Users of our portal know that as part of the “HOUSE IN A YEAR” project with FORUMHOUSE, we and our partners built a modern cottage in the Moscow region. During the construction of the house, materials and technologies were used to ensure the maximum level of comfort. In particular, specialists installed a water purification system, with the help of which residents of the cottage will receive drinking water. Therefore, within the framework of this article, in the format of a master class, we, with the help of an expert from the Group, will answer the following questions:
- How to choose a water treatment system in a cottage.
- How water is purified to drinking quality.
- What equipment is used for this?
Basic methods of purifying water from a well
There are three degrees of purification - coarse, medium and highest. However, in addition to this, intermediate cleaning stages are used, for example, aeration. Sometimes they become an independent stage of water treatment.
Thus, common water treatment methods are:
- Settlement (mechanical cleaning);
- Aeration, repeated mechanical cleaning;
- Ion exchange method;
- Ozonation;
- Reverse osmosis;
- Disinfection.
The items on this list are complemented by each other, depending on the configuration of the entire complex.
Moreover, some of them must be used (mechanical cleaning, aeration, disinfection). Reference! The need to use narrowly targeted methods and their specific type is established based on the results of the analysis.
Advocacy
Settlement itself is the process of precipitation of impurities due to gravity.
The liquid, passing through the reservoir (sump), moves at such a speed that the dirt has time to settle to the bottom.
Accordingly, the larger the size of the settling tank and the time spent, the better the quality of water treatment.
Note! There are several types of sedimentation tanks - horizontal, vertical and radial. They provide approximately the same quality of cleaning, but differ in the amount of space they occupy and the time required.
Removal of sediment from the bottom of the tank can be carried out automatically or manually through a sludge pipe. In the second case, as a rule, the sump tank is turned off from the system, it is emptied and the dirt is washed off with a stream from a hose (fire hose).
The mechanized method involves installing a scraper system , for which operation it is not necessary to turn off the tank. Sediment can be removed either by gravity or through special pumps.
Aeration
This stage of water treatment consists of saturating the water with oxygen. Its purpose is the oxidation of dissolved metals, as well as volatile substances (hydrogen sulfide and other gases).
It is produced by spraying water or, conversely, passing oxygen through it. Treatment plants typically use one of two types of aeration systems.
- Pressure. A distinctive feature is the implementation of aeration in a sealed container (aeration column). Air is pumped into it by a special compressor, and its excess is discharged by an air vent. The advantage of such a device is that a “second lift” pump is unnecessary. The disadvantage is the presence of additional valves and sensors, which significantly reduce the reliability of the equipment.
- Non-pressure. Often used as the first stage of water treatment, including settling. The main element here is the aeration tank, into which water from the well is supplied through an aerator. When sprayed, it almost immediately becomes cloudy and iron begins to settle to the bottom.
Ion exchange
As a result of ion exchange, not only mechanical purification of water occurs, but also its softening , that is, a decrease in the content of calcium and magnesium salts.
This preparation method is a process in which water passes through special filters.
They are filled with bulk ion-exchange material (ion exchangers), which “sucks in” salt ions during the passage (drainage) of liquid. Thanks to this, it softens.
The consumable material is an ion exchange resin , which is similar in appearance to fish caviar. This is a mixture of various chemicals, and its composition changes during operation, losing the desired properties. On average, the resource of 50 liters of metabolic substance before regeneration is 4-6 thousand liters of water.
However, the resin can be restored by adding a solution of ordinary table salt (approximately 200g per liter of resin). Thanks to this regeneration, one filling lasts up to three years.
Ion exchange process
Ion exchange has the following features:
- High quality of water treatment – both cleaning and softening;
- Ease of maintenance;
- The high cost of consumables and the need for special waste disposal.
Important! This method is usually used when the source is highly mineralized. (150-200 mg/l).
In the case of a treatment complex that works with hard artesian water, ion exchange columns are used - a system of several cylinders. As a rule, the operation of the column is almost completely automated.
