House with independent sewerage and water supply
Today we have to figure out how the sewerage and water supply of a private home can be organized in the absence of centralized networks. We will discuss possible sources of drinking and household water, methods of waste disposal and materials that are best used for installing water supply and sewerage systems.
Internal water supply and sewerage systems
Internal systems that supply clean water and drain wastewater are important, interconnected life support systems. Even compact country house projects cannot do without water supply and sewerage, and the design is carried out using the SP (set of rules) “Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings.”
This document is used under the following conditions:
- Internal water supply systems (cold and hot water), sewerage (sewage), as well as drains are designed.
- The project is created for a facility where permanent or long-term presence of people is provided. This includes industrial, public (not higher than 50 m), residential buildings (no higher than 75 m).
The provisions do not apply to facilities with more specific purposes, for example, places of production and storage of flammable and explosive substances. They require a special fire-fighting water supply system designed for other volumes and loads.
Cold and hot water supply system Source promklimat.ru
They are also not suitable for enterprises with special technological needs (for example, where industrial cooling systems are used), for systems that heat water for medical procedures, or water fire extinguishing systems.
Document structure
Chapter 1 is devoted to the scope of this SP. Chapter 2 of the SP on water supply and sewerage of internal networks contains regulatory links to documents, information from which was used in this set: GOSTs, other SPs, SanPiNs. Below (in Chapter 3) terms according to GOST are given, as well as terms with definitions found further in the text, designations and units of measurement are listed. The document further includes the following information:
- Chapter 4. General provisions. Issues of compliance with the standards of the materials, equipment, pipes, fittings used are considered, and the quality of wastewater is determined; lists the materials the use of which is not permitted. The buildings in which the installation of internal water supply and sewerage networks of this type are not permitted are listed.
Water supply diagram and meters Source strojdvor.ru
- Chapter 5. Plumbing. The parameters (quality and temperature) of water are listed, and it is also indicated what water (heat) consumption this system is designed for. It describes what water supply systems are provided, describes cold and hot water systems, and their hydraulic calculations.
- Chapter 6 Lists additional requirements for internal networks in non-standard environments. These include seismic areas, as well as places with possible soil deformation (subsidence, freezing). The chapter concerns the laying of pipes in basements, under the foundations of buildings, when constructing inputs into the building; Features of the work and precautions during installation are listed.
- Chapter 7. Describes the engineering equipment used: pipes, fittings, materials, equipment. The chapter lists the types of fittings and the places where they need to be installed. The installation of cold and hot water meters, spare and control tanks is separately stipulated. A separate issue includes pumping units, which can be designed with automatic, remote or local control.
Types of water pressure fittings Source blog-potolok.ru
- Chapter 8. Water disposal. It tells about different internal sewerage systems, the conditions for their selection; shows how to calculate waste flow for risers and horizontal pipelines. Limitations for laying an internal sewer network (hidden or open) are given, issues of ventilation, internal drains are considered, and a hydraulic calculation is provided.
- Chapter 9. Additional requirements for the arrangement of sewerage and drains apply where special natural or climatic conditions are observed. These include earthquake-prone areas and areas with subsiding and freezing soils.
- Chapter 10 Lists the requirements that must be met to improve energy efficiency. These include the installation of modern fittings, regulation of water pressure, zoning of water supply systems, and the use of effective thermal insulation materials.
- Chapter 11. Issues of reliability and safety during operation are considered, conditions of durability and maintainability are listed.
Sewerage installation in a multi-storey building Source kanalizaciya1.ru
- Chapter 12. Lists the sanitary and epidemiological requirements for water quality and cases when deviations from the standards are possible.
- At the end of the document there are appendices with calculations of water consumption under different conditions.
Water supply and sewerage: design subtleties
If design solutions are made with high quality, taking into account all requirements, the system will operate for a long time and uninterruptedly. When designing based on a joint venture for internal water supply and sewage systems of buildings, the following additional factors are taken into account:
- Operating conditions, frequency of use of water supply and sewerage systems.
- Relief of the territory where construction is planned.
- Soil characteristics (composition, characteristics).
- Estimated load on the network, pressure in the system, other parameters.
