The problem of sewage treatment has always been one of the main challenges that humanity has faced in organizing civilized places of residence. Already in ancient Rome there were public toilets in which water was drained through pipelines into special settling tanks, where household wastewater was purified from human waste products. At all times, people have tried to apply modern methods of purifying MUNICIPAL wastewater and to use the latest achievements of science and technology. Since the times of ancient Rome, much has changed in solving this large and important task, but the basic principles of cleaning have remained the same.
Composition of domestic wastewater
Pollutants in wastewater are presented in the form of solutions of suspended particles and sticky non-crystallizing substances (colloids). The composition contains minerals (40%). These are salts (nitrites, sulfites, chlorides, phosphates, etc.), dust and soil particles.
Organic impurities are formed after animals and people. Food residues enter household wastewater. Organic waste is fat-containing, carbohydrate, protein compounds, acids, fiber, etc. Organic pollution is characterized by:
- COD - the chemical need for O2 consumption: how much oxygen is needed for the final oxidation of organic waste.
- BOD of substances in domestic water is a biological necessity for O2 consumption: the amount of free oxygen for the oxidation processes of organic elements of wastewater by simple organisms. Without access to oxygen, the BOD process is completed on the 20th day (full BOD). The indicator is calculated for a certain period of time in the absence of light with a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius (BOD 5 - O2 consumption on the 5th day is 70% of the total BOD). These data make it possible to determine the quantitative content of organic waste and reduce the time for calculating BOD.
Table. Density of domestic wastewater per 1 inhabitant per day.
| List of constituent pollutants | mg/l |
| Suspended particles | 110 |
| BOD full | 180 |
| COD | 250 |
| Fats | 40 |
| Nitrogen-ammonium elements | 18 |
| Hydrochloric acid salts (chlorides) | 45 |
| Sulfuric acid salts | 40 |
| Residue (dry) | 300 |
| Petroleum products | 1,0 |
| Synthetic surfactants | 2,5 |
| Organic matter | 0,005 |
| Fe | 2,2 |
| Cu | 0,02 |
| Ni | 0,005 |
| Zn | 0,1 |
| Cr | 0,0033 |
| Pb | 0,004 |
| Cd | 0,002 |
| Hg | 0,0001 |
| Al | 0,5 |
| Mn | 0,1 |
| Fluorine compounds | 0,08 |
| R | 2,0 |
According to the FKKO directory, household wastewater is classified as hazard class 4. They pose a threat to the public and must be rendered harmless after use.
Wastewater treatment is affected by temperature. In the cold season, suspended particles settle 30% longer than in the summer under equal conditions. The efficiency of biological treatment decreases at 9 degrees Celsius and below. Therefore, water for purification cannot be supplied below 6 degrees.
A special group includes bacterial contamination. Microorganisms, bacteria, and pathogenic viruses live in wastewater. They have adapted to exist inside the human body, birds and animals. Once in the external environment, some of them die. The rest retain their pathogenic properties and continue to actively develop.
These are bacteria of tuberculosis, tularemia, brucella, cholera vibrios and other pathogens. The maximum permissible concentration of Escherichia coli was chosen as an indicator of the level of contamination. Its quantitative content determines the quality of water and the possibility of using it for domestic needs.
In addition to microorganisms, household wastewater contains eggs of parasitic worms: roundworms, whipworms, roundworms, etc. Common means (free chlorine) have no effect on them. They die from high temperatures and when exposed to sunlight (dry out). Helminth eggs die at 55 degrees Celsius in 10 minutes, at 60 degrees in 5 minutes, at 70 in 10 seconds.
SanPiN has established hygiene requirements:
- to water quality;
- to the conditions of wastewater disposal;
- to the construction and operation of facilities that may affect the state of water;
- to the organization of control over the quality of water resources.
Flotators
To separate insoluble substances, these units use air bubbles. Floaters are containers in which water accumulates, and a mixture of water and air is supplied from below using a special bubbling device. Air bubbles capture contaminants due to their stickiness and are carried upward, forming foam called flotation sludge. Obviously, this method is suitable for light dissolved impurities. Coagulants can also be added here, which enlarge particles of pollutants, if they are very small. The dose of reagents is selected optimally so that they do not destroy the air bubble.