Human participation is required to pour table salt into the container intended for this purpose, as well as to change the final filter cartridges or backfill.
Ozonation
This purification method is a process of saturating water with ozone, a form of oxygen. Since it is a powerful oxidizing agent, it is capable of destroying almost all bacteria, viruses and microbes.
In addition, such treatment precipitates all metals and salts . In this case, ozone is active for a short time, and then, passing through a carbon filter, it is transformed into oxygen. Therefore, when used correctly, it does not pose a danger to humans.
Reference! The operation of the ozonizing unit does not require consumables or human intervention.
The operating principle of the ozonizing unit is as follows:
- an ozone generator converts oxygen into active gas;
- the ejector pump saturates the water with it;
- The water then enters a self-cleaning carbon filter to complete its purification.
Moreover, it is also a destructor, converting residual ozone into oxygen. Next, the system sends the purification object to the consumer. More effective, environmentally friendly and economical water treatment methods do not exist today.
However, there are significant disadvantages:
- ozone treatment is not able to remove all phenolic highly toxic impurities;
- the price of an ozonizing unit is high;
- inhalation of ozone is dangerous (manifested if used incorrectly).
The water treatment complex includes several components and is located outside residential premises. In addition, its device involves significant financial expenditure. Therefore, the disadvantages of ozone cleaning are offset by the coordinated work of the entire complex.
Ozonation scheme
Reverse osmosis
The point of this popular technology is to “pull” water through a semi-permeable synthetic membrane. It allows only H2O molecules and some gases - carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide - to pass through.
Thus, the resulting water (permeate) is close to distilled. This is considered both an advantage and a disadvantage due to the lack of essential microelements. The remaining concentrate of impurities is usually drained.
The disadvantages of reverse osmosis filters are:
- The need for chemical removal of sediments from the membrane (regeneration) or its replacement;
- Low speed and work volume.
Note! Reverse osmosis cannot replace all stages of water treatment. Preliminary coarse filtration is required, as well as, in some cases, finishing treatment, for example, with ultraviolet radiation or passing the permeate through a carbon filter.
Disinfection
This stage of water purification (disinfection) is designed to destroy microorganisms remaining after preliminary filtration. Various methods of disinfection are used.
The most popular are the following:
Chlorination, which is used, as a rule, only for centralized water mains - at treatment plants. Often contributes to the formation of carcinogenic and other toxic substances.- Ozonation.
- Disinfection with silver, the principle of which is the binding of microorganisms with silver ions. It is characterized by low quality of disinfection and the harmful effects of silver itself, which accumulates in the body.
- UV radiation, which is one of the most effective methods of disinfection today (if the technology is followed, it destroys up to 99.9% of microorganisms). The main influence on the quality of radiation is the color and turbidity of the water, which is why it is used at the final stage of water treatment.
The disadvantages of the technology are:
- the need for special disposal of mercury lamps, as well as their replacement;
- low degree or lack of effect in case of deviations from the required conditions of use.
Important! Ultrasonic treatment and iodization have not found application in well water treatment systems.
Iodine tablets, for example, are suitable for use in the field, and ultrasound disinfects medical instruments. Boiling water is used exclusively in everyday life.
Method #1. Cleaning with a pipe or bailer
Cleaning well water from clay using a bailer (pipe or cylinder with a valve) is carried out in stages.
Raising the deep-well pump to the surface and freeing the well space from equipment and any objects.
Strong fixation of the bailer on the rope (possibly on a steel cable), and its smooth descent to the bottom.
As soon as the bailer reaches the bottom, it is raised on a cable by 50 cm, after which it sharply falls to the bottom under the load of its own weight.
A strong blow to the bottom of a hollow pipe or bailer provokes a shift in the clay layers, and clay and water enter the space of the pipe or bailer, since when it falls, the metal valve of the device opens the intake channel. As soon as the bailer begins to move upward, the valve closes the channel, and clayey water remains in the device. This process is repeated 3-5 times to fill the bailer, after which it is lifted up and released.
In one procedure, a bailer can lift up to 500 clay sediment (not including water). This method is very labor-intensive, takes a lot of time, but gives the greatest result.
Directional water treatment methods
There are both standard water treatment methods (settling, aeration, reverse osmosis) and highly targeted ones. Although they overlap and complement in many ways, it makes sense to consider methods for removing specific substances.
Sand
Silting or sanding of a well is a pressing problem, usually associated with erroneous calculations or installation of well equipment.
It is easy to remove sand from water - consistent filtration and settling helps.
However, solving the problem as a whole is not an easy task, requiring, at a minimum, cleaning the well. In the worst case, restoring the source is not practical at all.
Read about how to clean sand from well water here.
Iron
This impurity is almost always present, and we are not talking about its complete removal, but about reducing its content. As a rule, all or almost all water treatment methods help in the fight against iron , from sedimentation to reverse osmosis.
You can read more about purifying iron from well water here.
Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide removal is a set of measures that includes both direct water purification and well flushing or repair. Water purification is carried out in several ways:
- Aeration is the simplest, most effective and popular method of combating hydrogen sulfide. Due to the active saturation of the liquid with oxygen, foreign gases (including hydrogen sulfide) are oxidized and precipitate.
- Chlorination , treatment with potassium permanganate or iodine, rarely implemented in private water supply networks.
- Ozonation is also an effective way to remove hydrogen sulfide. Differences from aeration are the high speed and degree of purification, as well as the high cost of the equipment.
To eliminate the source of hydrogen sulfide, you must first find it. To do this, it is necessary to analyze the liquid taken at different stages of water treatment. It is likely that just washing or replacing the pre-filter will solve the problem.
However, often the source of these “aromatic” compounds is at the bottom of the well . Therefore, to cope with the task, the well is flushed, repaired or reinstalled.
You can get more detailed information by watching a video about purifying water from hydrogen sulfide and iron:
Lime
Calcium and magnesium salts are present in any source. Depending on the level of their content, water is called hard or soft. All filtration methods are suitable to one degree or another for softening water.
Starting from the pre-filter and ending with the final purification, lime particles are removed. For example, reverse osmosis provides a reduction in salt content up to 95-99%.
Reference! Other methods are also effective - sedimentation, aeration, ozonation, ion exchange, multi-stage mechanical filtration. Non-traditional methods are also quite effective - magnetic and electromagnetic filters.
You can get even more information about purifying water from lime here.
Manganese
Remove using methods similar to deferrization:
- filtration,
- aeration,
- coagulation,
- settling, etc.
One of the most effective methods is the use of filter media that accelerates the oxidation of metals (for example, BIRM).
As a rule, for large volumes of water, filtration and sorption columns with sand or similar filler are used. For small volumes, a household reverse osmosis complex is sufficient.
In cases of significant (for example, 15-fold) excess of the permissible norm, it is necessary to apply a whole range of cleaning measures:
- Installation of a dispenser for chlorine or chloride compounds (sodium hypochlorite);
- Installation of a chlorination tank (reactor);
- Deferrization;
- Multi-stage mechanical filtration;
- Reverse osmosis.
Important! Chlorinated water is not poured into a regular septic tank, but a separate pit is prepared for this purpose.
Nitrates (nitrogen salts)
Both the ion exchange method and the reverse osmosis method are suitable for removing nitrates. The first option involves the use of special nitrate-selective resins. Their volume depends on the volume of water treatment, for example, a standard package of Purolite A520E anion exchanger contains 25 liters of a substance that will cope with the removal of nitrates from 5 cubic meters. m. of water per week.
Accordingly,
the composition will also have to be regenerated once a week , which will require the consumption of 1 kg of table salt (NaCl).
Accurate calculations of all volumes are possible only if analysis and water consumption data are available.
Reverse osmosis filtration also removes nitrates. However, due to the low rate of osmosis, the volume of filtrate is insignificant. On the other hand, only drinking water needs to get rid of this impurity. Its required volume, on average, is no more than 10% of the total consumption.
