Pollution of the World Ocean today is one of the global environmental problems of humanity. The mountain of garbage in the Pacific Ocean has reached such a large size that it has become known as the “garbage continent.” At the same time, solid household waste is far from the only source of pollution of the world’s oceans. A significant contribution to the pollution of aquatic ecosystems is made by wastewater from enterprises.
For example, the Baikal Pulp and Paper Mill discharged industrial waste into Lake Baikal, where 20% of the world's fresh water reserves are concentrated, for a long period of time (from 1966 to 2013), which significantly deteriorated the quality of water in the lake. Factories that produce food, cars or plastic also cause enormous harm to the environment.
Today, liquid waste from enterprises has become the main source of water pollution. In this article we will look at changes in the composition of water after its use at an enterprise, types of regulation of industrial discharges, as well as methods for their purification. In addition, you will learn what the danger of industrial discharges is for reservoirs and what to do if there are suspicions that an unauthorized discharge is being made into the reservoir that you use for swimming, or into the area near which your well or borehole is located. industrial waste.
Acceptable indicators of waste impurities
The sewer system of a business or city system is checked for the amount of impurities in the liquid. Their maximum permissible rate in the drain is measured in millimeters per liter. So, the MPC indicators have the following values:
- Number of announced substances – 500;
- BOD – 500;
- COD – 800;
- Remaining dense matter – 2000;
- Essentially containing impurities – 20.
In addition, there are rules and regulations regarding the physical state of water. So, the temperature should not exceed 40 degrees, and the acid level should not exceed 8.5 pH. Control over the condition of wastewater discharges should monitor the amount of suspended elements and the maximum permissible concentration of hydrogen sulfide.
Control over sewerage
In order to control the condition of sewer and industrial drains, it is necessary to have specialized equipment. When connecting to a common system, you need to check whether their sewer system has a well, which serves to regulate the quality of wastewater. What do such nodes look like and what are their features? These are wastewater sampling points that should be located within the plant area.
Attention! GOST provides for the mandatory implementation of ensuring free access to the well for employees of control authorities and performing analysis.
Sampling of wastewater is a mandatory procedure. Therefore, if the production of industrial organizations can potentially harm the environment, then it is necessary to install control points. Enterprises bear full responsibility for compliance with this GOST standard.
Classification of wastewater treatment plants
If there is an excess of the quantity by at least one indicator when discharging waste into the general sewer system, then this is a violation of the law, and the defendant will suffer an administrative penalty. For example, if the temperature is more than 40 degrees or the amount of salt is above the maximum permissible concentration, then the owner of the drain is obliged to carry out preliminary treatment.
Attention! Only if all the rules and guest regulations are met can we talk about the preservation of the ecological state of the environment. Irresponsibility in this matter can lead to a global catastrophe.
MPC of harmful substances
Maximum permissible concentrations of maximum permissible concentrations are a sanitary and hygienic standard established by law. Maximum permissible concentrations of maximum permissible concentrations of harmful substances and their compounds in water are certain concentrations, under the daily influence of which over a long period of time, pathological changes or diseases do not occur in the human body, controlled by modern research methods at any time in a person’s life and subsequent generations.
