After the header of the document there is an extract from the technical conditions according to which the experiments were carried out. This section contains calculation formulas, a list of necessary test equipment, conditions and procedures for carrying out work.
After completing all installation work on the sewerage system, it is necessary to test the communication using the spill method. This is done in order to identify defects in the installation of drains, channels, sewer outlets, internal drainage systems, etc. The result of the inspection is included in the act, the form of which is approved by SNiP (Appendix “D” SP 73.13330.2012 “Internal sanitary systems of the building” - updated version of SNiP 3.05.01-85). In everyday life, such a document is called the “Act of Sewerage System Spilling”; in narrow circles of professionals, the same document has the official name “Act of testing internal sewerage systems and drains.” This stage of construction of sewerage communications is mandatory and cannot be canceled. The verification activities themselves are carried out using the full spill method, provided that at least 75% of the drain holes are opened in a single period of time.
Important: it is possible to put a bunch of sewer outlets into operation only on the basis of an act of carrying out all the proper manipulations and obtaining a positive result.
Below in the material there is an example of how to correctly fill out the document.
Quality control of the sewer system must be carried out at all stages of its construction. First of all, the compliance of materials with standards and requirements is checked. Next, the installation process of the system is monitored. The last thing to do is to test the fully assembled sewer system.
What to check
Checking the functionality of the sewer system includes:
- testing of the internal sewerage system;
- checking the tightness of pipelines;
- determining the performance of wells;
- storm drain testing.
What applies to the internal sewerage system
The internal sewer network includes:
- plumbing products, including household appliances that drain water;
- internal pipelines connected to a common sewer riser;
- central sewer riser equipped with a drain pipe.
What applies to the external sewerage system
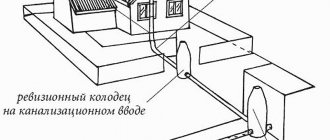
The external part of the sewer network includes:
- pipelines carrying wastewater from the house to the disposal site;
- wells that need to be installed at junctions, branching pipes or differences in network height;
- wastewater treatment plants;
- storm drains and storm water inlets.
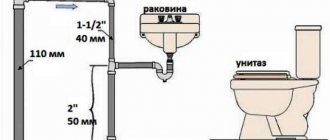
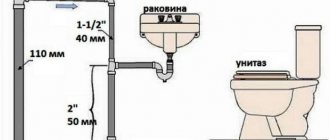
- plumbing fixtures and their connections with outlet pipes;
- local sections of a horizontal pipeline with pipes flowing into it from plumbing fixtures;
- sewer risers;
- outgoing pipe.
executive documentation
a19.7 as-built survey of the plan and longitudinal profile of underground networks download. a19.8 diagram of welded joints with distances indicated on it download.
a19.9 conclusion on the quality of welds from the pump. a19.10 download the act on conducting a hydraulic test of the pressure pipeline for strength and tightness. a19.11 download the act on conducting a hydraulic test of a gravity pipeline for leaks.
a19.12 pipeline flushing (disinfection) certificate download.
a19.13 conclusion of the sanitary-epidemiological service.
a19.14 download the test report for the external fire-fighting water supply system for water yield and operability of fire hydrants.
Testing of sewerage for spillage and SNiP standards
After installing the sewer system, before moving on to finishing work inside and backfilling trenches outside, the drainage network must be tested to ensure the tightness of the nodes, pipelines and their connections. The external system and internal network are checked in various ways, regulated by the fundamental document of builders - SNiP. How to test the tightness of pipes and sewer connections by pouring, filling, and other methods, and what data is entered, if necessary, into the inspection report, you will learn by reading the article.
- Representatives from the customer organization.
- Representatives from the general contractor. These persons are responsible for the correct installation of drains in case they do not comply with technical and operational standards during a spill.
- Members of the design organization who were involved in the development of the communication project being tested.
- A representative of a company or organization that was engaged in soil research at the site for the installation of external or internal communications. This office bears full responsibility for the inconsistency of the data received on the site regarding environmental and climatic conditions for the construction of sewer communications.
Sewer spill act
Video: Testing the sewer system for leaks Responsibility for the performance of the sewer system The check is carried out by a commission consisting of:
- representatives of the company that compiled the project, area of responsibility - carrying out calculations and drawing up drawings;
- the company that carried out the research on the ground - the correctness of the given climatic conditions and environmental conditions;
- the organization that carried out the installation of the sewer system - quality of installation, compliance with standards;
- the customer – the correctness of the inspection when putting the sewer network into operation.
Each commission member has a clearly defined area of responsibility. After the inspection, an acceptance certificate is drawn up, which is signed by all members of the commission.
An important condition for the preparation of this document is the procedure for vesting powers in the members of the commission, for which the necessary orders of managers must be created. Also important are the certification documents of all members of this commission, confirming the qualifications of the participants to conduct research or monitor the progress of its implementation.
Parties involved in the review
If we are talking about more or less large-scale construction, where several organizations are involved, not counting the customer, tests of sewer systems are carried out by all of them, after which the results are documented in the appropriate inspection report.
Typically, inspection of the sewerage system involves:
- the organization that compiled the project and is responsible for the correctness of calculations and selection of materials and components;
- a company that analyzed climatic and soil conditions and made recommendations for the design of the external components of the sewer system;
- a contractor who was directly involved in installation work related to the laying of internal and external sewer networks and is responsible for compliance of the activities carried out with the project and existing requirements specified in SNiP;
- a customer who controls the correct testing of discharge pipes, connections and some functional units of the sewer network inside the building and in the external section of the wastewater disposal system.
