Every day a person needs water for domestic and industrial needs. It is polluted by substances that pose a threat to the environment, nature, and people. Therefore, before wastewater is reused, poured into the soil, or a reservoir, it will undergo biological treatment.
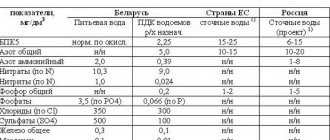
Biopurification and sedimentation allows you to get rid of pathogenic microorganisms and bacteria by only 90%. Some organisms remain viable for 2 to 10 weeks. They can only be eliminated by disinfection, for example, ozonation, chlorination and treatment with UV rays. In this case, the percentage of water purity is 99.4 - 99.99%.
How does the biological treatment method work?
Cleansing using microorganisms is usually carried out after mechanical removal of contaminants. Insoluble particles precipitate, and the remaining substances are subject to further processing.
The essence of the work is based on the ability of certain bacteria to break down organic compounds. As a result, simple substances such as water, carbon dioxide and methane are formed. Microbes and protozoa use the resulting products to maintain their own vital functions.
Microorganisms also obtain energy from nitrogen, which is contained in wastewater in the form of ammonia and nitrate compounds. The composition of mineral salts includes phosphorus and potassium, which are necessary for feeding bacteria. The rich content of these substances in wastewater causes intensive proliferation of microbes, thus causing natural purification in the tanks.
Wastewater treatment Source vse-o-santehnike.ru
Cleaning in artificial conditions
Bioreactors with biofilm. “Wastewater is treated through consumption by biofilm through the process of aerobic oxidation of organic pollutants and oxidation of ammonia nitrogen. Air is used for oxidation. Various types of loadings are used for the development of biofilm” [1]. Bioreactors are designed in such a way that the floating load does not leave through the overflow along with purified water, but remains inside the container, without accumulating in one place, filling the volume of water.
Biofilters. There are two types of biofilters: with volumetric loading (such as gravel) and with flat loading (for example, disk type - the fixed material rotates on a shaft). “Wastewater flows through a circular tray in which semi-submerged disks mounted on a shaft or a bulk load located in a mesh drum rotate. Biofilm develops on these surfaces. Aeration occurs due to the periodic passage of the biofilm through the air” [1].
Aero tanks. In its classic form, this is a reservoir equipped with aerators located in its lower part and through which compressed air is supplied to the water volume using blowing equipment. Aerators can be disk, membrane, tubular.
What does household wastewater consist of?
Modern houses must have plumbing and sewer systems. People use the first for drinking and household needs, and with the help of the latter they remove contaminated liquid. And although the level of impurities in wastewater does not exceed 1%, it cannot be reused until it has been treated.
The composition of wastewater varies significantly depending on the location and time of sampling. Typically, a liquid contains both solid and soluble elements. Inorganic substances can be eliminated with a simple filter, but organics require a more complex approach. If measures are not taken, there is a risk of decomposition of biological compounds, which leads to the formation of a putrid odor and spoilage of water.
Effluents may contain residues of fats, detergents, phosphates and chloride compounds, nitrogen, sulfate and petrochemical products. These substances do not disappear anywhere on their own, so biological wastewater treatment is used to remove them.
Particular attention should be paid to this issue in country houses that are not connected to a centralized water supply. A well and a cesspool are usually located on their sites. Under unfavorable circumstances, untreated wastewater may end up in the tap, which will lead to the risk of poisoning of all residents.
Wastewater treatment Source vagner-ural.ru
Biological products
Biological products are used to perform the following tasks :
- Decomposition of organic matter: fats, carbohydrates, proteins;
- Stimulation of activated sludge operation;
- Reducing the volume of by-products in the form of sediment;
- Acceleration of the processing process;
- Decrease in biochemical oxygen consumption (BOD, COD);
- Build-up and restoration of activated sludge.
Manufacturers produce drugs that contain a certain number of strains of natural bacteria.
Each biological product contains different strains of microorganisms , which are selected depending on the composition of the wastewater.
Attention. The manufacturer in the description of its products indicates what kind of pollution it copes with.