Sewerage in the basement of an apartment building Source pro-remont.org
Design of internal water supply and sewerage systems of buildings is based on the following materials:
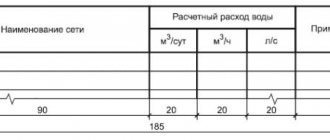
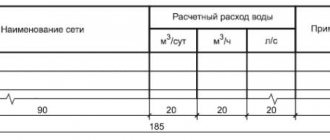
- Results of hydraulic calculations. They determine the parameters of the environment: flow of cold, hot water, waste water (maximum, average, per unit of time), consumption rate by the consumer, circulating water flow in the system, as well as pressure and pressure loss, heat loss of hot water supply, speed of water movement through the pipes.
- Determination of system characteristics. Based on the joint venture for internal water supply and sewerage, the diameter of the pipes is set, suitable fittings and equipment parameters are determined.
- Drawing up a diagram of pipe laying, determining the optimal location for treatment facilities and pumping units.
- Sanitary standards requirements. Thus, the temperature of hot water in residential buildings should be within +60-65°C, regardless of what heating system is used. The rule does not apply to preschool institutions, where the temperature should not be higher than 37°C.
Sewage diagram in a private house Source waterstok.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in water supply, sewerage and related work
Requirements for water supply and sewerage systems
Internal water supply refers to systems of pipes that supply cold or hot water, usually in two directions: to sanitary fixtures (household, industrial, or children's and medical institutions) or to fire hydrants.
The choice of a source of cold water for domestic water supply is influenced by sanitary, hygienic and fire safety standards, which is why water is supplied in two ways: from centralized or local sources. Based on the purpose of the object, water pipelines of the following types, different in design, are designed:
- household and drinking water (cold water supply network, cold water supply);
- hot (hot water supply network, DHW);
- industrial purposes;
- negotiable;
- firefighter.
In residential construction, internal cold water and hot water networks are designed in accordance with the joint venture for internal water supply. Their schemes consist of technological risers, inlets, distribution lines and shut-off and control valves; the accounting system is also turned on.
General scheme of water supply and sanitation Source kanalizaciyalite.ru
The following requirements apply to cold water and hot water pipelines:
- The service life of pipes and connecting parts is at least 50 years (if the water temperature is kept at 20°C and the pressure is within normal limits), or at least 25 years (temperature 75°C).
- The technical part of the networks is made of metal; in other places it is possible to use polymer materials that meet the technical conditions.
- In new or reconstructed buildings, cold and hot water meters are installed to organize separate accounting of water intake. The meters are supplemented with mechanical or magnetic-mechanical filters and shut-off valves.
Water disposal is designed on the basis of a joint venture for sewerage of internal networks.
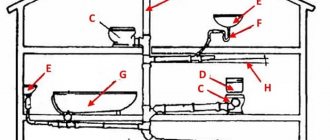
The internal sewage system depends on the purpose of the building (for example, residential or industrial), and may include the following systems:
- Household. Provides for the removal of wastewater from residential premises, includes all sanitary fixtures (washbasins, toilets, drains from showers and bathtubs).
Household cold and hot water meters Source 365news.biz
- Production. Disposes industrial wastewater. This includes drainage from fire extinguishing.
- United. It removes wastewater from the first two categories.
- Internal drains. The system is needed to drain rain and melt water from the roof of the house, with output to the external network.
Wastewater disposal is organized according to the principle of gravity flow through closed free-flow and pressure pipelines. For installation, pipes and connecting parts with a service life of at least 25 years, made of cast iron, polymers, as well as chrysotile cement products are used; The use of steel pipes is prohibited.
Internal drains (from the roof) are prohibited from connecting to domestic sewerage; they are diverted outside (bypassing internal networks), and one of the external networks (rain or alloy sewer) is used for connection. Gutters are installed on the roof to collect water. They are placed taking into account the structure of the building, the topography of the roof and the capabilities of the funnel itself (catchment area). For any design features of the roof, the maximum distance between adjacent drainage points is set; it should not exceed 48 m.
Drains on a flat roof Source stroykroff.ru
Water treatment
Another extremely important point when installing water supply is water treatment, which involves performing special technical operations to process incoming water in order to bring its quality characteristics into compliance with established sanitary standards and consumer requirements.
This includes:
- water clarification,
- cleaning from mechanical impurities,
- demineralization,
- disinfection and disinfection,
- adjustment of acidity and alkalinity indicators, etc.
For this purpose, we install special highly efficient filter mechanisms.
