The presence of a well, sewerage, drainage basin or laying of cables are integral components of the arrangement of the territory of a private farm. In addition to compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards and technical requirements, each owner counts on the long-term operation of these communications, therefore, first of all, attention is paid to reinforced concrete products. Their reliability, with the correct selection of the required dimensions of concrete rings for the well and proper installation, guarantees more than 100 years of trouble-free operation of the treatment system.
Concrete rings.
Pros and cons of reinforced concrete rings
Concrete is convenient due to the following characteristics:
- Sizes – wide choice of models.
- Concrete grades and additives can be selected so that they can withstand high loads, humidity and freezing.
- The products do not require special treatment or care.
- Long service life - up to 100 years.
- Easy to install.
- It is possible to produce concrete components directly on site on your own.
- Low cost.
The disadvantages may be:
- Large section weight.
- The need to use a crane during installation.
- If installed incorrectly, it will be difficult to waterproof the connections.
- Problems with dismantling and replacing sections.
Construction of a log house over a well
Having made a well gate from logs, you can make through holes in it to insert a metal pin for the handle.
To construct wells, a chain is usually used, attached in the middle of the gate. To protect the structure from rain, you need to take care of preparing the roof by choosing a suitable design. The above-ground part of a well made of reinforced concrete rings is usually a log house. To build a roof or house, beams and sand-cement blocks are used. The construction is carried out in the same style as the residential building.
To cover a wooden frame, you can use a canopy, the design of which is selected depending on the functions of the structure. It should provide protection from precipitation. To properly design a well at your dacha, you will need to present an overall picture of the finished house decorating the site.
If the price of the log house is not satisfactory, then it can be replaced with a cheaper material, for example, artificial stone. Natural building material is used mainly to create decorative wells that perform an aesthetic function. To make the top of the well, wood is often used - a beautiful and reliable material.
For pillars, logs with a smooth or carved surface are used. For the blind area around the structure, you can use concrete or paving slabs. The roof can be open or closed.
A well made in accordance with the requirements of SNiP requires the use of modern construction technologies. This ensures the establishment of a functional water supply system. This is the only way to install cold and hot water supply to the house.
Marking, choosing which ones are better to put
Prefabricated reinforced concrete rings for wells are made from Portland cement of a grade not lower than M200. In a factory product, the main dimensions are D1 (external diameter), D2 (internal), H (height). In trade catalogs we find the following standard ring abbreviations:
- KS (wall) – small-diameter products designed to protect networks inside load-bearing walls. Resistant to lateral loads.
- KO (support) - used as a basis for structures and communications.
- KVG - well water-gas parts, due to the possibility of arranging hermetically sealed connections, are recommended for laying communications of the above types.
- KFK are part of a network for the removal and accumulation of feces.
- KLK - thanks to the stability of the material and the strength of the connections, they can withstand heavy loads of the storm drainage system.
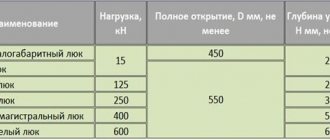
The structure will be marked type KS-10-9 (wall, 100 mm wall thickness, 900 mm height).
P (slabs) have standard sizes for arranging bottoms (it has a base) and floors (needed to move from a larger diameter to a smaller one).
Typical internal diameters of concrete links - sizes: 70, 100, 130, 150, 200, 250 cm.
Briefly about the main thing
Plastic rings simplify the construction of a drinking well; they eliminate the need to install concrete rings or line the internal walls with bricks. The materials used are plastics with different properties; some are extremely resistant to aggressive environments, others tolerate negative temperatures well.
In the private sector, plastic structures are most often used for the restoration of drinking wells, installation of wells and sewage systems. They can be prefabricated, welded and seamless, differ in size and the presence of additional elements.
