The sewerage system is one of the most important inventions of mankind, known since ancient times, but has not lost any of its relevance and significance. Even the principle has changed little, having been enriched only with special mechanisms and devices.
Sewerage is a necessary and extremely important system of sanitary facilities for people. As a rule, it covers the entire settlement, so it directly affects all its residents. Let's take a closer look at this issue.
What is sewerage
Sewer networks are one part of the overall water supply and sanitation system that performs the functions of collecting and removing wastewater and organic waste. Somewhat simplified, this is an extensive network of pipelines that enter every city building and ensure the removal of wastewater to a specialized structure. The somewhat biased attitude of most people towards sewage is completely undeserved, since its importance and responsibility cannot be exaggerated. Suffice it to remember that all outbreaks of epidemics occur in backward countries with a complete lack of infrastructure.
The composition and operation scheme of the complexes may be different. This is due to the size of the settlement, the number of buildings and people living in them. The functioning of the sewer network requires water, which is used to transport solid waste. No other methods have been invented, so sewerage is part of the water supply complex, being one of the priority parts of the city infrastructure. The operating conditions of the system are quite harsh; it operates all year round and needs protection from freezing. To do this, pipelines are placed underground, to a depth exceeding the level of soil freezing in winter. Considering that the network permeates the entire city, entering every house, one can quite clearly imagine the volume and extent of the spread of the complex.
Sewer networks
Gravity
Most often, autonomous sewer systems use the gravity principle. The operation of gravity sewerage directly depends on the slope of the pipelines, which was performed at the installation stage of the system. The presence of a slope ensures that the drains move under their own power, using gravitational force. The degree of slope is affected primarily by the diameters of the sewer pipes.
Too small a slope will lead to waste starting to clog the pipe - and this can lead to a breakthrough, which will be very difficult to eliminate. It is also not worth making a large slope: the wastewater will move too quickly, which will have a bad effect on the quality of self-cleaning of the pipeline, and the waste storage facility will have to be installed deep underground.
Sewerage with natural waste transportation has many advantages.
The main advantages of this design:
- ease of operation and installation;
- low cost of arrangement;
- independence from electricity.
The disadvantage of gravity sewerage is that it cannot function if the sump tank is located at a great distance from the building.
History of origin
The history of sewerage goes back many centuries. The oldest known system is the one in the ancient Indian city of Mohenjo-Daro, which was discovered during excavations. It is about 4600 years old. Systems are known in Ancient Rome (a striking example is the Great Cloaca, which still operates today, serving as a storm sewer) or Ancient China (in the city of Linzi). The description of these finds indicates
Medieval Europe lagged noticeably behind in this regard, since the invasion of barbarians swept away almost all the remains of Roman buildings, and there was no one to maintain and generally deal with social systems. The re-emergence of the network, which occurred at the end of the 17th century, was forced, caused by epidemics of infectious diseases that brought the entire European civilization to the brink of extinction.
In Russia, the history of sewerage is similar to Europe. The wastewater disposal systems were built according to the Roman style, but the use of wood instead of marble made them short-lived, and during the reign of Ivan the Terrible they were abandoned. This led to an outbreak of plague at the end of the 18th century. It is known that in Moscow neither water supply nor sewerage were fully created until the very beginning of the 20th century.
In the modern world, the development of sewer systems, thanks to technological advances, has been brought to perfection. New plumbing devices, materials, methods of processing and disposal of waste have appeared. Standards and requirements have been developed for sanitary and technical support of systems, violation of which threatens with serious penalties or even criminal prosecution.
Briefly about the main thing
Internal water supply and sewerage systems, together with external sewerage networks, form a single system that ensures living comfort. Any life support system begins with development. Design is carried out on the basis of regulatory documents: SP, SNiP, GOST, SanPiN. Only in this case is it possible to achieve uninterrupted functioning of the entire complex during a given service life.
The design of both life-support systems is linked to each other, as well as to the working documentation of the facility. For each system, factors influencing its parameters are identified, and the necessary calculations of loads, pressure, watercourse speed, and other parameters are carried out. A properly designed and installed system will cope with any load; Proper selection of materials for pipes plays an important role in long-term operation.