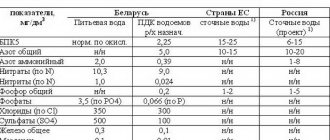
Table 1. Regional MPCs of wastewater in the Russian Federation and the European Union
| Water quality indicators, chemicals | Maximum permissible concentrations of maximum permissible concentrations of wastewater from industrial enterprises: | ||||||||
| EU | Moscow | Saint Petersburg | Yaroslavl | Tula | Kursk | Izhevsk | Ekaterinburg | MPC RH | |
| pH | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 |
| Iron (Fe), mg/l | 2-20 | 1 | 0,4 | 0,1 | |||||
| Copper (Cu, total), mg/l | 0,1-4 | 0,02 | 0,004 | 0,001 | |||||
| Zinc (Zn2+), mg/l | 0,5-7 | 0,1 | 0,03 | 0,01 | |||||
| Cadmium (Cd, total), mg/l | 0,01-0,6 | 0,005 | 0,003 | 0,005 | |||||
| Nickel (Ni2+), mg/l | 0,5-3 | 0,1 | 0,01 | ||||||
| Chromium (Cr6+), mg/l | 0,1-0,5 | 0,1 | 0,07 | 0,02 | |||||
| Chromium (Cr3+), mg/l | 0,5-5 | 0,1 | 0,4 | 0,07 | |||||
| Aluminum (Al3+), mg/l | 1-10 | 0,04 | |||||||
| Lead (Pb, total), mg/l | 0,2-1 | 0,06 | 0,006 | ||||||
| Silicon (SiO32-), mg/l | 1 | ||||||||
| Tin (Sn, total), mg/l | 2-10 | ||||||||
| Manganese (Mn), mg/l | 0,2 | ||||||||
| Calcium (Ca2+), mg/l | — | 150 | 180 | ||||||
| Hardness, mEq/l | — | ||||||||
| Sulfates (SO42-), mg/l | — | 250 | 100 | ||||||
| Chlorides (Cl-), mg/l | — | 170 | 300 | ||||||
| Nitrates (NO3-), mg/l | — | 23,5 | 40 | ||||||
| Phosphates (PO43-), mg/l | — | 1,5 | 1,6 | ||||||
| Ammonia and ammonium salts, mg/l | — | 23,1 | 3 | ||||||
| Petroleum products, mg/l | 0,1-5 | 0,5 | 0,3 | 0,05 | |||||
| Surfactant, mg/l | 2,5 | 0,9 | |||||||
| Superfloc A-100 Flocculant: anionic polyacrylamide amine - 95% active moisture - 4.5%, impurities - 0.5%, mg/l | 0,25 | ||||||||
| COD, mg/l | 150-400 | 270 | 176 | ||||||
| Suspended substances, mg/l | 50-60 | 150 | 103 | ||||||
| Dry residue, mg/l | — | 500 |
Article by specialists from the Russian Chemical Technical University named after D.I. Mendeleev: Validity and unreasonableness of using various lists of maximum permissible concentrations for wastewater from galvanic production
Table 2. Maximum permissible concentrations of wastewater MPC in the EU
| Belgium | France1 | Germany | England and Wales2 | Italy3 | Holland | Spain | Portugal | |
| Discharge into the city sewerage system (GK) or into a fishery reservoir (RF) | RHV | GK | RHV | |||||
| Silver (Ag), mg/l | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | ||||
| Luminium (Al), mg/l | 10 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1-2 | 5 | ||
| Cadmium (Cd), mg/l | 0,6 | 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,01 | 0,02 | 0,2 | 0,1-0,5 | 0,2 |
| Cyanide (CN free), mg/l | 0,1 | 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,5 | 0,2 | 0,5-1 | 0,1 | |
| Hexavalent chromium (Cr VI), mg/l | 0,5 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,2 | 0,1 | 0,2-0,5 | 0,1 |
| Total chromium (Cr), mg/l | 5 | 3 | 0,5 | 1 | 2 | 0,5 | Cr(III) 2-4 | Cr(III)3 |
| Copper (Cu), mg/l | 4 | 2 | 0,5 | 2 | 0,1 | 0,5 | 0,2-10 | 2 |
| Fluorine (F), mg/l | 10 | 15 | 50 | 6 | 6-12 | 15 | ||
| Iron (Fe), mg/l | 20 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2-10 | 5 | ||
| Mercury (Hg), mg/l | 0,1 | 0,005 | 0,05 | 0,05-0,1 | 0,05 | |||
| Nickel (Ni), mg/l | 3 | 5 | 0,5 | 1 | 2 | 0,5 | 2-10 | 5 |
| Nitrites (NO2), mg/l | 1 | 0,6 | 1 | |||||
| Phosphorus (P), mg/l | 2 | 10 | 2 | 10 | 15 | 10-20 | 10 | |
| Lead (Pb), mg/l | 1 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,2 | 0,2-0,5 | 1 | ||
| Tin (Sn), mg/l | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 10 | 2 | |
| Zinc (Zn), mg/l | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 3-20 | 5 | |
| COD | 300 | 150 | 400 | 160 | 150 | |||
| EDTA, mg/l | ||||||||
| Petroleum products, mg/l | 5 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 5 | 0,1 | 20-40 | ||
| Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) | 1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | |||||
| Suspended substances, mg/l | 50 | 60 | ||||||
| Total salt content, mg/l | no restrictions on sulfates | no limits | no limits | |||||
| Total content of heavy metal ions (IHM) | 15 | no limits | 50kg/year/general 20kg/year/metal | 3 | E metals 15–20 mg/l | |||