Each of the representatives of the parties participating in the tests and signing the final inspection report is responsible for inaccuracies and shortcomings that arose during testing of sections of the system, individual nodes or the entire network as a whole.
External sewerage test report for spillage: sample
- Work acceptance procedure
- Specifics of drawing up a test report
During testing of external sewerage using the spill method, the same document is drawn up as during testing of the internal sewage system. The form of the act itself is not a form of strict reporting and can be drawn up by the customer, contractor or subcontractor. Also, during experiments on an external water drainage system, one of the forms SNiP 3.05.04-85 can be used, which is the general form of the acceptance document for completed work when installing or repairing wastewater drainage.
Work acceptance procedure
When accepting such work, the tests themselves are carried out first, which can be:
- Hydraulic - only non-pressure drainage systems are exposed to them, be it wastewater pipelines or storm sewers. testing is carried out in areas between wells by filling the system with process water. The tests are carried out in two stages - checking pipes and connections before filling the soil and checking the performance of the entire sewer system after filling the soil. Tests are carried out by pumping water into wells or receiving grids for 30 minutes; during the tests, the performance of the system is measured and the tightness of seams and joints is monitored. Tests may also be performed to determine the ability of pipes and connections to withstand the maximum allowable pressure throughout the entire drain.
- Pneumatic - during such tests, the ability of the waste system to withstand the design pressure is checked, according to GOST standards or design documentation. For such a series of studies, specialized organizations with the necessary equipment and licenses are involved; the process itself includes checking the pressure in the system or in its individual sections when supplying air under pressure.
If during the experiments the entire system met the standard indicators of SNIP 3.05.04-85, then an acceptance certificate for the work performed is drawn up, otherwise a defective statement and a drainage troubleshooting report are drawn up. During periodic monitoring, tests are also carried out at enterprises with drinking water pipelines external drainage systems during disinfection or treatment with special reagents.
Specifics of drawing up a test report
Regardless of the type and method of verification, the document must contain the following points: The header of the document, which should indicate the date of preparation and the city in which the document is drawn up and signed. The indication of the city is mandatory, since the signing of the act may occur outside the populated area where the installation or repair of the water drainage system was carried out. Also in this part of the document the name of the organizations and the full name of the managers must be indicated, as in the charter of the organizations that carried out control, testing and technical or designer supervision of the progress of work. Also in this paragraph there should be footnotes to the design marks and coordinates of the sewer system, in accordance with the general plan or special sections of the construction project. Sample of filling out the document header After the document header there is an extract from the technical conditions according to which the experiments were carried out. This section contains calculation formulas, a list of necessary test equipment, conditions and procedures for carrying out work. When filling out this paragraph, data taken from measuring instruments during research are used. If the act itself does not contain this section, then there should be a link to the test report, which describes the process in detail and all calculations are made. All results can be summarized for convenience in a single table. Sample of filling out the section on measurements and calculations. The last item is the decision of the commission, which indicates the result of the tests and the conclusion that the drain system is ready to be accepted for operation. In case of discrepancy, the reason is indicated and links to defective statements and acts for correction and revision are provided.
If the pipeline has passed all tests, the full data of all members of the acceptance committee and their signatures are indicated, after which this document becomes the basis for drawing up a statement of disagreements or a statement of work performed, according to the conclusion of the expert commission.
An important condition for the preparation of this document is the procedure for vesting powers in the members of the commission, for which the necessary orders of managers must be created. Also important are the certification documents of all members of this commission, confirming the qualifications of the participants to conduct research or monitor the progress of its implementation.
Testing the internal sewer network
When carrying out test work, it is required to be guided by SNiP “Sewerage. External networks and structures.” According to this document, the following is checked:
- compliance with the developed project;
- testing sewerage pipelines for strength and reliability of joints;
- correctness and reliability of installed devices and flushing elements;
- verticality of mounted risers.
Testing of nodes
Compliance with the design is checked visually. Each element of the system must be located exactly in the place where it is indicated on the plan or drawing.
All installed devices must be cleared of debris and thoroughly washed. They should not have visible damage (chips, cracks, etc.) or bending. When installing devices, deflections must not be allowed.
The risers are checked for verticality with a plumb line.
Pipeline testing
Pipeline inspection can be carried out hydraulically or pneumatically.
A hydraulic sewer test involves pumping the system with water, and a pneumatic test with air.
The system can be checked with water if the ambient temperature is not less than 5ºC. In other cases, it is recommended to use the pneumatic method.
If the house has more than one floor, then the system is checked on each of them separately. To temporarily disconnect a floor from the general sewerage system, plugs are used that are inserted into the inspection.
Pipeline testing is carried out according to the following scheme:
- All pipes are checked for the presence of construction debris. If necessary, they are washed;
- Horizontal sections of the pipeline undergo drainage testing. To do this, at least ¾ of all drains are opened. The fenced off section of the sewer system is completely filled with water. If no leaks are detected within 10 minutes of operation, the test is considered passed;
- to check vertical sections of the pipeline, water is supplied under pressure not exceeding 0.08 MPa. The sewerage test for the tightness of pipelines is completed if no leaks or ruptures in the system are detected within 15-20 minutes.
If one or more sections of pipes are found to be leaking, the problem must be corrected and the test must be carried out again.