Ratings 0
Types of sewer systems
There are different types of sewage systems that operate according to their own principles or perform specific functions. Based on functionality and location, they are distinguished:
- internal sewerage . Unites all pipelines connected to plumbing fixtures (baths, sinks, toilets) and combined into a single channel;
- external sewerage . A network of underground pipelines through which wastewater moves to settling tanks;
- treatment facilities . They clarify wastewater, remove pollutants and organic waste, and return it to water bodies.
Example of indoor and outdoor device
According to the tasks performed, sewer systems are:
- household (household and fecal). Designated in the documentation K1;
- stormwater (K2);
- industrial (K3).
Sewerage K1 can be:
- centralized , i.e. the pipeline leaving the residential premises is connected to the general structure of the city sewerage system;
- autonomous _ Sewage and organic waste are stored and subsequently removed, or clarified, processed and disposed of in our own low-capacity treatment facilities ( septic tanks ).
Basically, the systems consist of pipelines. The share of other equipment is relatively low and is concentrated in wastewater treatment plants. These are pumps, separators and other devices that transport, pump and dispose of wastewater. The technical characteristics and composition of these units depend on the volume of wastewater and the general parameters of the system.
You may also like - How the sewage system works in an apartment building
Diameter selection
The range of pipes used for the installation of domestic sewer systems is quite narrow and falls within the size range from 40 mm to 220 mm. In accordance with current building codes, as well as manufacturers’ recommendations, the following diameters are used:
- 50 mm – sinks, sinks (single and paired);
- 75 mm – shower trays, urinals, bathtubs;
- 110 mm – toilets, central sewer risers, drain valve outlet;
- 110-150 mm – installation of a complex sewerage system, carried out in the basement;
- 160 mm – branch from the central riser to the external septic tank.
Polymer pipes have a particularly wide range of standard sizes, which is due to the manufacturability of their production PHOTO: ua.all.biz
The principle of operation of the sewerage system
Let's look at how a public or individual sewer system works:
Centralized networks
The design and composition of centralized systems are approximately clear to most users, although almost no one has a detailed understanding. The composition of the network has a strict order, although outwardly it may look chaotic. The internal sewage system is connected to the external part of the system, which consists of several groups:
- yard;
- street;
- collectors.
External networks have a non-pressure structure, i.e. wastewater moves by gravity. To do this, all pipelines are installed at a certain slope, determined by SNiP or departmental standards. The organization of external networks is carried out according to different types:
- general alloy Both domestic and storm water are sent to a single receiver;
- separate _ For storm and domestic wastewater, own collectors are used, not combined into one complex;
- semi-separated . A common alloy collector is used, but the wastewater is delivered through separate lines.
Wastewater contains a large number of active or aggressive components. This is especially noticeable in industrial systems, where a large amount of enterprise waste enters the wastewater. This puts forward specific requirements for the material of pipelines and wells. In their production we use:
- cast iron;
- polyethylene;
- polypropylene;
- fiberglass;
- polyvinyl chloride;
- reinforced concrete pipes and rings for collectors.
There are pipes made from other materials, but they are short-lived and are currently practically not used.
Video description
About the intricacies of drainage systems in the following video:
- Sand catcher. A filter structure on which sand suspended in water from trays is deposited.
- Inspection (inspection) wells. Help monitor and maintain storm drainage elements.
Linear CS, in accordance with the requirements of SNiP for water supply and sewerage of external networks and structures, must be installed with a slight slope towards the collector. If for some reason the slope cannot be ensured, then the water will not be able to move by gravity; then the system is supplemented with a pump.
Calculation of a storm sewer boils down to determining its diameter, for which the following data is used:
- Drainage area. The area of the roof, paths and platforms is taken into account - all surfaces with a waterproof coating.
- Location of existing underground communications.
- Terrain conditions: soil features and average precipitation.
Installation of a storm drain in a private house Source inservo.ru
Autonomous systems
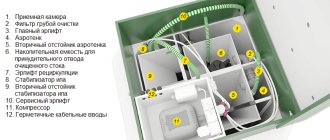
The emergence of autonomous complexes occurred relatively recently, with the development of individual housing construction. Installing your own sewer system was an attractive idea that made it possible to create modern and comfortable living conditions in a private house or cottage. Initially, only internal lines that carried wastewater into cesspools or containers were popular. But the need for frequent cleaning and removal of waste created a lot of problems, which forced us to abandon the old method and look for other options. The main type of autonomous sewage system that is common today is called a septic tank. It allows you to either completely abandon waste removal and sewer cleaning, or significantly increase the interval between these actions.
The principle of operation of a septic tank is to settle wastewater and process solid waste using special bacteria. As a rule, a septic tank is a closed container divided into several (2-4) adjacent compartments. Once in the first compartment, the wastewater gradually settles, and solid fractions settle to the bottom. There is an overflow hole at the top of the compartment. As it fills, partially clarified waste flows through it into the next compartment. They undergo further settling and clarification in the second compartment until it is filled to the top and begins to release clarified water further. The final node is either a filtration well or a filtration field.
A well is a type of collector that does not have a bottom. Typically, it consists of several concrete rings set on a bed of sand and gravel. Getting into it, clarified water is absorbed through the layer of bedding into the soil, further purifying itself.
The filtration field is one or more pipes with multiple holes along the entire length. The incoming water is discharged from them into a layer of gravel and sand, being further purified and absorbed into the soil. Unlike a well, pipes do not need to be buried to great depths, but a considerable area must be allocated for them. Considering the size of land plots, the preference given to wells is understandable. The only limitation is situations where the site has high groundwater levels.
More details about septic tanks in the article - Sewerage in a private house - step-by-step installation with your own hands
How are complexes selected?
Before purchasing systems, be sure to communicate with specialists and managers of the company from which you are going to order the equipment. When choosing, you need to consider the following important factors:
- the depth at which communications (pipelines) are laid;
- environmental features;
- degree of saturation of pollutants in water;
- productivity of existing treatment facilities.
Stormwater treatment plants must be able to handle the load and effectively remove contaminants from the water. As practice shows, before purchasing complexes it is necessary to carry out appropriate calculations. For example, you need to find out the flow of wastewater, the rate of precipitation for each month and the SNiP coefficient, which determines the surface of the water. The dimensions of the complex largely depend on the drainage area, weather conditions, the characteristics of the facility where they will be installed, and, naturally, the location of the water discharge. Only after competent calculations carried out by specialists is a model selected.
Rain and melt water
Rainwater is formed as a result of precipitation. They are divided into rain and melt, resulting from the melting of ice and snow. A distinctive feature of rainwater runoff is its episodic nature and sharp unevenness. Water from washing and watering streets and drainages is close to rainwater in terms of the qualitative characteristics of pollutants and is removed together with it.
Wastewater
Waste water is water that is used for domestic, industrial or other needs and is contaminated with additional impurities that have changed its original chemical composition and physical properties. Additionally, water flowing from the territory of settlements and industrial enterprises as a result of precipitation.
Depending on the origin, type and qualitative characteristics of impurities, wastewater is divided into three main categories: domestic [1] (household and fecal), industrial (industrial) and rainwater (atmospheric).
Wastewater tertiary treatment
The mechanical and biological stages of purification remove 90% of pollutants, but do not rid the water of microorganisms, which is dangerous for the environment. Therefore, additional purification is necessary.
Bioreactors for deep purification
Bioreactors are used to oxidize inorganic substances and convert them into organic ones. Reactions occur on the surface of special disks. Autotrophic microorganisms need oxygen, so aeration of the liquid is activated.
Filters for wastewater treatment
Filtration occurs through sand. Wastewater is supplied from bottom to top. The filters themselves are located below other settings. The contents of the filters are automatically updated.
Ultraviolet water disinfection
Chlorination, ozonation, gamma irradiation, alternating current, ultrasound, and ultraviolet radiation are used to disinfect water.
Ultraviolet irradiation is an effective method that allows you to destroy all pathogens - bacteria, viruses, protozoa, fungi. Turbidity reduces the effectiveness of irradiation, so higher power is required. Gradually, contaminants settle on the UV lamp and it needs to be cleaned.
Types of chlorination: superchlorination, double chlorination, with preliminary ammoniation. Ultraviolet irradiation has an advantage over chlorination - it does not leave an odor, is not harmful to health, and does not pollute the environment.
Ultraviolet water disinfection.
Phosphate removal
Phosphates are found in laundry detergents and other detergents. They pollute the environment, causing water bodies to bloom. To remove phosphoric acid salts, sealants are used before the biological treatment stage and sand filters.