Order services
Sewerage: external networks and structures
Sewerage refers to a system of pipelines designed to collect and transport wastewater; There are three types of sewer systems (CS): domestic, industrial and storm water. Each of them can be local or centralized, the difference lies in the volume of transported waste.
The CS is designed on the basis of the provisions of the joint venture on external sewerage and related documents, GOST, SanPiN, and other joint ventures. Set of rules 32.13330.2018 “Sewerage. External networks and structures" has a narrower scope. It is used in the design and reconstruction of compressor stations for wastewater of domestic and natural (rain, melt water) origin, as well as industrial wastewater, similar in composition to domestic wastewater.
Laying the external compressor station Source ecomont.ru
Components of the external CS
Competent design, correct selection of components and compliance with the rules specified in the documents will ensure the correct operation of engineering communications. Environmental safety and how quickly an emergency situation can be corrected depend on the project. The external CS consists of the following groups of equipment:
- Pipeline. It is completed from pipes of different materials and parameters (length and cross-section).
- Wells. According to their purpose and method of use, they are divided into inspection (revision), drainage, as well as rotary and differential types.
- Issues and receivers. They direct wastewater to a treatment tank.
- Collector. The main channel of the city compressor station, a large-diameter pipe located underground. A collector collects wastewater from a certain area and transports it to a treatment plant.
- Pumping stations (pumping). They are used in wastewater treatment plants to supply wastewater in small volumes.
Pipes for external compressor station Source ytimg.com
- Treatment facilities. Engineering structures that purify wastewater to an acceptable condition that does not disturb the ecological balance. They vary in volume and power, and are often used in private areas. The group includes septic tanks of various designs, treatment wells, and aerators.
Features of CS design
Water supply and sewerage are two parts of this water consumption system; they are inextricably linked with each other. The characteristics of internal systems invariably influence what parameters the external CS will have. Therefore, the design of external sewerage is carried out in conjunction with the water supply network.
To avoid emergency situations during operation, calculations and installation of sewer pipelines are carried out on the basis of joint ventures of external networks and water supply and sewerage structures. Building codes and sanitary requirements are mandatory for companies of all types of property. They must be observed by individuals who intend to make their home more comfortable with the help of an autonomous external sewage system.
Septic tank is one of the options for CS Source iseptik.com
The way in which domestic and rainwater will be discharged also depends on the following external factors:
- Soil features. They must be studied before starting the design of the SC, as this affects the choice of installation method and further operational safety. Particular attention is paid to unstable, heaving soils.
- Features of groundwater. Their regime is studied: quantity, aggressiveness (predominant chemical type), level of occurrence.
- Features of the local winter climate. The depth of soil freezing is taken into account when choosing material for thermal insulation of pipes.
- Estimated volume of wastewater. In the residential sector, it depends on the number of residents who will use water supply and sewerage. In public buildings and industrial facilities, calculations are carried out according to different criteria.
The project specifies the distances from the compressor station to residential and industrial buildings, and the distance to treatment facilities. If it is necessary to cross a CS across a highway or railway, its procedure is also justified in the project, and the arrangement is regulated in accordance with the joint venture for water supply and sewerage of external networks and structures.
The correct slope is important for the functioning of the system Source trubovod66.ru
Plumbing installation
Despite the apparent simplicity of this process, it is best to entrust the installation of plumbing (plumbing, sewerage) to a specialist, because all these devices are quite expensive. But if you already have experience in performing such work, it is quite possible to do this part of the work yourself. The main thing is to carefully consider the installation locations of various devices, this will allow you to reduce the number of pipelines being laid, and therefore reduce the cost of the system.
With a competent approach to the design and use of high-quality materials, sewerage and water supply systems will serve you for a significant period of time.
Video description
About water supply and sanitation of residential buildings in the following video:
Depth of CS and choice of materials
The project indicates the minimum depth of the pipeline, which is associated with economic reasons and thermal engineering calculations. Usually the parameters of existing networks are taken into account; the pipes are laid 30-50 cm below the freezing point of the soil. The choice of maximum depth is influenced by the type of soil, the diameter of the pipeline, the method of installation (laying), and the material of the pipes.
For the installation of sewerage networks, pipes made of the same materials are used as for water supply networks. The main criterion is resistance to aggressive media and abrasive waste particles. The joint venture for water supply and sewerage of external networks and structures allows the use of products made of polypropylene, polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride; steel, cast iron, reinforced concrete options are possible.
