Related Articles
Is housing prices expected to rise further, and what prospects do experts voice?
2 weeks ago
Engine spare parts for Isuzu
July 9, 2021
What you should know when replacing brake hoses yourself
July 4, 2021
During the commissioning of sewer systems, specialists conduct an external inspection of the pipeline, instrumental and technical checks. Recently, television inspection equipment has often been used - https://vistaros.ru/stati/teleinspektsiya-truboprovodov/kupit-sistemu-dlya-teleinspektsii-trub.html to be able to inspect pipes from the inside.
Acceptance procedure
After receiving an application to Vodokanal to connect a new sewer system to municipal wastewater networks, an acceptance committee is formed whose responsibilities include:
- Reconciliation of executive and technical documentation with design documentation.
- Identifying deviations from the approved project, checking permitting documents for these changes.
- Inspection of communications on site.
- Identification of errors and shortcomings during construction (time is assigned for correction).
When the defects are eliminated, the commission members sign the act and the structure is put into operation.
During the on-site visit, the commission checks:
- Do the locations of fasteners and methods of fixing pipes correspond to those specified in the project?
- Is the pipeline securely fastened?
- Angles of pipeline connections (kinks, which provoke frequent clogging, are unacceptable).
- The slope of the horizontal pipeline must correspond to the design data.
- The riser must be positioned vertically; a deviation of several degrees is permissible in accordance with the standards.
- The height of the exhaust part of the sewer system must correspond to the design.
- No blockages or construction debris in the pipes.
- Reliable fastening of plumbing fixtures.
- Quality of materials, reliability of installation, necessary equipment.
To check the tightness of the pipeline system, hydraulic tests are carried out. To do this, 75% of the plumbing fixtures connected to the site are opened. The system is considered to have passed the test if no leaks are detected at the joints, fittings and pipes. The result is certified by an act (appendix to appendix 4 of SNiP 3.05.01).
Reconstruction of NVC networks
When carrying out major repairs or restoration of a building, it is necessary to pay attention to the existing service life and assess the general condition of the NVC networks. If their design life has long expired, then it is necessary to order a complete reconstruction of the NVC networks. During the reconstruction process, the following components are subject to complete replacement:
- storage tank together with a pumping group;
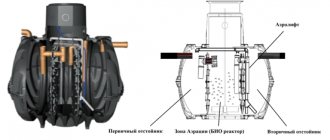
- local treatment facilities, which are designed to filter and timely drain stormwater with the performance required for a specific area and conditions;
- filter cartridges to ensure the necessary environmental safety requirements.
For all questions regarding the design, installation and reconstruction of external utility networks, please contact.
Video diagnostics
Communications owners resort to video diagnostics at the stage of handing over the object to the contractor in order to assess the quality of work and, if necessary, have photo and video materials that can be used in court.
Depending on the length of the pipeline and the diameter of the pipe, different devices for teleinspection are used:
- Pushable module (chamber on a cable) - used for pipes with a diameter of 70 to 400 mm or in places where the robot can get stuck.
- Floating module (boat with a camera) – used for large-diameter flow-through sewerage.
- Robot (self-propelled system with a camera) – for diagnosing long-distance pipelines with a diameter of 150 to 1200 mm.
Photos and video materials transmitted by the camera can be viewed in real time on the remote control monitor or saved on digital media. Depending on the equipment model, you can get a color image of 420-480 TV lines. Illumination is provided by LEDs.
Testing of external sewerage network
Composition of the external sewerage system
The objects included in the external sewerage network include: pipelines, wells (in places of differences in network heights and branches), existing treatment facilities (WTP), for example, septic tanks, storm water inlets and storm drains.
Pipeline Exam
External sewer lines are also classified as non-pressure. The first preliminary testing is carried out immediately after installation of the pipeline, even before filling it with soil, and if thermal insulation of pipes is used, then the test is carried out before the final completion of this type of work. The second testing (acceptance) is carried out after backfilling the laid pipeline.
The first is a visual inspection, during which the correct location of the pipeline is checked: compliance of the locations of wells and pipe lines with the design documentation. Geometric characteristics are checked, such as the straightness of the lines, whether there is any altitude subsidence of the branches, and compliance with the required slope with a decrease in the route to the treatment plant is checked.
All connections are also visually inspected. They are checked for correct installation and absence of defects. The results of this examination, as well as the results of other inspections, are recorded in the acceptance documentation.
After this, they begin the hydraulic examination of the laid line. Testing is carried out sequentially for each TP section located between two adjacent wells (the tested sections of the main line are separated from the network using plugs for the duration of the exam). Wherein:
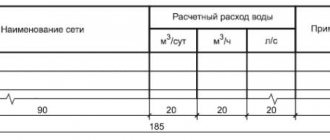
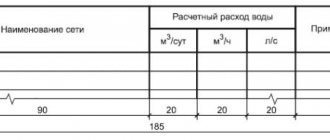
- If the pipes are laid in dry soils, or in wet ones (and in the second case, the groundwater level (GWL) next to the upper well is at a depth greater than half the distance from the well hatch to the pipe shell), then the volume of water that was added to the pipe is determined pipeline. Ngv > ½ Nt. (to make it easier to navigate, see the picture below)
- If the pipes are laid in wet soils, and the depth of the groundwater level in the specified location is less than half the height Ht, then the volume of water entering the water supply system from the ground (infiltration) is determined. Ngv < ½ Nt.
