data. The recommended values look like this:
- the internal part of the sewer from all plumbing fixtures - 50 mm;
- toilet pipe - 110 mm;
- public riser - 110-160 mm;
- external part of the sewerage system - 160-220 mm (for the private sector and multi-apartment residential building);
- central highway and industrial enterprises - from 500 mm.
With the correct cross-section of the collector, the fullness of the pipe will be approximately 0.3-0.5 of its total diameter.
Calculation of reservoir filling
The fullness of the pipe is calculated using the formula: Y= h/d. Here the value h is the maximum liquid level in the system, d is the internal cross-section of the collector. Normally, the result should range from 0.3 to 0.6.
An example of calculating the filling level of a sewer pipe in the private sector: the initial data is taken as the filling level of the collector within 60 mm, while the cross-section of the pipe is 110 mm. According to the above formula, 60/110 equals 0.55. The value is normal.
Calculation of pipe capacity
At the time of designing the system, the throughput of the pipeline must be calculated - the estimated wastewater flow rates are determined. This parameter is calculated relative to the day, hours and seconds, depending on the purpose of the building (residential, enterprise, etc.). Secondary waste flow is calculated in liters; for daily and hourly data is calculated in m3.
Data for average costs:
- Qcp.day= p · Nр / 1000 m³/day;
- Qcp.hour= n · Nр / (24 · 1000) m³/hour;
- qav.sec= p · Nр / (24 · 3600) l/sec.
Where:
- n - average standards of water disposal per 1 resident (in liters);
- Nр – estimated number of inhabitants.
For maximum spending:
- Qmax.day = Qcp.day · kday = n · Nр · kday / 1000 m³/day;
- Qmax.hour= p1 · Nр · ktotal / (24 · 1000) m³/hour;
- qmax.sec= p1 · Nр · ktot / (24 · 3600) l/sec.
Where k are the unevenness coefficients: kday – daily, ktotal – total.
To determine the maximum throughput of the collector, use the formula: q = aХv, where the value of a is the area of the live cross-section of the flow, and v is the speed of wastewater transportation.
The norm for maximum speeds for each type of pipe (manufacturing material) is considered to be 8 m/s (metal) and up to 4 m/s (concrete, plastic). If the speed actually turns out to be higher, it needs to be dampened by turning the system or installing differential wells.
All hydraulic calculations must be carried out sequentially. However, more often, craftsmen use not formulas for calculations, but the data given in SNiP (in the form of tables), or use an online calculator.
Construction of a sewer collector
When constructing a sewer system on their own, all owners of private housing are faced with the concept of “sewer collector”. It should not be confused with a heating manifold - they are not the same thing.
When constructing a sewer, heavy equipment is often used
So, the sewer is the main channel of the drainage system.
It is a pipeline consisting of sewer pipes laid in trenches and collection and treatment tanks. A city sewer is nothing more than a large-diameter underground pipe, several hundred kilometers long, which collects and transports wastewater to treatment plants, filtration fields, and discharge points.
The following can serve as collection and cleaning containers in the domestic sewage system:
- Cesspool. It is a waterproofed structure for collecting wastewater and waste. Its device is simple and accessible. However, a system with such a structure cannot be called safe and comfortable: waste that falls into the pit does not undergo cleaning, can end up in the ground and is a source of unpleasant odor in the area.
- Septic tank. Unlike cesspools, septic tanks are more modern and environmentally acceptable structures. They allow you not only to collect waste, but also to clean it.
According to the method of installation, the sewage system can be gravity or pressure. A gravity collector is a pipeline laid at a certain angle: wastewater in such a system passes to the collection and treatment site through an inclined pipeline. A pressure collector is installed where it is not possible to build an inclined pipeline (due to the high level of soil water and soil characteristics). It consists of a pipeline, a pump or pumping station, and tanks for collecting and processing wastewater.
Determination of effective storm sewer parameters
If a storm drain is installed in parallel with the fecal-domestic system, for correct calculations the following data must be taken into account:
- norm of annual precipitation in the region;
- area of the serviced facility;
- type of coating (concrete, soil, tiles);
- soil properties on the site;
- mass of rainwater drained.
All data, except the last point, is taken from the local geodetic service. Using the information obtained, gutters are selected according to their throughput. For example, let's calculate data on storm drainage trays using the formula: Q=q20∙P∙φ
Values:
- Q is the average annual volume of storm water in the region;
- q20 — coefficient for the region;
- P is the area of the object from which water will be drained;
- φ is the water absorption coefficient for different types of materials.