Ratings 0
Product dimensions: height, diameter, weight, volume in cubes
Depending on the material (concrete, reinforced concrete), its brand, height, wall thickness. The dimensions of concrete rings for wells are determined by their purpose. Below are the most applicable options for reinforced concrete structures, indicating the main parameters and weight:
| Product brand code | Purpose | Dimensions (wall thickness, material consumption) for reinforced concrete parts of the well |
| KS 7-9 | Small-diameter underground communications: sewerage, drainage, wells, gas | H = 90 cm; D = 70 cm; T (wall thickness) = 9 cm; weight – 380 kg; volume – 0.628 m3; concrete volume – 0.15 m3 |
| KS 10-9 | Pumps, caissons for fire hydrants, drinking and waste wells. Most used on private plots | H = 90 cm; D = 100 cm; T = 9 cm; weight – 600 kg; volume – 1.198 m3; concrete volume – 0.24 m3 |
| KS 15-9 | Industrial pipelines, gas and sewer wells | H = 90 cm: D = 1.5 m; T = 9 cm; weight – 1000 kg; volume – 4.31 m3; concrete volume – 0.4 m3 |
| KS 20-9 | Cesspools, storm drains, main communications | H = 90 cm; D = 2 m; T = 9 cm; weight – 1480 kg; volume – 6 m3; concrete volume – 0.59 m3 |
How to check the size of rings for a well according to GOST
Choosing a well ring manufacturer is usually a headache. There are usually several manufacturers of different sizes. Who to give preference to? You can collect reviews from your neighbors and choose a couple of manufacturers. Then it’s worth driving around and seeing with your own eyes, because “normal quality” is different for everyone. What to look for and how to inspect well rings? This is how the same GOST defines verification.
Measurements are taken along two perpendicular diameters. This means that one of the points is selected. The second one will be located opposite it, and the other two will be located perpendicular (a straight line drawn at an angle of 90° - as in the figure).
How to check the size of a concrete ring for a well
- At four points, located in pairs opposite each other, the wall thickness is measured. Moreover, it is advisable to check this parameter from below and from above. If the rings are locking, check the parameters of the tenon/groove - they must match. And it is also necessary to control both from above and from below.
- Also at four points, check the height of the ring.
Plates and rings are checked using the same method. Four points are selected - two on perpendicular lines and measurements are taken at them. The measured values must match. Permissible deviations are no more than 1.5%.
Making reinforced concrete rings at home
If you need:
1) Non-standard sizes. 2) One or more rings of different widths. 3) One additional ring.
And if there are no special requirements for the precision of manufacturing the structure, then you can make them yourself. Having calculated the cost of a factory-made product, its delivery and installation, you can judge the feasibility of independent concrete work at home.
First of all, the required volume for concrete rings is calculated: outer and inner diameters, height. Based on design loads (self-gravity, weight of communications, thrust force of water, possibility of soil displacement), a structure made of pure concrete or reinforced is selected.
The reinforcement can be either steel or combined (using fiberglass, lighter, non-corrosive).
Based on these data, you will understand what volume and composition of concrete will be required for the product. When making your own well rings, you need large volumes of mixture - for which you may need to rent a concrete mixer. The approximate consumption for the manufacture of a product with a diameter of 150 cm is 0.3 cubic meters of ready-made concrete mixture.
For independent production you will need:
- cement grade M200 and higher;
- fittings;
- concrete mixer;
- wheelbarrow and large containers;
- form for filling - two collapsible circles, nested one into the other. Metal and wood are suitable for the form. To make formwork, cut up old metal barrels are suitable for the mold.
The inner part of the formwork must be at least 100 mm higher than the outer part.
How to make formwork with your own hands?
- Install the formwork, securing it vertically and sealing the seams.
- Install a reinforcing frame (welded or fastened rods).
- Prepare concrete according to the formula:
cement – 1 part;
sand – 2.5 parts;
washed crushed stone – 3-4 parts.
Water should not make up more than 50% of the mass of the concrete mixture. To increase the plasticity of the solution when laying it, add liquid detergent (1 tsp per 10 l) or dissolve washing powder (1 tbsp). To increase strength, use PVA glue or potassium glass in volumes of no more than 2%.
Attention! It must be produced at temperatures above 10 degrees. The finished product must be protected from direct sunlight and getting wet.
- Pour slowly, in layers no more than 20 cm high, stirring with a metal rod. Each of the layers must “settle down”, otherwise cavities will form.
- Upon completion of pouring, level the surface of the mixture and, if necessary, strengthen the embedded parts.
- Leave the product to set. To avoid cracking at high temperatures, wrap it in polyethylene. The minimum curing time is 4 days. The estimated period of strength gain is 21 days.
- First, the inner part of the formwork is removed, then the outer part.
Characteristics
1.3.1. Designs must meet the requirements of GOST 13015:
— in terms of strength, rigidity and crack resistance, while there are no requirements for testing structures by loading;
- according to the actual strength of concrete (at design age and tempering age);
— frost resistance and water resistance of concrete;
- according to the thickness of the protective layer of concrete to the reinforcement;
— to steel grades for reinforcing and embedded products, including for mounting hinges;
- for protection against corrosion.
1.3.2. Structures should be made of heavy concrete in accordance with GOST 26633 classes or grades of compressive strength specified in the working drawings of the structures.
1.3.3. The normalized tempering strength of concrete is taken equal to 70% of the class or grade of concrete in terms of compressive strength.
The specified standardized tempering strength of concrete can be reduced or increased in accordance with the requirements of GOST 13015.
1.3.4. The water absorption of concrete structures must correspond to that established by the design documentation of a particular structure or specified when ordering structures.
1.3.5. For the reinforcement of structures, the following types and classes of reinforcing steel are used:
— thermomechanically strengthened rod of the At-ShS and At-lVC classes according to GOST 10884;
— hot-rolled rod of classes A-1, A-11 and A-111 according to GOST 5781;
— reinforcing wire of class VR-1 according to GOST 6727.
1.3.6. The shape and dimensions of reinforcement and embedded products and their position in structures must correspond to those indicated in the working drawings.
1.3.7. Welded reinforcement and embedded products must meet the requirements of GOST 10922.
1.3.8. In cases provided for by the working drawings of wells, running brackets must be installed inside the wall rings, located along the height of the ring every 300 mm and protruding from the inner surface of the rings by 120 mm.
Running brackets should be made of reinforcing steel class AI or A-P according to GOST 5781.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, wall rings may be manufactured without running brackets, provided they are installed on the construction site.
1.3.9. The running brackets must be protected from corrosion in accordance with the instructions of the working drawings of the wells.
1.3.10. The values of actual deviations of the geometric parameters of structures should not exceed the limits specified in table. 1.
Table 1
In millimeters
| Name of deviation of geometric parameter | Name of geometric parameter | Prev. off |
| Deviation from linear size | Height (thickness) of the structure: | |
| up to 180 | + 5 | |
| » 300 | + 8 | |
| » 1000 | + 10 | |
| St. 1000 to 1600 | + 12 | |
| » 1600 » 2500 | + 15 | |
| » 2500 | + 20 | |
| Inner diameter of working chambers, wall- | ||
| outer and support rings, outer diameter of floor slabs and bottom, diameter of manholes and holes for pipelines: | ||
| up to 1000 | + 6 | |
| St. 1000 to 1600 | + 8 | |
| » 1600 » 2500 | + 10 | |
| » 2500 | + 12 | |
| Length and width of base and road slabs | + 10 | |
| Position of holes and cutouts | 10 | |
| Deviation from flatness of the lower surface of floor slabs (when measuring | Outer diameter of floor slabs: up to 1000 St. 1000 to 2500 » 2500 | 4 |
| from a conventional plane passing through three points) | 6 8 |
1.3.11. Requirements for the quality of surfaces and appearance of structures are in accordance with GOST 13015. At the same time, the quality of surfaces of structures (with the exception of joint surfaces) must meet the requirements established for category A6. The surfaces forming a joint between structures, which are sealed at the construction site, are subject to the requirements established for category A7.
It is allowed, by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, to apply to all surfaces of working chambers, wall and support rings the requirements established for category A7.
Features of installation and operation
Some sizes of concrete rings are up to 70–200 kg, which allows them to be laid manually or using homemade devices. Special equipment will be needed if the additional equipment weighs 1,000–1,500 kg.
In this case, concrete rings with a lock are sealed with construction mixtures, as well as jute. If necessary, the inside is coated with a deep penetration primer, and then covered with mixtures that increase water resistance (entirely or just the joints). The simplest primer for reinforced concrete is a solution of PVA glue in water (1 to 8).
During operation, it is important to monitor the condition of the joints: they will be the first to show shifts in soil masses and the possible need for excavation work. Joints must be regularly sealed - using primer, jute, etc.
Restoration of reinforced concrete structures consists of sealing the ring with a lock and further filling the crack with concrete with pre-treatment with a deep-setting primer. If necessary, metal staples are applied to the crack.
Why are additional rings needed?
When it is impossible to install conventional ones, additional rings are used for the well. They solve problems caused by the width, slope or height of a standard through-hole. The height of the additional ring is less than 40 cm, so it allows you to bring the shaft to the desired height if this is not possible with a regular one. From a specialized company, you can order additional rings based on individual measurements so that they exactly match the structure being built.
When designing a well, much attention is paid to the decorative component. Rarely do owners agree to simply have a head sticking out on the property, covered by a hatch
For such cases, the upper rings with a beautiful relief are cast.
Preparatory stage of arrangement of reinforced concrete concrete structures
We carry out the following work:
We determine the location where the well will be installed. There are several methods: using frames, based on geodetic surveys and electrical-vertical sounding. It is best to use all methods together.
On a note! The optimal time for constructing a well is August-September. They are also dug in winter, after 3 weeks of frost, when the upper layers of the soil freeze and they do not recharge the aquifer.
- We clear the area from bushes, trees, garbage and old buildings.
- We select the type and size of reinforced concrete rings (RCR), and also calculate their number.
- If necessary, we arrange temporary access roads for lifting equipment that delivers the necessary materials, as well as digging a pit (if you decide to drill a mine using a mechanized method).
Important! We do not recommend turning (that is, rolling) reinforced concrete rings over long distances. This is fraught with the fact that chips and cracks may form on the surface of the product.
Regulatory Requirements
GOST-8020-90 defines the qualities characteristic of reinforced concrete rings. It describes the markings, scope of application, and parameters of standardized structures. The strength indicators of various types of concrete used for pouring rings are indicated in GOST 10180.
GOST 10060 contains information about the frost resistance of the product, and GOST 12730 - about the water resistance coefficient. Reinforced concrete structures differ not only in parameters, but also in markings. It is used to separate the purposes of products.
Several products with abbreviations such as:
- KO are reference models used for the lower region of the entire system;
- KFK are reinforced concrete products used for the construction of water outlets or sewerage systems;
- KLK are models that are manufactured for urban water drains and sewer lines.
In addition to the letter designation, numbers are indicated in the marking. They indicate the height and diameter of the structure. Reinforced concrete products are equipped with additional elements, such as covering the bottom. In this case, the plate is marked PP or PC. Plates intended for the bottom are designated PD.
Such structures impart airtightness to the structure. They are installed at the top and bottom to protect the structure from groundwater. In drinking wells, slabs are used to protect against various contaminants and groundwater.
Gypsum fiber sheet GVL
Gypsum fiber sheet GVL is an environmentally friendly building material based on gypsum and cellulose fibers (fluffed cellulose waste paper). GVL has increased strength. Compared to plasterboard, gypsum fiber sheet has increased rigidity, moisture resistance and heat resistance. GVL is moisture resistant, hard and durable. It is not exposed to fire and has a smooth surface, so no primer is required before finishing. Gypsum fiber sheets are used when installing dry floors, for exterior work, and for assembling frame house structures. It is suitable for work in buildings and rooms with wet conditions according to SNiP II-3-79.
When is it being built?
A non-buried columnar foundation (NSF) is a grid of point supports that are not immersed deep into the ground, but transfer the load from the structure directly to the surface of the land plot.
The following are most often built on such pillars:
- log,
- panel boards,
- frame houses,
- baths,
- utility blocks,
- extensions,
- summer kitchens, etc.
NSFs are erected not only based on the light weight of the structure, but also in the presence of a solid soil foundation.
It is advisable to build foundations of this type on rocky, coarse soils in areas with low seismological hazard and absence of soil movements. It is possible to install NSF on heaving foundations. This will be discussed below in a separate chapter.
Construction of a filtration well: functions, diagram, device
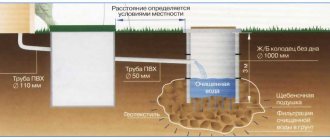
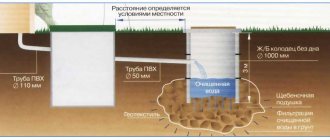
A well designed to filter wastewater is installed in the sewer system after the septic tank.
Its task is to accept wastewater that has undergone preliminary treatment and then pass it through a layer of soil, which, in this case, acts as a filter.
Most often, this water treatment element is installed if there is no possibility of draining wastewater into the central sewer network or underlying soils.
Photo: filtration well
1. Manhole cover 2. Exhaust pipe 3. Neck body 4. Insulating cover 5. Supply pipe 6. Outer gravel layer 7. Well body 8. Shield 9. Internal filter layer
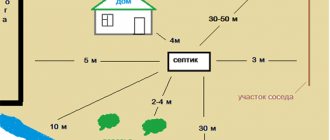
Important! When planning a site for a filtration well, it is worth considering the distances to nearby buildings and wells for drinking water (according to SNiP this is no closer than 10 and 30 meters, respectively). It doesn’t matter what shape the filtration structure will have, but if you plan to construct a sewer well from concrete rings, then something like a foundation is made around the perimeter of the base
It does not matter what shape the filtration structure will have, but if it is planned to construct a sewer well from concrete rings, then something like a foundation is made along the perimeter of the base.