The depth of placement depends on the freezing point of the soil Source superdom.ua
Storm drain
Stormwater is implemented in two ways, in the form of a point or linear system. A point system is storm water inlets with drainage pipes, protective grilles and filters that retain sand. A linear system is needed in order to not only collect, but also transport water; it is formed using the following elements:
- Storm water inlet. Provides collection of atmospheric and melt water, has the appearance of a grate, and is installed under the drainpipe, along the paths.
- Door tray. A type of rainwater inlet with similar functions. Installed at the entrance to the house or at the gate, it drains water and dirt into the sewer system.
- Tray (gutter). Element of surface (storm) drainage. The trays are laid in trenches, they organize the movement of water by gravity, for which they are provided with a slight slope towards the compressor station.
- Pipes. Like trays, they drain water, but are laid underground.
Exterior view of the rainwater inlet Source saucyintruder.org
Modern water treatment
Modern septic tanks use a number of wastewater treatment methods: mechanical, chemical and biological. Biological treatment is recognized as the optimal method. This method uses microorganisms that themselves destroy organic contaminants. .
In practice, several methods of waste disposal are possible:
- diversion to the terrain,
- drainage of water through a perforated pipe by gravity,
- drainage of water by gravity into a drainage well,
- discharge to the storage system.
In addition, follow these guidelines:
- Discharge of wastewater from a septic tank into the ground is used for subsurface irrigation of agricultural crops. The sludge that is then removed from the septic tank serves as fertilizer.
- A system for draining water directly into the ground is possible for sandy or sandy loam and loamy soils.
- To drain wastewater into heavy loams, a special engineering solution will be required.
Video description
About the intricacies of drainage systems in the following video:
- Sand catcher. A filter structure on which sand suspended in water from trays is deposited.
- Inspection (inspection) wells. Help monitor and maintain storm drainage elements.
Linear CS, in accordance with the requirements of SNiP for water supply and sewerage of external networks and structures, must be installed with a slight slope towards the collector. If for some reason the slope cannot be ensured, then the water will not be able to move by gravity; then the system is supplemented with a pump.
Calculation of a storm sewer boils down to determining its diameter, for which the following data is used:
- Drainage area. The area of the roof, paths and platforms is taken into account - all surfaces with a waterproof coating.
- Location of existing underground communications.
- Terrain conditions: soil features and average precipitation.
Installation of a storm drain in a private house Source inservo.ru
Well for water supply
The well is considered one of the most accessible and common sources of water for private homes. This method is preferred if the water is at a depth of 5-15 meters. Depth and productivity are the main criteria when constructing a well. The water in the source must be sufficient to meet the needs. If you have a well, you can provide your home with liquid in the amount of 500 liters per day.
The well should not be located close to above-ground buildings (at least 5 meters). And also to sources of possible pollution: sewers, toilets, landfills (at least 50 meters).
The procedure for performing actions when constructing a well:
- Determining the location of the well using ionomer frames.
- Selection of building materials: reinforced concrete rings, brick, stone, processed logs.
- Digging a well manually or using special equipment.
- Interior and exterior finishing works.
One of the advantages of supplying water to a private home using a well is that in the absence of electricity, water can be extracted from it manually using a rope and a bucket. In addition, the price for digging a well is much less than for installing a well, especially an artesian one.
A few more advantages of wells:
- Service life - about half a century;
- There is no need to collect a package of official papers to install a well on your country property;
- All work on cleaning and disinfecting the well is convenient to carry out, thanks to the large diameter of the rings;
- Availability of clean water, free of rust and chlorine.
Briefly about the main thing
Internal water supply and sewerage systems, together with external sewerage networks, form a single system that ensures living comfort. Any life support system begins with development. Design is carried out on the basis of regulatory documents: SP, SNiP, GOST, SanPiN. Only in this case is it possible to achieve uninterrupted functioning of the entire complex during a given service life.
The design of both life-support systems is linked to each other, as well as to the working documentation of the facility. For each system, factors influencing its parameters are identified, and the necessary calculations of loads, pressure, watercourse speed, and other parameters are carried out. A properly designed and installed system will cope with any load; Proper selection of materials for pipes plays an important role in long-term operation.
Ratings 0