Having determined the throughput of the tray using this formula, gutters are selected in accordance with their technical characteristics. As a rule, this parameter is indicated on the product.
Location rules
The design of a collector in a private house has a lot of nuances and begins with the design of the system. A special role here is played by the correct placement of the component parts of the device.
The efficiency and safety of the system depends on the correct placement of the collector.
The location of the elements of the sewer system is influenced by the terrain, the climate in the region, the depth of soil freezing and the occurrence of groundwater. In addition, the types and parameters of equipment (pump, septic tank) should be taken into account. The need for equipment at the entry point for the sewer truck will depend on this.
To ensure safe sewerage, experts advise:
- Place the septic tank at a distance of 5 m from a residential building and 1 m from residential buildings;
- Locate treatment facilities at a distance of 30 m from wells and wells with drinking water;
- Place VOCs at a distance of 10 m from rivers and streams;
- Place waste collection and treatment stations at a distance of 30-50 m from the nearest natural bodies of water.
Before building a collector, you should consult with specialists.
To lay the sewer main, you should choose pipes that are resistant to corrosion and aggressive agents. The angle of inclination of the collector must be calculated based on the diameter of the pipes: the larger the diameter of the pipeline, the smaller the slope the system should have. In order to prevent overflow of the water supply and treatment facilities, it is necessary to first calculate the collector.
Calculation of external sewerage
To design the outer part of the collector, calculate the following data:
- The length of communication from the outlet from the house to the connection to the septic tank or central highway.
- Pipe diameter (for private construction, tubes with a cross-section of 110, 160 or 220 mm are used).
- Waste volume. The norm is 2 cubic meters per person per month.
- The presence of turns and drop wells along the length of the communication.
To install a free-flow system, a slope must be observed. If, due to the peculiarities of the terrain, a pressure section of the sewerage system is installed, a special caisson is installed for the sewage pump and a siphon is installed. It will protect a section of the system from exposure to sub-zero temperatures and stagnation of fecal matter.
What does a drainage system project include?
The project is a package of technical documentation with a complete description, engineering calculations and installation recommendations. It also includes:
- estimate and specification indicating recommended units, materials and devices;
- data on the economic efficiency of the system, its safety and reliability;
- detailed layout of pipes, units, pumps, and other elements.
The documentation developed during the design of the sewer system becomes a “road map” for the installation specialists. Accordingly, the operational characteristics of communications directly depend on the correctness of the design.
If you need a flawlessly functioning, reliable and durable sewerage system, order its design from!
free consultation with a specialist
Calculations for large diameter pipes
At high costs, the question of choosing the pipe diameter arises. For example, for a flow rate of Q = 20 l/s, at least three options are suitable:
The first option is a 200 mm pipe, a slope of 6 ‰.
The second option is a 250 mm pipe, slope 3.5 ‰.
The third option is a 300 mm pipe, a slope of 5 ‰. (for this diameter the speed should already be at least 0.8 m/s)
Collection and analysis of initial data for design
Designing sewer networks requires some preparation, which consists of drawing up technical specifications, even if the work is carried out independently. This way you won’t have to redo the work several times.
List of initial data to be prepared:
- System type: autonomous or connected. To tap into a centralized sewer, you will need documents for the house and permission to make the tap.
- With an autonomous system, you need to decide on the disposal method (biological station, septic tank, sealed storage tank, cesspool).
- Geological data: soil freezing depth, aquifer depth, location of reservoirs, location and depth of a well or borehole (with autonomous water supply), soil data.
- Precipitation data (when designing storm sewers).
- Based on the recommendations of SNiP, calculate the peak load, depending on the number of people living and plumbing equipment. If the residence in the house is seasonal, this is also taken into account in the calculations.
- Draw up a floor plan indicating drainage points from bathtubs, showers, washbasins, sinks, toilets, bidets, washing machines and dishwashers.
Terms and price of designing water supply and sewerage systems
The cost of developing design or working documentation for an object is calculated individually; the design price depends on the following factors:
- area of the designed facility;
- functional purpose of the object;
- the need for a specialist to inspect the facility;
- location of the designed object (affects if it is necessary to carry out an inspection of the object).
Design cost calculation
To calculate the timing and cost of designing a water supply system for your facility, send a request by email or using the form on the website, our specialists will prepare a commercial proposal in a short time.