Clay
Fine clay in water is a common phenomenon. The most likely causes are incorrect calculations of the depth and location of drilling, as well as errors when installing casing or other equipment.
For example, a deep-well pump is often chosen to be too powerful or fixed too deep. If the presence of clay is a feature of a given aquifer, then this, as a rule, leads to a short well life - 3-5 years, after which its major reconstruction is required.
The most effective method of removing clay into sediment is settling the liquid with preliminary coagulation of impurities . Moreover, a radial settling tank, operating on the principle of a centrifuge, is preferable to others. Conventional multi-stage filtration, ending with reverse osmosis, can also make water clear and drinkable.
Materials for filtration equipment
The efficiency of cleaning depends on the quality of the filtration material; a limited number of them are used in wells, the main ones being:
- Stainless steel. In addition to strength, the material has flexibility and excellent corrosion resistance; the durability of stainless steel is tens of years. It is used to make strong meshes and wires that are mounted on top of the pipes. The disadvantages include the high cost of stainless steel products.
- Plastic. Plastic is another common material for the manufacture of filters in water sources; meshes and cords are made from it, which are cheaper than stainless steel. Plastic is corrosion-resistant and inert to most chemicals, easy to install and has a long service life. The disadvantages of plastics include low physical strength, which does not allow them to withstand heavy loads at significant depths.
- Non-ferrous metals. Copper, brass, and bronze can be used in the manufacture of water filters without any restrictions; they have high corrosion resistance and a long service life. Soft alloys with a high copper content are recommended for use at shallow depths to avoid deformation from strong water pressure. In the manufacture of filter elements, brass mesh and thick wire made of brass or copper are used.
Rice. 4 Filter for casing pipe - installation in the well
- Steel. Steel filters are susceptible to corrosion and can be used as a budget option in water intake sources intended for technical needs. Increased content of iron oxide in water as a result of iron corrosion of more than 0.3 mg. per liter leaves a yellow residue on water main equipment and plumbing fixtures. Galvanized steel also rusts over time to form zinc oxides, which are harmful to human health - this material is not recommended for use in water filter elements.
Complex cleansing
After analyzing the water extracted from the well, they determine the type of equipment necessary for highly targeted water treatment. For example, ion exchange columns are installed, as a rule, only when there is an excessive content of salts and minerals.
However, almost any treatment system includes the following components:
- Mechanical prefilter , possibly self-cleaning. Retains large particles of sand, iron, etc.
- A hydraulic accumulator is a reservoir that often acts as a sump and is always switched on. Designed for uninterrupted water supply.
- An aeration tank , which is also a settling tank. Saturates the liquid with oxygen, promotes oxidation and precipitation of dissolved metals, salts, and minerals.
- Second lift pump , creating or increasing pressure after aeration.
- Iron remover , which is a subsystem of 2-3 cylinders filled with filter media. At this stage, water is also softened and impurities up to 1 micron in size are removed.
- Disinfection unit , which can be represented by either a reactor for dosed chlorination (or mixing with hydrogen peroxide) or a UV irradiator.
- The final filter is usually carbon. Designed for additional water purification from chemical reagents. Can be replaced or supplemented with a reverse osmosis unit.
Note! Water treatment sometimes serves different purposes (for example, for a swimming pool or washing a car). Depending on the goals, branches are made at different stages - technical, household, drinking. This approach greatly contributes to saving consumables and time.
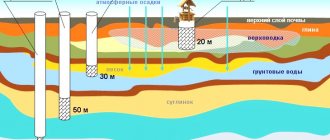
Scheme of water purification in a country house to drinking water
Below you can see a diagram of complex water purification from a well for a country house:
Goals
If you plan to use water in everyday life, especially for drinking and cooking, cleaning it from clay is necessary. It allows:
- reduce turbidity - even in small concentrations, clay suspension reduces the transparency of water and makes it unsuitable for drinking;
- soften water and remove impurities from it - water containing dissolved clay, in terms of hardness, as a rule, does not meet the requirements of GOST “Drinking Water”, and is also often unsuitable for domestic needs;
- eliminate odor - drinking water, according to regulatory documents, should not have any foreign odors.
