The state of the environment largely depends on the quality of industrial wastewater treatment. Every year the situation is only getting worse, so the task of developing more modern and efficient water treatment systems for enterprises is especially acute. They can work according to a single scheme - for example, the management of the organization signs an agreement with utility services on discharging wastewater into the centralized sewer system in the form in which it is, or after pre-treatment.
Standards for the composition of industrial wastewater for discharge into sewers and treatment of industrial wastewater
Industrial wastewater contains various aggressive substances that destroy city treatment plants and sewer pipelines. When they enter a body of water, they have a negative effect on both the composition of the water and the living organisms in it. Therefore, before cleaning, you need to check the maximum permissible concentrations of biological and chemical substances and take measures. Requirements for wastewater must be taken into account when designing reconstruction and installation of industrial institutions. Factories should operate using technologies with minimal or no waste, and water after purification should be reused - this will help preserve the resources of our planet and protect the environment from negative external influences.
Basic requirements for wastewater discharged into the central sewer system:
- BOD – no more than the maximum permissible value specified in the design documentation for the treatment plant;
- wastewater should not cause disruptions or interruptions in the operation of sewerage systems or treatment facilities;
- wastewater should not have a temperature of more than 40 degrees and a pH of more than 6.5-9.0;
- the presence of sand, shavings, and abrasive particles in drains is unacceptable (they are the main cause of the formation of sediment in sewer units);
- the drains should not contain impurities that clog grates and pipes;
- absence of aggressive components that cause destruction of pipes and other cleaning elements – 100%;
- There should be no explosive components in wastewater, as well as biodegradable, viral, toxic, bacterial and radioactive impurities.
In situations where the discharged wastewater does not meet the specified parameters, it is pre-treated.
Ultrafine mechanical filters.
The principle of the string-membrane cartridge is unique in that it does not require cartridge replacement, constant maintenance, or additional costs.
Artesian string-membrane technology differs from other conventional technologies. There are no deep pores in the Artesian filter, and dirt does not stick to the string, dirt is easily washed out when washing the filter and does not need to replace cartridges. MECHANICAL CLEANING The pore size between the strings is up to 1 micron. The pores allow the smallest H20 molecules to pass through, and retain contaminants, such as: clay, rust, peat, turbidity, color, hardness salts, manganese, iron and other heavy metals.. Retains all contaminants except the H20 molecule and minimal impurities in the form of useful calcium minerals , magnesium, zinc, potassium. At the mechanical cleaning stage, it retains contaminants by 98%, such as: turbidity, impurities of rust, clay, peat, hardness, hardness salts, dissolved iron, heavy metals, odors, tastes, bacteria and other contaminants. Designed for dachas, cottages, private houses, offices, swimming pools, schools, kindergartens, municipal facilities. Close
Types of industrial wastewater pollution
During treatment, all substances negative for the environment must be removed from the wastewater. Main types of impurities:
- coarse suspended particles - methods such as sifting, settling and filtration are used to eliminate them;
- coarse emulsified substances – separation, filtration and flotation;
- microparticles - first filtration is carried out, followed by coagulation, flocculation and pressure flotation;
- stable emulsions - they are removed using thin-layer sedimentation, pressure flotation, electroflotation;
- colloidal particles – microfiltration and electroflotation required;
- oils – separation, flotation, and then electroflotation are carried out;
- phenols – biopurification, ozonation, sorption using activated carbon, flotation, coagulation;
- organics – biological treatment, ozonation and final sorption with activated carbon;
- heavy metals - first electroflotation is carried out, then sedimentation, electrocoagulation, electrodialysis, ultrafiltration and ion exchange;
- cyanides - chemical oxidation, electroflotation and electrochemical oxidation are used to remove them;
- tetravalent chromium - first, chemical reduction of water is carried out, then electroflotation and electrocoagulation;
- trivalent chromium – electroflotation, ion exchange, precipitation and filtration;
- sulfates - they are removed by settling with reagents and further filtration, the final stage of purification is reverse osmosis;
- chlorides - reverse osmosis, evaporation in a vacuum environment, electrodialysis;
- salts – nanofiltration, reverse osmosis treatment, electrodialysis, vacuum evaporation;
- Surfactants – sorption with activated carbon, ozonation, flotation, ultrafiltration.
All wastewater pollution is divided into chemical, mechanical, thermal, biological and radioactive. In each industry, the composition of wastewater will be different. Inorganics, including toxic ones, are usually present in the waters of nitrogen, sulfate, and soda enterprises that work with acids, ores, alkalis, and heavy metals. Organics are most often found in wastewater from the oil industry, organic synthesis plants, etc. The third contaminant - a mixture of organics and inorganics - is formed in wastewater as a result of galvanic treatment.
Mechanical filtration
Mechanical treatment, as a rule, is preparatory before deeper treatment of wastewater.
Thanks to it, various impurities, solid particles, sand, and clay are removed from the water. If mechanical cleaning is not carried out, the filters will quickly fail.
Mechanical filtration is also excellent when preparing process water. Thanks to purification, chemical elements are removed from the water, so that the technical fluid can be reused.
Classification of industrial wastewater
Since different enterprises use certain harmful substances in their work, the nature of wastewater pollution will be different. Conventionally, according to the type of pollution, industrial wastewater is divided into 5 groups:
- The first one contains impurities of suspended particles and mechanical inclusions (including metal hydroxides).
- The second is that it contains oil-containing impurities and oil emulsions.
- The third is impurities of volatile substances.
- The fourth is cleaning solutions.
- Fifth - organic and inorganic, impurities have pronounced toxic properties (these are metal ions, chromium compounds, cyanides).
Categories of drains
Industrial manufacturing processes require liquid. As a result, industrial wastewater is generated. The liquid comes into contact with sources of contamination: chemicals, solids, gases. At the same time, it loses its natural properties and needs to be cleaned for recycling or disposal. Based on the technological process that is the source of pollution, categories of EPS are distinguished.
Industrial wastewater
This type of EPS is formed directly during production. In industrial enterprises, the flow occurs constantly, which explains the need for systematic accounting of wastewater.
Common types:
- Industrial condensate.
- Solutions of galvanic or pickling baths.
- Soda solutions.
- Ammonia solutions.
- Food colorings.
- Toxic components.
Auxiliary system drains
They have an environmentally friendly composition. EPS of auxiliary industrial systems do not contain toxic components. The liquid was obtained as a result of the operation of additional buildings at an industrial enterprise.
Examples of auxiliary system drains:
- Drains from showers, restrooms, dining rooms.
- Water in heating installations.
- Cooling unit drains.
Water from utility and service workshops
This category includes wastewater generated as a result of the operation of administrative buildings, utility shops, and material warehouses. Potential sources of pollution include mechanical repair shops and electrical shops.
Methods for treating industrial wastewater. How industrial wastewater is treated
Various methods are used to remove contaminants from industrial wastewater. The choice of purification method depends on the initial composition of the water and its required quality after purification. If there are several pollutants, combined methods are used. The main methods for removing impurities:
- Mechanical - straining, settling, filtration.
- Chemical – neutralization, flocculation, neutralization.
- Physico-chemical – flotation and stripping.
The most popular cleaning method is settling, but it has its drawbacks - for example, the long duration of the process of removing impurities and the relatively low percentage of removal of harmful substances (50-70% is already considered a good indicator). Flotation is a more effective, but at the same time expensive solution. The cleaning efficiency of this method, if the technology is followed, can reach 98%.
Reagent treatment significantly increases purification rates - up to 100% of mechanical impurities and up to 99.5% of emulsions and petroleum products. The disadvantage of this method is the high cost and complexity of maintaining the treatment plant. Reagent-free coagulation is used to remove metals and their oxides.
Stripping or desorption are the main ways to combat dissolved gases and surfactants. To remove detergents from water, combined methods are used - this can be ion exchange, extraction, coagulation, adsorption, destructive destruction, foam separation and/or chemical precipitation. The optimal combination is selected taking into account the composition of the initial wastewater and the requirements for it.
Wastewater from pickling lines and galvanic production is subjected to reagent treatment, which can reduce alkalinity or acidity, precipitate and coagulate heavy metal salts. Depending on the production capacity, diluted and concentrated solutions are either mixed and then neutralized, clarified, or the solutions are neutralized (separately) and clarified in different concentrations.
Purification of industrial wastewater by changing its chemical composition
The chemical and physical composition of wastewater is determined by a set of methods at each stage of water treatment. Some stages can be excluded in the absence of certain contaminants. Purification of industrial wastewater by changing its chemical composition involves:
- purification accompanied by the formation of sparingly soluble electrolytes;
- purification accompanied by the formation of complex or slightly dissociated compounds;
- purification through the process of decomposition and synthesis;
- cleaning by thermolysis;
- purification in redox, electrochemical processes.
Application of biological methods for purification of industrial wastewater
When deciding on the advisability of using biological treatment of wastewater from enterprises, it is necessary to take into account such a point as the presence of pollutants in wastewater that are prone to biochemical destruction. The cleaning efficiency is also influenced by the following factors: the presence of toxic substances, the level of biomass nutrition, the structure of impurities, nutrients, active reaction of the environment, increased mineralization. That is, bioremediation is used only for those wastewater that meet fairly strict criteria.
In what case can industrial waste be discharged into the general city sewerage system without hindrance?
Wastewater from industrial enterprises almost always contains various impurities that negatively affect the performance of the sewer network, urban wastewater treatment plants of a populated area, and reservoirs (if discharged into them). Therefore, before the start of cleaning, the content of the maximum permissible concentration of harmful impurities is monitored. Enterprises need to use waste-free and low-waste technologies, recycling and reuse water supply systems.
Magnetic water converters
Constant magnetic fields are emitted from polygradient high-power magnets.
The filter service life is 30 years and is not consumed. Using a filter, you can purify water from scale, hardness, calcium, magnesium and hardness salts. All plumbing, equipment, heating devices, and machines will not become overgrown with scale. If before treatment the hardness looks like needles under a microscope - they easily stick to all plumbing fixtures, then after magnetization scale does not appear in the water, and the shape of the hardness is transformed into a spherical shape, which is not capable of sticking like scale to equipment and plumbing fixtures, as well as water softens and destroys existing scale in the pipeline. You can save on energy bills because increasing hardness means it costs more to heat the water, instead of using a lot of electricity to heat the water to build up scale in the water. Without scale, energy costs are reduced by 15%. Close
Requirements for industrial wastewater for discharge into the central sewer system
When planning the discharge of wastewater into the sewer network, you need to make sure that it meets established standards, namely:
- BOD20 does not exceed the indicator specified in the construction design;
- wastewater will not cause interruptions in the operation of the sewerage network and treatment facilities;
- the temperature of the wastewater does not exceed 40 degrees, and the pH is in the range of 6.5-9;
- There are no impurities that can lead to clogging of pipes, wells and grates in the sewer system, as well as substances that can cause destruction of pipelines.
Also, the wastewater should not contain flammable, explosive gases, impurities, non-biodegradable substances, toxic pollutants, or surfactants. The COD of wastewater should be higher than BOD5, but not more than 2.5 times.
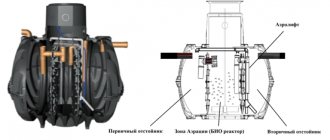
Operating principle of treatment structures
As a rule, at the very beginning there is a mixing of liquids in which the concentration of pollutants differs. This process takes about a day.
Then, by adding lime milk, hydrogen chloride, sulfate acid or carbon dioxide to the liquid, the neutralization step occurs.
The hot wastewater is then cooled and explosive gases are removed.
Equipment for wastewater treatment of industrial enterprises
The list of equipment required for wastewater treatment depends on the contaminant removal methods used at the enterprises. Basic:
- Mechanical filters are devices for primary purification from insoluble contaminants. There are disk, press type, vacuum belt, plate, mesh, as well as pressure and non-pressure.
- Settling tanks are tanks that have a horizontal, vertical or radial design. It is in them that physical and chemical water purification occurs using reagents.
- Centrifuges are devices used to dehydrate mechanical contaminants. The separation of sediment and liquid occurs in a drum in the form of a cylinder.
- Aerotanks are biological treatment tanks.
If you comply with the requirements listed above, the disposal of wastewater from industrial enterprises will not cause damage to the ecological situation of the environment.
Manufactured equipment
Water and wastewater treatment equipment
|
Accessories for water and wastewater treatment equipment
|
Purification of wastewater from various impurities
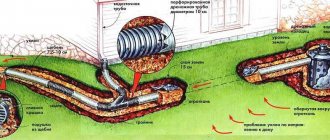
Local wastewater treatment system for an enterprise
Local wastewater treatment at enterprises of different types of industry can be carried out in various ways, corresponding to the removal of various types of contaminants:
- Open hydrocyclones operating under pressure are used to remove suspended solids from industrial wastewater.
- Fine suspended substances and sludge products that are valuable for further disposal are removed using continuous or batch centrifuges.
- Wastewater is purified from heavy metals, as well as petroleum products, oils, fats, resins and other similar impurities that do not precipitate, using various flotation units.
- Gases in a free state, dissolved in wastewater, are removed using various degassers operating both at atmospheric pressure and under vacuum, using hollow nozzles, various nozzles and a bubble layer of liquid.
Backfill columns – comprehensive water purification.
Complex systems with 10 loading options and various modifications.
A number of chemical elements are used in the columns, such as: Ion exchange resin, granular carbon sorbent, silicon, quartz sand, and others, backfilling with MWF and Birm for iron and heavy metals. Backfills are necessary for the purification of water from chemicals, iron, scale, bacteria, oil products, gases and other contaminants. It is possible to regenerate mixtures in columns and restore their service life for further secondary use. Close