In the case of a preliminary test, the hydrostatic pressure at the highest point of the pipeline is determined. Its value is determined by the excess of the liquid level in the riser/well above the pipe shelyga or these levels above the water main water supply located above the shelyga. For non-pressure ceramic, reinforced concrete and concrete mains, the hydrostatic pressure is assumed to be 0.04 MPa. The test time is 30 minutes. During this period, if necessary, add water to the riser or well so that its level does not drop by more than 20 cm. If no water leaks were found during inspection, then the test is considered successful.
Acceptance testing is different from staging testing. The pipeline under test is filled with water and left to stand:
- For reinforced concrete pipes - 72 hours;
- If the line is made of other materials – 24 hours.
After this, the tightness of the joints is determined by the volume of water added to the upper well during exfiltration. During infiltration, the volume of water flowing from the ground in the lower well is determined. SNiP regulates the maximum volumes of added or inflowing water. The values depend on the diameter of the pipes and the type of their material and range from 1 to 8 liters. If during testing the liquid volumes do not exceed the standard values, the testing is considered successful.
The standards provide for random inspection of sections of the main line in situations of water shortage. Test areas are selected by the customer in the following quantities:
- With a total pipeline length of up to 5 km – 2-3;
- For a length of more than 5 km - 30% of the length, divided into several sections.
If the results of random testing are found unsuccessful, the entire highway is subject to inspection.
Pneumatic tests are carried out in cases where the air temperature is below 0⁰С or when there is no water for hydraulic. They are carried out similarly to those described above.
Well Exam
Not all of them are tested. Thus, wells that have neither external nor internal waterproofing, as well as those in which the design does not provide waterproof walls, are not tested. Those wells that are subject to examination can be tested simultaneously with pipelines (acceptance tests) or separately from them (preliminary). They are tested on:
- Adding water (objects with internal waterproofing);
- Inflow of groundwater into wells - for wells with external waterproofing.
Exams are considered successful if the amount of added or inflowing water does not exceed standard limits. In this case, the permissible volumes of inflow or addition of water are calculated per 1 meter of well height. This value is the same as for 1 meter pipe length.
Water supply systems and pressure pipelines for external sewerage
Pressure networks of external sewerage and water supply are also examined for strength and tightness in two stages: preliminary and acceptance. Before testing begins, waterproofing of joints and welded joints must be checked. All necessary fittings, pressure gauges and flange plugs must be installed on the TP. Areas undergoing hydraulic testing are filled with water and air is removed from them.
The technology of intermediate and acceptance testing differs. In the first case, the pressure in the main section is increased to Pi (test pressure), and it is maintained by pumping water for 10 minutes. In this case, a decrease in pressure by more than 0.1 MPa is not allowed. The value of Pi for preliminary tests is indicated in the project (often it is a quarter more than calculated). After holding for 10 minutes, the pressure in the system is reduced to the calculated value and the TP and its components are inspected to see if there are any violations.
After the strength exam, leak testing is carried out. In this case, the test pressure is Pg. First, the pressure in the network is brought to this value. Measure the level of liquid in the measuring tank and note the start time of the test. After 10 minutes, water is taken from the measuring tank and added to the system to bring the pressure in it to Pg. Again, note the time and level of liquid remaining in the tank. Determine how much of it was taken from the tank. If the exam is successful, the volume taken from the measuring tank for pumping the system (l/min) will not exceed the standard.
Testing of water supply systems and hot water supply systems is carried out by specialists, guided by SNiP 3.05.04-85.
Documentation required
To obtain permission to connect the sewer system to the city network, the owner must send an application to Vodokanal and attach the following documents:
- A list of characteristics of the sewer system (length, depth, year of commissioning, number and description of fire hydrants, wells and shut-off valves, thickness and material from which the pipes are made).
- General plan of the site where underground communications are described.
- As-built drawings of sewer and water supply networks, which indicate the length and diameter of the pipeline, diagrams of wells and the material from which the pipes are made.
- Schemes indicating the division of balance zones of water-bearing and sewerage systems (schemes are agreed upon with the balance holder and persons acting as managers of sewerage and water supply workshops).
- Financial documentation for the sewer network (estimates, accounting).
Source of the article: https://vistaros.ru/
Features of the work
Installation of external utility networks may be accompanied by the following difficulties:
- the most accurate calculation will be required to ensure the appropriate level of quality and optimize costs;
- high quality installation of all communications for future long-term trouble-free operation of already created networks and reducing the risk of equipment failure before the end of the design life;
- an individual approach to installation and taking into account all possible risks.
By contacting, you insure yourself against all the above risks and receive timely and high-quality installation of external utility networks.