Popular biological products:
| Name | Purpose of use | Price |
| Biofos | Domestic wastewater treatment | 43 RUR/25 mg |
| bioExpert BIO STARTER | Stimulation of the development of activated sludge in a septic tank or cesspool | 565 RUR/400 g |
| Unibac (compost, start, winter, effect) | Treatment of domestic and industrial wastewater, build-up of activated sludge | 470-750 rub./0.5 l. |
Wastewater treatment methods
There are two main methods for purifying domestic and industrial wastewater - natural and artificial. Small volumes of liquid can be purified under natural conditions, but currently large amounts of contaminated water require additional treatment. Usually a whole range of artificial methods is used, and natural cleansing is used as a supplement. Common wastewater treatment methods:
- Mechanical. At this stage, filters and water settling are used. For this purpose, special grids, sieves and traps are used. After the initial purification, the liquid is sent to a settling tank, where after some time the inorganic substances precipitate. In all modern systems, water goes through this stage of purification, but it is not enough to completely remove all contaminants. Chemical and biological components cannot be eliminated in this way.
- Chemical. It involves the use of special reagents that react with substances in the water and lead to the formation of an insoluble precipitate. As a result, it is possible to almost completely get rid of solid particles, and the organic content is reduced insignificantly.
- Physico-chemical. This is a combination of the two previous methods, which allows you to act on all types of contaminants. The most commonly used methods are coagulation, extraction and electrolysis.
- Biological. This method requires microorganisms that naturally purify water from organic impurities during their life processes.
Station for biological purification Source kvadrat.ru
Systems
For artificial aerobic cleaning, the following structures are most often used:
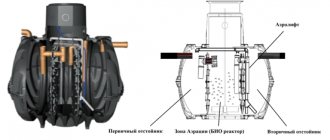
- An aeration tank is a reservoir in which wastewater is mixed with activated sludge. It is often divided into several chambers where different stages of biotreatment occur. The tank is equipped with an aerator - an oxygen supply system.
- Biotank is a type of aeration tank in which a special loading allows you to increase the total amount of biomass.
- Biofilter is a pool with drainage at the bottom. Wastewater treatment occurs through mineralization. Biocenosis is a film of aerobic microorganisms.
- A biological treatment station is a local structure that is installed where it is not possible to install a common sewage system. Treated wastewater is discharged into the ground, and the waste is used as fertilizer. The stations process wastewater volumes from 5 to 1000 cubic meters. m. VOCs are purified from 98-99% of contaminants.
Anaerobic treatment processes often take place in the following traditional facilities:
- An anaerobic lagoon is one or more settling tanks where wastewater is kept from 1 week to 2 months. Gases are released into the atmosphere.
- A septitank is a closed-type settling tank in which the sediment from the resulting solid particles rots and is broken down by anaerobes.
- A digester tank is a structure that looks similar to a septitank. But in the tank there is mixing, heating and control of basic parameters.
Biological wastewater treatment methods
Water purification by microorganisms occurs in the following facilities:
- Aero tanks;
- Biofilters;
- Biological treatment stations;
- Membrane bioreactors;
- Biological ponds.
Water purification facility Source rahada.ru
Aero tanks
Such biological wastewater treatment facilities are designed for mechanically treated liquid, which interacts with activated sludge located in the tank. The process takes place in special containers consisting of several departments and equipped with aeration systems. Activated sludge contains many bacteria that feed on organic waste. For their life to function, they require appropriate conditions that are constantly maintained in the reservoir.
Aerotank for water purification Source ru.wikipedia.org
First of all, bacteria need oxygen so they can reproduce. With a constant supply of air, microorganisms begin to absorb organic substances from the water, thus naturally cleaning the tank. Over time, organic reserves decrease, and oxygen consumption also begins to decrease. At this moment, the liquid moves to the following sections.
In further sections, the water is treated with the help of special nitrifying bacteria, which convert the nitrogen contained in ammonium salts into nitrites. There is also another type of microbe in the pond that absorbs nitrites. As a result of this process, nitrates are formed. Ultimately, after complete processing of the compounds, the wastewater enters the secondary settling tank. Here, activated sludge forms sediment, and clean liquid moves into reservoirs.