Photo: sewer well made of concrete rings. Gravel, expanded clay, broken bricks and other material with a fraction size of approximately 10 to 70 mm are poured inside the well.
Outside, along the entire perimeter, bedding is made from the same composition as inside the well, but not more than 1 m. The supply pipe should be approximately 15 cm above the filter layer.
Important! To prevent erosion of the bottom filter, a wooden shield pre-treated with an antiseptic compound is placed under the stream of water.
Disadvantages of SRC
Great care is required when installing the well structure. No distortion is allowed
Otherwise, there is a high probability that the ring will burst (and it’s good if it is the top part, otherwise you will have to spend a lot of time dismantling the already mounted elements). The large weight of the well rings is also considered one of its disadvantages. For example, one product with a diameter of 1.0 meter weighs about 600 kilograms. That is why loading/unloading and installation will most likely require special equipment.
Finding a place for a water source
When building a well, it is important to correctly determine the depth of the horizon of clean drinking water, calculate and purchase the required number of concrete rings, equipment for arranging the hydraulic structure itself and the water distribution system. It is also important to choose the right place and time to dig a well.
Choosing the right location for a well depends on several factors:
- Geological exploration data. There are many ways to search for water in an area, but nothing more reliable than geological studies of the area has yet been invented.
- Information about nearby sources. It would be a good idea to ask your closest neighbors how deep their wells are built and what the quality of the water is.
- Suitability of water for drinking. It is imperative to submit a water sample for chemical and microbiological analysis to the nearest sanitary station. Experts will determine the concentration of chemicals and the presence of pathogenic bacteria.
- Soil type. The complexity of digging wells, the need to use special equipment, etc. depend on this. Ultimately, all this affects the cost of the finished well. It is most difficult to build a well on rocky soils.
- Terrain. The greatest difficulties arise when building a well on a hillside. The ideal option is a flat area.
- Distance from sources of pollution. Wells are dug at a considerable distance from cesspools, septic tanks, compost heaps, and barns. It is undesirable to place them in lowlands where rain and melt water flows, as well as water mixed with agricultural fertilizers.
- Degree of distance from home. The closer the water source is to the house, the more convenient it is.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Thin floor screed on a concrete base
In this case, the excavation should be placed so that it does not interfere with travel or block access to outbuildings or utility rooms.
When constructing water supply and sewerage, you should focus on SNiP 2.04.03-85. This is necessary to prevent contamination of drinking water sources, erosion of building foundations, and disruption of systems.
What is the structure made of?
Supporting reinforced concrete sections for wells can be a combination of a bottom slab and a stacked top. But the tightness of the connection between them will be problematic. This seam, which is the deepest, will be subject to the greatest stress. Solution: instead of two products, take one - a structure with a bottom. Having the shape of a glass, it goes into the shaft first. This bottom can withstand heavy loads. Height – from 300 to 1,000 mm. Marked with the abbreviation KCD, they can be flat or chamfered at the end.
Above, standard high sections (HS) are mounted one on top of the other, sealing the connection. If it is necessary to bring the structure to the desired level, they are complemented by an additional ring, characterized by a low (up to 400 mm) section (standard heights 100, 150, 300 mm). Additional parts are marked according to structure: K (type), D (inner diameter, cm), H (height).
Well sections with a lock - do not have a smooth end, but are equipped with a chamfer (there is a recess on one edge, and a protrusion on the opposite). Such a factory-made part greatly facilitates installation and sealing of the connection.
In operation, a reinforced concrete barrel with a lock is more resistant to deformation under lateral loads. Under reinforced concrete, the locks have metal embedded parts welded to the reinforced frame.
Fastening brackets, as well as plates with bolts, are used for connecting reinforced concrete products. Structures with a lock require additional strengthening on moving, freezing soils.
Uneven loads that occur in autumn and spring are especially dangerous for a well (the lower layers of the soil freeze in a peculiar way and thaw later than the upper ones).
The well needs running brackets for maintenance and visual inspection of its condition. A metal running bracket made of stainless steel or coated with plastic is placed into the product during casting or mounted afterwards (in the provided mounting holes or drilled ones) on dowels. They are installed at a distance of 300 mm from each other. The joints between the brackets and the pipe walls are sealed with cement.