| 1. France: Water consumption: 8 liters per 1 m2 of treated surface for each washing stage. 2. Environment Agency of England and Wales. 3. Reduced maximum concentration limits for harmful substances have been adopted by law in some areas (for example, the catchment area of the Venice Lagoon). 4. Maximum permissible concentrations of maximum permissible concentrations of fishery reservoirs |
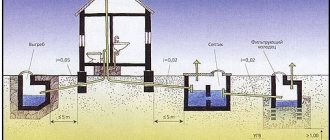
Ways to clean an offline system
MPC is a sanitation standard regulated by the country's legislative framework. When installing an autonomous sewer system, you should know all the permissible indicators for the amount of substances. To perform a discharge analysis, you can take a water sample to an environmental organization yourself, or wait for an inspection. It is worth considering that the diagnostics of wastewater is characterized by the frequency established by the control campaign.
If the results of the analysis are negative, then you need to review the wastewater treatment system for the enterprise. Today, the following methods are considered the most popular methods of sewer filtration:
- Chemical method. Only professionals in this field can carry out such a cleaning process, since the substances are dangerous to human health. This method is applicable in the industrial field.
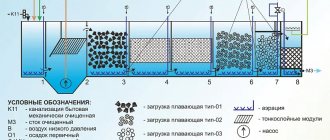
- Biological purification. This method is characterized by the use of special phosphorus microorganisms. It is used in filtration installations: septic tanks, aeration tanks and stations.
- Combined cleaning. This method combines the first and second methods.
It is very important not to forget that it is not recommended to discharge clarified wastewater into a reservoir; it must be sent to the ground for further treatment. MPC is a norm from which it is prohibited to deviate. If, after analysis, a violation of the rules is revealed, then paying a fine is the minimum punishment for it.
MPC of harmful substances
Maximum permissible concentrations of more than 960 chemical compounds have been established for water, which are grouped into three groups according to the following hazard indicators (LPH - limiting hazard indicator): sanitary-toxicological (s.-t.), general sanitary (general), organoleptic (org. ). Maximum concentration limits for some harmful substances in water bodies are presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Maximum concentrations of harmful substances in water bodies for domestic, drinking and cultural water use, mg/l
| Substance | LPV | MPC |
| Aluminum | S.-t. | 0,5 |
| Ammonia (by nitrogen) | Org. | 1,5 |
| Acetone | S.-t. | 2 |
| Benzpyrene | S.-t. | 0,000005 |
| Petrol | Org. | 0,1 |
| Bromine | S.-t. | 0,2 |
| Beryllium | S.-t. | 0,0002 |
| Bor | S.-t. | 0,5 |
| Bismuth | S.-t. | 0,1 |
| Benzene | S.-t. | 0,1 |
| Dimethylamine | Org. | 0,3 |
| Diethyl ether | Org. | 0,3 |
| Iron | Org. | 0,005 |
| Isoprene | General | 1,2 |
| Acetic acid | General | 0,1 |
| Synthetic fatty acids C5 - C20 | Org. | 0,1 |
| Manganese | Org. | 1 |
| Copper | S.-t. | 3 |
| Methanol | Org. | 0,1 |
| Oil | S.-t. | 0,0005 |
| Mercury | S.-t. | 0,03 |
| Lead | Org. | 1 |
| Carbon disulfide | General | absence |
| Sulfides | S.-t. | 0,05 |
| Formaldehyde | S.-t. | 0,0001 |
| Elemental phosphorus | General | 1 |
| Zinc | Org. | 0,5 |
| Ethylene | Org. | 0,5 |
| Molybdenum | S.-t. | 0,25 |
| Urea | General | 1 |
| Cadmium | S.-t. | 0,001 |
| Ethylene glycol | S.-t. | 1 |
Maximum permissible concentrations of harmful substances for fishery reservoirs and watercourses are established for 521 ingredients, grouped into groups according to the following LPs: toxicological, organoleptic, fishery and general sanitary. Water for drinking animals, according to standards, should not be inferior to the quality of drinking water, however, the requirements for organoleptic properties may be slightly reduced. Only in exceptional cases, in areas with a shortage of fresh water, in agreement with the sanitary-epidemiological service and veterinary supervision, is it allowed to use water of high mineralization for washing and watering animals, preparing feed and cleaning premises. The most stringent requirements must be placed on the condition of water used in livestock farming, since infection of animals through water and the development of epizootics cause enormous damage to the national economy.
It should be noted that the currently used methods for assessing water quality using the system of maximum permissible concentrations of pollutants do not provide a complete picture of the state of natural waters and are not a sufficient guarantee of their protection from pollution. The conditions under which the discharge of municipal and industrial wastewater into reservoirs and watercourses is possible are determined by the “Rules for the protection of surface waters from wastewater pollution” and the “Rules for the sanitary protection of coastal sea waters”, approved in 1974. But these rules are designed to ensure the purity of the reservoir only at the sites of drinking, cultural and household or fishery water use points. This approach has already led to the fact that many rivers in our country are polluted locally or continuously throughout almost their entire length. In stagnant and low-flowing reservoirs, self-purification processes proceed even more slowly and emergency situations often arise. Such phenomena occurred in Lake Ladoga, one of the sources of water supply for St. Petersburg, and in many large reservoirs. All modern treatment facilities are built using destructive treatment methods, which boil down to the destruction of water polluting substances through their oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, decomposition, etc., and the decomposition products are partially removed from the water in the form of gases or sediments, and partially remain in it in the form of soluble mineral salts. As a result, so-called non-toxic mineral salts enter natural waters in quantities corresponding to the maximum permissible concentrations, but many times higher than their natural concentrations in the aquatic environment. Therefore, the discharge of wastewater into rivers and reservoirs, which has undergone deep purification from organic compounds of nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur and other elements, nevertheless increases the content of soluble sulfates, phosphates, nitrates and other mineral salts in the water, causing eutrophication of reservoirs, their “blooming”. » due to the rapid development of blue-green algae; the latter, dying, absorb a lot of oxygen and deprive the water of its ability to self-purify.
Modern industry annually synthesizes many new substances; the establishment of their maximum permissible concentrations is inevitably delayed, especially since, when these substances enter water, they can create new, unexplored combinations of compounds with unknown properties.
Thus, the existing MPCs developed by the sanitary and hygienic service do not fully reflect the impact of alien substances on aquatic ecosystems.
Cleaning methods
Pollution can be divided into:
- mechanical (insoluble particles);
- chemicals (toxic substances);
- bacterial (pathogenic bacteria and fungi);
- radiation (radioactive elements);
- physical (the state of aggregation of a substance or other characteristics, for example, temperature, has changed).
The choice of optimal treatment methods is possible only after quantitative analysis of wastewater. The degree of purification and the selection of effective equipment and filter elements depend on the composition of the pollution and the volume of wastewater.
Various methods and their combinations are used to purify industrial discharges. Straining, settling and filtration are mechanical cleaning methods. Filtration is the most common method of water purification. In metallurgy, up to 90% of insoluble contaminants are purified in this way. However, in the food industry, this method can remove no more than 5% of contaminants.
When applying physicochemical cleaning methods, I use precipitating reagents, electric current and temperature changes, freezing, and evaporation.
MPC classification
Sampling of wastewater at the enterprise is carried out by special environmental organizations. The peculiarities of their analysis are to identify maximum permissible concentrations based on various indicators. If there is any excess of the norm, then GOST provides for punishment of the person who caused harm to the natural environment.
Hygienic MPCs combine substances that, if exceeded, can cause harm to human health or lead to deterioration in water quality. The standard regulates the amount of toxic elements in water bodies and water storage areas.
One of the most dangerous impurities can be the chemical type. There can be a large amount of substances of this nature, so their maximum permissible concentrations are divided into the following groups:
- Excessively dangerous concentrations;
- Impurities with a high level of danger;
- Hazardous elements;
- