The state of the environment directly depends on the degree of treatment of industrial wastewater from nearby enterprises. Recently, environmental issues have become very acute. Over the past 10 years, many new effective technologies for treating industrial wastewater have been developed.
Treatment of industrial wastewater from different facilities can occur in one system. Representatives of the enterprise can agree with utility services to discharge their wastewater into the general centralized sewer system of the settlement where it is located. To make this possible, a chemical analysis of the wastewater is first carried out. If they have an acceptable degree of pollution, then industrial wastewater will be discharged together with domestic wastewater. It is possible to pre-treat wastewater from enterprises using specialized equipment to eliminate pollutants of a certain category.
What should industrial wastewater be like?
Industrial wastewater constantly contains some impurities that can have a negative impact on the quality of operation of treatment facilities, as well as the involved sewer network. Water use regimes are often violated in situations where waste is discharged into natural bodies of water. To ensure that industrial wastewater does not have a negative impact on the equipped sewer network, the functional mode of the treatment system must be observed taking into account the minimum permitted levels of harmful impurities.
Such a requirement must be complied with during the design, construction and commissioning of new and renovated industrial facilities. In addition, enterprises need to use technical means to minimize the amount of waste, as well as mechanisms for re-supplying water.
When planning work to discharge wastewater into the sewer system, you need to make sure that the following requirements are met:
- The BOD20 level should not exceed the level provided for in the design design of the treatment system used for sewerage;
- The composition of wastewater should not disrupt the normal functioning of the sewer network, as well as equipped treatment structures;
- The drains should not be hot, the maximum permissible temperature is 40 degrees, and the permissible PH level range is 6.5 - 9.0;
- Wastewater should not contain impurities that can settle on filtration screens or cause the formation of deposits on pipes and wells;
- There should be no harsh surfactants;
- The COD level of wastewater should not be more than 2.5 times higher than BOD5.
Wastewater treatment must be carried out in a situation where the above requirements are not fully met.
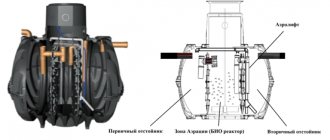
Treatment plants
Most often, treatment facilities look like a system of sealed tanks and pipelines, compactly located on the production site. In addition to the structures themselves, an access road and sediment and excess silt treatment facilities are being designed.
The design of wastewater treatment facilities is carried out individually for each enterprise, depending on the volume of wastewater and its contamination. A well-designed cleaning scheme reduces the concentration of contaminants in the drain to minimum levels.
Treatment facilities of a large enterprise
Standards established by SanPiN
Since at a certain time all industrial wastewater ends up in natural reservoirs and open reservoirs, sanitary norms and rules become relevant.
These standards include:
- The maximum possible concentration level of maximum permissible concentrations of organic or synthetic components, toxic substances, all kinds of decomposition products of biomaterials, which significantly have a negative impact on the natural environment;
- The BOD level provides information about the oxygen content involved in the oxidation reaction during a certain reporting period (BOD5, corresponds to 5 days);
- Any enterprise is obliged to monitor the level of COD. This value sets the required volume of oxygen to allow the complete decomposition of organic matter into various components. The indicator of chemical oxygen consumption determines the volume of various organic impurities contained in wastewater. It is these organic substances that have the greatest impact on natural bodies of water.
These indicators are considered very important in the issue of regulating the state of wastewater before being sent to water bodies.
Basic information on wastewater treatment
The procedure for cleaning industrial wastewater is carried out by removing various harmful components from their composition. A technologically complex production process involves processing wastewater as a raw material in order to obtain a finished product in the form of ordinary clean water. The nature of the contaminants largely determines the choice of cleaning technology.
Types of cleaning technologies:
- Mechanical;
- Chemical;
- Combined;
- Incineration or thermal disposal;
- Biological;
- Physico-chemical;
- Conventional wastewater disinfection.
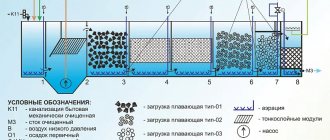
First of all, all wastewater must undergo a mechanical cleaning procedure. Through filtration and gradual settling, large and small mechanical components are carefully removed from the water. Specially equipped facilities are used to remove coarse elements.
Such structures include:
- Lattices;
- Primary settling tanks;
- Membrane elements;
- Sita;
- Equipped sand pits;
- Septic tanks.
Low-density pollutants are removed using special oil traps and so-called gasoline oil traps. The biological method is considered one of the most natural cleaning methods. The technique is based on the use of natural biochemical and physiological natural processes, self-purification of various reservoirs and rivers. Types of biological treatment facilities:
- Aero tanks;
- Special biological ponds;
- Biological filters.
This technique is particularly effective in the treatment of domestic wastewater, waste generated during the processing of petroleum products, paper products and artificial fiber. If a chemical method is used, various reagents are added to the wastewater. The most common ones are:
- Sorption;
- Centrifugation;
- Ion exchange purification using electrochemical reagents;
- Evaporation;
- Crystallization by evaporation;
- Flotation;
- Neutralization;
- Hyperfiltration;
- Extraction.
At the disinfection stage, wastewater is chlorinated, as well as ozonated using ion exchange resins, high pressure and ultrasonic devices.
If the above methods of wastewater treatment do not show the required result, the wastewater undergoes a disposal procedure in specially equipped burners. This technique is characterized by the greatest reliability and maximum cheapness. When the waste is injected into a lit torch, the liquid gradually evaporates, and the impurities it contains simply burn out without a trace.
Advantages
In contrast to biological, mechanical and physicochemical influences, chemical treatment leads to complete changes in the structure of compounds.
Biological treatment occurs under mild conditions under the influence of microbes, to the influence of which not all pollutants are susceptible.- Mechanical cleaning allows you to remove mainly large particles of impurities.
- During physical and chemical cleaning, changes occur on the surface of dirt particles, but their composition does not fundamentally change.
Dissolved components that have a pronounced acidic or alkaline character, oxidizing or reducing properties can be converted into harmless compounds only through deep chemical transformations.
Characteristics of biological treatment methods
In populated areas, the biological method of wastewater treatment is often used. This technique makes it possible to process waste from one or more private houses, as well as from densely populated areas of a populated area. Activated sludge begins to form during biological treatment. This component contains a large number of different microorganisms that contribute to the effective breakdown of wastewater. In terms of their consistency, all these substances are similar to whitish flakes of inorganic origin.
Industrial wastewater also contains heterogeneous substances. Sewage often contains components of natural origin, such as fatty acids and surfactants, which are considered the main substances contained in household chemicals. The main technical device necessary to perform biological treatment is a device that helps increase the oxygen concentration in water. This creates optimal conditions for the development of aerobic bacteria.
The use of such microorganisms promotes the oxidation of waste and natural components contained in wastewater. At the same time, rot and bad odor are removed from the water.
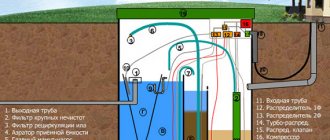
Main stages of biological treatment:
- Pre-cleaning involves removing large fragments from sewage.
- Mixing wastewater with various sludge components. Specially designed technical devices allow sludge to interact more intensively with water, promoting the oxidation process. In such a situation, natural substances can be completely removed.
- Procedure for separating sludge components. After this, the procedure for receiving wastewater to a specially designated place is carried out. This tank is shaped like an inverted pyramid. In this case, the process of sediment formation at the bottom of the container is carried out, followed by the removal of liquid that has undergone complete cleaning. Such sludge components can be used repeatedly for the purpose of biological treatment of industrial wastewater.
Process waters are substances formed after the interaction of sludge with wastewater. After purification, the liquid can be used to water crops.
Classification
Wastewater is water that has been used or passed over contaminated surfaces. They are of purely industrial, economic or atmospheric origin and are divided into the following types:
- Industrial wastewater is water used in technological processes.
- Economic pollution. They appear from toilets, laundries, showers, catering establishments, which are necessarily available at enterprises.
- Atmospheric runoff refers to streams of rain, melted snow flowing down the roofs of workshops, warehouses, garages, car washes, and other surfaces.
All three types of wastewater exist at industrial facilities. For example, in mechanical engineering enterprises water is used for the following purposes:
preparation of source materials;- energy transfer in heat exchangers,
- changes in the temperature of the raw material mass, products, equipment parts;
- preparing large quantities of working fluids;
- economic needs of the enterprise.
The ratio of volumes of dirty flows from various sources is determined by the specifics of the enterprise and the level of organization of each type of work.
Physico-chemical cleaning methods
Using purification using a physical-chemical method, inorganic components are removed from wastewater and hard-to-oxidize organic matter is broken down.
There are several main methods for treating industrial wastewater using physical and chemical methods:
- Coagulation;
- Flotation;
- Ion exchange;
- Adsorption;
- Extraction;
- Dialysis, etc.
You should also list the opportunities provided by this cleaning method:
- Deep wastewater treatment;
- Removing non-oxidizable toxins from water;
- Treatment structures do not take up much space;
- Sensitivity to changing loads remains minimal;
- It is always possible to make the cleaning procedure fully automated;
- There is no need to monitor the activities of living organisms;
- Recovery of substances is possible;
- Cleaning processes have been fully studied and tested many times during the practical application of this technique.
For the most effective method of treating sewage, it is necessary to take into account existing sanitary requirements.
Features of mechanical wastewater treatment
Mechanical cleaning involves performing the following actions:
- A straining technique in which water is passed through a specially made screen. With the use of such devices, it is always possible to sift out various coarse components. To ensure that the performance of such filtering devices is as high as possible, water passes through them under high pressure;
- Filtration is performed using several purification devices. The filter system is constructed only from the simplest materials. Filters are filled with activated carbon, sand, small metal fragments, gravel, and fiberglass materials.
- Method of settling. The main essence of this technique is the separation of water in several chambers, in which the process of settling large and small fragments is carried out. The chamber is filled with water, which then settles. In most cases, a sand trap is used as a settling tank.
The duration of this procedure can be up to several days.
Types of industrial pollution
An important characteristic of impurities entering water is solubility:
- Some of them form true solutions in which the particle sizes of foreign substances do not exceed 1 nm.
- Others form colloidal systems with larger grains. Their diameter can reach half a million nanometers.
- Still others do not dissolve in water at all and form heterogeneous systems with impurities in suspension.
The state of the water flow is of fundamental importance for choosing the right approaches to its purification.
Interesting. For wastewater with a large amount of insoluble contaminants, the decisive step is mechanical separation.
The composition of impurities also differs fundamentally. Foreign substances are of the following nature:
- inorganic (mineral components);
- organic (carbon-containing compounds);
- biological (microorganisms, viruses, some fungi).
At enterprises producing leather, wool, vitamins, and some medications, biological pollutants predominate in wastewater; in mining complexes - mineral components.
The degree of aggressiveness of wastewater varies from strong (concentrated acids and basic substances) to zero.