- disinfect water at the initial stage of purification, since clay suspension often contains dangerous microorganisms, algae, protozoa and other biological objects.
Nuances of choice
Well filters for private and country houses are the lower part of the casing pipe, equipped with perforation. The height of this section of the pipe, as well as the geometric shape of the holes, depend on the properties of the soil of the aquifer.
Drilling specialists , . However, if you have to make a choice yourself, it is advisable to know the characteristics of their types.
Slot or hole type strainer
Slit filters are used when the aquifer consists mainly of rocks prone to collapse.
This could be, for example :
- rocky and clastic soil;
- pebbles;
- coarse sand.
The slots should be located longitudinally, in a checkerboard pattern, and the width should correspond to the size of the fractions.
The difference between a perforated filter is the smaller throughput of the holes. However, the need for just such a design is justified by the scope of application - fine-grained soil.
These filters are called mesh filters because of the mesh wound around the pipe. It can be plastic or stainless steel, and also have different weaving, depending on the predominant breed. For example, for large hard fractions (pebbles), a square-shaped mesh is used . Its purpose is to protect perforations from clogging.
Gravel Well Screen
It is, in fact, an addition to the casing pipe perforated from below. The purpose of the design is to protect slot or hole perforations from clogging with soil. The gravel filtration device requires a shaft diameter that exceeds the dimensions of the casing pipe by 10 centimeters or more.
Reference! This method is used only for shallow sand or “Abyssinian” wells.
Choosing a filter for hard water
This choice directly depends on the content of various salts in the produced fluid, the flow rate of the well, as well as the required volume of softened filtrate.
, a filter jug at the end of the chain is sufficient When permissible standards are significantly exceeded, as a rule, ion exchange units are used.
You can read more about hard water filters here.
What to do if the well does not pump?
So:
- If the water source is not pumped, then certain mistakes were probably made in its construction.
- Maybe the depth of the well is much greater than in the calculations.
- There is also reason to believe that the pumping equipment for pumping was chosen incorrectly.
- There is an option that there is simply not enough water at this depth.
- For this reason, it is worth continuing drilling to a more aquiferous layer in the area.
- It may be that sand is constantly present in the source. There is water, but it is dirty.
- In this case, you should pay attention to the pump and filter.
- Pumping won't help.
- Such a source can be pumped for several years.
- This is due to the fact that there is sand next to the aquifer, and its layer in the ground was affected by drilling.
To avoid problems with the construction of a water source on the site and in its further operation, you should contact special companies that will provide professional well drilling services and give guarantees for their work.
Removing sand and clay
The particles of these impurities are large in size and visible to the naked eye. Since such contaminants are insoluble in liquid, it can be cleaned of sand and clay mechanically. Coarse filters are installed at the entrance to the system. If you neglect their installation, other filter elements will quickly become clogged and fail. Large fraction impurities can cause damage to the pump that lifts liquid from the well.
Coarse filter.
The mechanical coarse filter has the shape of a flask with a replaceable filter element. It traps particles whose size exceeds 50-80 microns. Additionally, a fine filter must be installed in the water treatment system of a private home. It is capable of trapping particles up to 5 microns in size.
Silicon
The silicon content in water coming from a well, a well or a centralized water supply system is not standardized. Scientists have not established whether impurities of this chemical element are dangerous to the human body. The established restrictions apply only to the industrial production of alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages. The silicon content in feed water for steam boilers is also limited, since this element causes the formation of silicate scale.
To purify well fluid from silicon, you can use the ion exchange method or reverse osmosis technology. The latter method ensures the removal of 99% of silicon impurities. However, in the presence of salts of this element, a sparingly soluble precipitate forms on the filter membrane, clogging it.
Older, but also effective methods for purifying liquids from silicon compounds are lime precipitation and the use of magnesium sorbents.