Types of domestic wastewater
Domestic water contains colloids in soluble form and organic elements that do not dissolve. They are divided into:
- fecal;
- economic.
The concentration depends on the presence of clean water from the water supply network. Domestic water is formed after using water for household needs: after cooking, in baths, laundries, in hospitals, public and residential buildings, etc.
They contain physiological secretions of humans and animals, and household organic waste. Biological pollutants pose a danger to the human body. These are bacteria, fungi, parasite eggs. Inorganic components are salts of various substances. Their concentration in wastewater reaches 45-58%.
The water contains canned and non-canned substances. The former do not react and cannot be broken down into their constituent elements during the treatment of domestic wastewater.
The second type of pollutants is eliminated using biological treatment. Sand, slag, silt, and algae residues are physical pollutants. Biological – microorganisms and fungi.
Often wastewater is contaminated with chemical products: pesticides, heavy metals, compounds of chemical elements, etc.
Tilt angle
An important point is the angle of inclination of the pipeline. This point is important when constructing gravity systems. If it is impossible to maintain the required angle of inclination, it is necessary to plan the construction of a pressure system in which wastewater is pumped using a fecal pump.
Many home craftsmen who undertake independent installation underestimate this point, and meanwhile, errors in both directions reduce the efficiency of the system.
If the angle is not large enough, the flow will move through the pipeline at low speed. In this case, some of the large inclusions will have time to precipitate in the pipes, and this is fraught with the formation of blockages. Too large an angle will also disrupt the normal movement of the transported medium. The water will drain too quickly, not having time to carry away heavy inclusions, which will linger in the pipes, forming blockages.
The optimal angle of inclination depends on the diameter of the pipe that is used to create the pipeline. The smaller the diameter, the greater the slope angle should be. So, if pipes with a diameter of 50 mm are selected, then a slope of 3 cm per meter should be observed. When using 100 mm pipes, the slope should be 2 cm.
Sources of education
Domestic wastewater is the same in every city and town. They contain:
- Waste water from the toilet. It contains feces, urine, paper, detergents, cleaning products and other household pollutants.
- Domestic wastewater from washing, bathing and showering.
- Water after cooking and washing dishes, cleaning, etc.
Up to 20 percent of water is used for kitchen needs, 25 percent for water procedures, 20 percent for laundry, and 35 percent for toilet flushing. Kitchen and toilet flushes pollute household waste the most.
In buildings with a central water supply and heat supply, the average norm per resident per day is 250, in the absence of it - 100 liters.
Industrial waste
They also include household items. In addition, there are industrial polluting components: residues of fuels and lubricants, reagents, metal oxides, and production waste. In addition, there are atmospheric ones - these are rain and melt water flowing from the industrial area. Storm wastewater treatment is carried out only when installing storm sewer systems. Main types of pollutants:
- mineral impurities formed during production activities;
- organic impurities, typical for food processing and pharmaceutical enterprises;
- organomineral, these are products of the processing of oil, gas, and plant raw materials.
Drains may contain toxins, acids, alkalis, and much more.
Wastewater quality indicators
The quality characteristics of water are determined by the following key parameters:
- volume of suspended particles;
- density of sedimentary substances;
- the presence of nitrogen-ammonium substances, salts of phosphate acids;
- content of surfactants and fats;
- chemical demand for O2 (COD);
- biological requirement for O2 (BOD);
- acidity level (pH). The fundamental indicators are COD, BOD, pH.
The pH indicator characterizes the activity of hydrogen. It is used to determine the acidity of water. If the liquid has a pH level greater than 7 units, the liquid is considered alkaline, and if less than 7, then it is acidic.
General characteristics of domestic wastewater:
- The liquids have a cloudy white or gray color, a characteristic fecal odor, and slight transparency.
- By chemical components: minerals and organic elements.
- Pollutants are present in colloidal, soluble and suspended forms.
- The presence of microorganisms: fungi, bacteria, viruses, parasites.
- The discharged water has a pH level of 7.2-7.8.
Particles in the effluent can be:
- large size from 0.1 mm;
- emulsions and suspensions in the form of foam up to 0.1 mm;
- colloids (0.1 µm);
- solutions up to 0.1 nm.
Wastewater containing biological and organic impurities is dangerous. They contain pathogens of infectious diseases. They should not get into rivers or soil. Such wastewater is transported to treatment plants, where biological treatment is carried out.
Selection of sewer design
To choose the right cleaning system, you need to consider a number of factors:
- total daily fluid intake;
- preferred type of sewer structure;
- mode of use of the sewer structure;
- location of the object.
Some devices may work offline. Others require electricity or other forms of energy to function. Certain systems cannot be used when groundwater is close to each other.
When arranging a treatment system, you should be guided by existing sanitary standards. If it is necessary to use a sewer truck to remove waste, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of free access to the waste storage site.
Domestic wastewater treatment
Modern technologies that are used to remove contaminants from household wastewater are so advanced that water can be reused without fear. It is used for irrigation and technical needs.
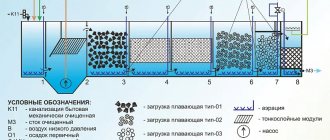
Mechanical cleaning
Mechanical cleaning methods are used at the initial stage. It is used to extract coarsely dispersed residues in wastewater by settling and filtration. For these purposes, coarse filters are used in settling tanks. Using this method, up to 70% of contaminants are removed. The whole process is divided:
- settling;
- straining;
- filtration.
Mechanical methods are used in storm drains to prevent debris from entering the sewer system.
Settling tanks are used with and without heat treatment of the sludge. High temperature treatment is used to disinfect parasite eggs and infectious bacteria. The sediment is heated with steam to 115 degrees Celsius.
Treated sludge, related to mineral fertilizers, can increase plant productivity. Their introduction into the soil should ensure the absence of parasite eggs and pathogenic viruses.
Stages of domestic wastewater treatment
Biological treatment
Biological treatment is used to process domestic wastewater. Deep biological treatment plants process organic compounds using protozoa. They break down contaminants into gas and water using oxygen.
Bacteria need O2, so special conditions are created for them. Anaerobic bacteria process organic matter in sealed containers. This releases methane. Such installations require a ventilation system.
Norms
Strict cleaning requirements only apply to industrial areas. At the same time, the standards indicate specific permissible concentrations of various chemicals regarding sources of non-industrial origin. Their discharge into soil or open water bodies without treatment is not permitted.
For household wastewater discharged into water bodies, regulatory requirements for content and concentrations apply.
Generally accepted standards are specified in SanPiN No. 4630–88:
- The pH value should be between 7.4-7.8.
- The average phosphate content is 0.95 mg/dm3.
- Sulfate content – 28.5 mg/dm3.
- Chloride content – 62 mg/dm3.
Important! It is prohibited to discharge untreated sewer water into water bodies. Failure to follow this rule results in administrative liability.
Elements of treatment facilities
The following HELYX equipment is used to create household cleaning systems:
- pipes and pipeline parts
- pumping stations
- wells
- ultraviolet disinfection systems
- special purpose containers
- sorption filters
- sand separators
- separators
- petrol oil separators
Sewerage
There are storm, domestic and industrial sewers. Sometimes they are closed into a single complex. At the same time they are sent to treatment plants. In private homes, an autonomous system is being developed that allows for the purification of household liquid waste in a closed cycle with the subsequent use of process water.
Disinfection
Purified liquids contain a large number of bacteria, including pathogenic ones, so they must be disinfected before being discharged into a body of water. For disinfection the following are used:
- sanitation with chlorine-containing reagents;
- ozonation;
- ultraviolet irradiation.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Chlorination involves the use of chlorine, a toxic substance, so working with it requires special care. The liquid after chlorination must be kept for at least half an hour to remove chlorine compounds. For this purpose, contact tanks are used.
Purified liquids contain a large number of bacteria, including pathogenic ones, so they must be disinfected before being discharged into a reservoir
Such tanks, with high productivity, occupy significant areas. Ozonation is an expensive, energy-intensive procedure and is carried out in sealed structures. UV disinfection is limited in performance.