Aero tanks for wastewater treatment Source delfin.one
Membrane bioreactor
Biological methods of wastewater treatment include the use of a membrane bioreactor. The role of membranes is to create a kind of barrier to contaminants that pass through them. These elements are tubular, hollow fiber and flat frame. In addition to mechanical filtration, the activity of microorganisms is used.
The membrane reactor can be used both at the final stage of liquid purification and for preparatory purification before nanofiltration. In this way, it is possible to effectively remove excess salts from wastewater.
Process mechanism
To improve the quality of wastewater, two methods are used: aerobic and anaerobic biological treatment. In the first case, the process occurs with the help of oxygen, in the second - without it.
Important. In each treatment facility, a specific biocenosis is formed (a set of living organisms capable of processing pollution).
The cleaning mechanism depends on the chosen method and biocenosis.
Technological scheme of aerobic cleaning
The agent is biofilm or activated sludge.
This is a collection of bacteria, fungi, protozoa, representatives of microfauna of one or another genus/group with given characteristics.
The classic aerobic cleaning scheme looks like this:
- Wastewater enters the anaerobic zone of the aeration tank-secondary settling tank. There they are mixed with activated sludge.
- Oxygen is pumped into the installation and, if necessary, components that facilitate processing are introduced.
- Two biochemical processes occur: oxidation of organic carbon and nitrification.
- One or more recycles are carried out: the water is again mixed with activated sludge and enriched with oxygen.
- The processed wastewater settles - gravitational separation of the sludge mixture occurs.
- Excess activated sludge is sent for processing, and part of the mass is returned to its original position.
- Purified water is sent for further treatment or discharged into a reservoir.
The cleaning steps differ in different systems, but the essence of the method remains the same.
Anaerobic
This method is used when the wastewater contains a large amount of organic pollutants, solid sediments and activated sludge. During methanogenesis (the so-called anaerobic treatment process), pollutants are converted into biogas , which consists of methane and carbon dioxide.
Technological scheme of classical anaerobic treatment:
- Wastewater enters the compartment where methane fermentation occurs. After the interaction of anaerobic bacteria with pollution, methane, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide are formed. These gases are utilized.
- The digested sludge enters the next compartment, where sludge is dewatered in a centrifuge. Then the purified water is discharged into the reservoir.
- The dewatered sludge enters the drum dryer. The released water is disposed of.
- Dry sludge is disinfected and becomes a material for composting.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Biological wastewater treatment has notable advantages:
- Small amount of waste substances. As a result of processing, simple compounds arise that can be easily removed from the liquid. The resulting methane is used to heat buildings, and the soil is fertilized with sludge.
- Autonomous operation of devices. They do not require the addition of reagents, and the processes can be controlled by 1 person.
- Affordable cost of the method compared to other methods of liquid purification.
- Environmentally friendly and natural process. This cleanup does not harm natural resources or ecosystems.
The method also has disadvantages:
- It is difficult to maintain a constant number of microorganisms. Reducing their number will lead to insufficiently effective wastewater treatment.
- Construction of treatment facilities can require large amounts of funding. Over time, the investment pays for itself.
- The importance of strict adherence to liquid purification technology. Deviation from the rules will lead to a decrease in the effectiveness of the method.
- Not all types of organic matter can be recycled. Toxic substances can destroy bacteria, so it is important to carefully test the water for their presence and promptly remove toxins.
Aerobic and anaerobic bacteria - what are they?
Microorganisms used in the wastewater treatment process are divided into aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic ones exist only in an oxygen-containing environment and completely break down organic matter into CO2 and H2O, while simultaneously synthesizing their own biomass. The formula for this process is as follows:
CxHyOz + O2 -> CO2 + H2O + bacterial biomass,
where CxHyOz is an organic substance.
Anaerobic microorganisms cope normally without oxygen, but their biomass growth is small. Bacteria of this type are needed for oxygen-free fermentation of organic compounds with the formation of methane. Formula:
CxHyOz -> CH4 + CO2 + bacterial biomass
Anaerobic techniques are indispensable at high concentrations of organic matter - which exceed the maximum permissible for aerobic microorganisms. With a low organic content, anaerobic microorganisms, on the contrary, are ineffective.
Bioremediation
Biological wastewater treatment provides almost 100% clean water.
Various biostation options are possible:
- bioponds;
- filter fields;
- aero-, digesters;
- filter wells;
- bioreactors;
- sand filters.
Only bioremediation is not used as an independent method. It is first necessary to get rid of inorganic impurities mechanically and disinfect the water.
Storage type structures
Such structures are designed to receive the bulk of precipitation of any intensity. The main element is a storage tank where surface runoff accumulates. What exceeds the norm is discharged through the separation chamber. The accumulated wastewater is sent for treatment through a pump.
Flow-type structures
This method is used to remove wastewater from small areas - garages, gas stations, shopping center parking lots, highway drainages. Water enters the distribution section: contaminated water is sent to filters, relatively clean water is sent to the discharge point via a bypass line (bypass).
During peak loads, equipment breakdowns are possible, then it is better to use structures with storage tanks.
How is sludge treated?
Activated sludge is used for wastewater treatment, but is a material that must be disposed of periodically. This does not apply to the product itself, but to the harmful microorganisms it contains. To remove them, anaerobic bacteria are used, which do not require access to oxygen to function.
Most often, this technology is very convenient in the following devices.
- Dry toilets are installed not only in suburban and summer cottage areas, but also in private homes. This system does not require frequent maintenance; it is enough to periodically pump out waste.
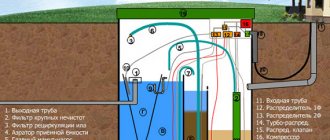
- Septic tanks. They are very convenient because they use a drainage system, through which the wastewater is independently cleaned and disposed of. Modern septic tanks are divided into several sections, which allows for better cleaning.
- Sedimentation tanks, which are created for the purification of large volumes, up to 1400 cubic meters. m. They have the same principle of operation as in ordinary septic tanks.
In septic tanks and sedimentation tanks, not only the waste liquid is purified, but also the sludge is processed by exposing it to the functioning of anaerobic bacteria.
Types of treatment facilities
Sedimentation tanks and filters are designed to neutralize surface water before discharging it into the city network. Septic tanks, aero- and digester tanks, bioponds, irrigation and filtration fields are used for wastewater.
Structures are divided into types according to their purpose. They differ in the volume of wastewater treated and the stages of the process.
Sewage treatment plants
By sewer we mean a combination of domestic and industrial wastewater that enters the city’s wastewater treatment plants through a separate sewer system. Domestic wastewater in its pure form is rare; more often it contains salts and petroleum products.
The following types of sewage treatment facilities are used:
- local devices;
- individual autonomous designs;
- block systems and modules.
Construction proceeds in several stages, based on the required degree of cleaning:
- Mechanical treatment reduces the content of suspended matter by 40-60%, BOD, which determines the degree of organic contamination, by 20-40 mg/l.
- Biopurification – up to 15-20 mg/l.
- Physico-chemical methods further purify wastewater to meet the standards for discharge into water bodies.
Domestic wastewater treatment plants
Domestic wastewater treatment plants are intended for residential buildings, small businesses, and camp sites far from the central sewer system. They process wastewater containing feces, food debris, sand, detergents - organic matter that can be biodegraded.
For domestic wastewater, a biological treatment system is used, based on an aerobic process in a bioreactor. Maintenance of domestic wastewater treatment plants is required to maintain efficient operation. It includes:
- removal of retained insoluble inclusions;
- calculation of the amount of sludge;
- checking oxygen content;
- control of work according to chemical indicators;
- checking the serviceability of elements.
Industrial waste water treatment plants
The liquid used by enterprises in technological processes must be purified to the required parameters. The equipment depends on the nature of production and the specifics of pollutants.
For example, purification steps for alcohol production:
- mechanical;
- biological;
- deep;
- Ural federal district plus release into a reservoir;
- dehydration and moisture utilization.
Meat processing and production of beverages, including beer, juices, kvass:
- mechanical method;
- bioremediation plus release to sewer;
- collection, dehydration, disposal.
Glass industry:
- mechanical cleaning;
- physico-chemical;
- biological plus release into the city collector;
- collection, dehydration, disposal.
Stormwater treatment plants
Rain moisture is clean, but it is saturated with harmful substances from asphalt, grass, and roofs. Therefore, stormwater treatment facilities are required. They provide mechanical processing from the following stages:
- Sump. Gravity forces large particles to the bottom.
- Thin layer module. An oily film from the water surface is collected on hydrophobic plates.
- Sorption fiber filter. Captures what was missed in a thin layer.
- Coalescent module. Here the particles of petroleum products are separated from the 0.2 mm that end up at the top.
- Carbon filter after purification. Completely removes petroleum products.
What methods of removing pollution exist?
Natural water is a complex disperse system containing a huge amount of dissolved and suspended impurities of various phase compositions, mineral and organic nature. It is impossible to use a universal method to remove such a variety of substances. Water treatment processes involve a whole range of methods and biological technologies for water purification, each of which is focused on eliminating a specific group of substances.
Depending on the direction of exposure and the instruments used, there are four main types of water purification methods:
- Physical methods of water preparation.
- Removal of dissolved pollutants using reagents - chemical methods.
- Combined effects on polluting substances by physical and chemical processes.
- Biological water treatment.
Physical methods of water purification are in demand mainly at the preparatory stage of water treatment. This is filtration, straining, settling. They are aimed at eliminating large inclusions from water volumes that can disrupt the operation of equipment and quickly destroy selective filter materials during further processing and selective purification of water.
Chemical methods are based on the ability of compounds to enter into chemical reactions with each other. By introducing special reagents to trigger certain interactions, it is possible to convert toxic contaminants into non-hazardous compounds, bind them into poorly soluble complexes or insoluble precipitates that can be easily removed by filtration or other separation methods.
Physico-chemical processes combine the combined effects on the water supplied for purification by physical phenomena and chemical reagents. Such methods are based on the properties of the impurities being removed, which are activated by specially introduced substances that initiate chemical and physical processes. With the help of physicochemical purification, both mineral pollutants and organic matter, metal ions, and dissolved gases are removed.
Biological purification methods are relatively new, but promising methods for removing unwanted elements and compounds from water with the participation of living microflora, special bacteria, and fungi. The essence is the selective absorption of pollutants from water by living organisms as a nutrient material for their life activity.
Septic tank made of concrete rings
This type of local treatment plant, working on the anaerobic principle, despite its simplicity and cheapness, requires a thoughtful approach. Here are the features this type of septic tank may have.
Chief engineer Dmitry Zadrutsky:
– Although this type of treatment facility is often built independently on a site, a number of features of this type of septic tank should be taken into account:
- In this type of septic tank, purification occurs by pouring wastewater from chamber to chamber. And that’s why they install 3-chamber septic tanks made of concrete rings.
- It is necessary to pay attention to the diameter of the rings. The volume of the septic tank depends on this. The greater the number of people living, the greater the volume of the septic tank and the number of chambers needed.
- If there is a high groundwater level in the area, then in order to avoid the seepage of contaminated water into the soil, better sealing of the septic tank is required.
- For better wastewater purification, you can use special bacteria, and for additional wastewater treatment, it is recommended to install a filtration field.
The disadvantages of this type of septic tank include:
- Complexity of installation and large volume of excavation work;
- Unlike plastic septic tanks, complete tightness of the joints of the rings is not ensured;
- The need to use special equipment and a crane to install a septic tank.
You can dump toilet paper, personal hygiene products into this septic tank and drain from the washing machine, but dumping from the dishwasher is no longer desirable, because... fatty deposits form on the walls of the main pipe. It is impossible to use water for irrigation, and it is necessary to periodically call a sewer truck to pump out the septic tank.
Additional treatment of household wastewater
In some cases, after the biological stage, water must undergo additional purification.
This is needed when:
- They are planned to be released into low-power reservoirs, especially those intended for fisheries;
- They will be used in industry or for domestic purposes.
A common method of post-treatment is settling in bioponds with natural and artificial aeration . In such reservoirs, favorable conditions are created for the massive development of microorganisms that break down the remaining pollutants and fight pathogens.
Reference. Beneficial bacteria reduce the number of E. coli by 99% and destroy helminth eggs.
The water settles in bioponds for several months and, after satisfactory laboratory analysis, reaches its final destination.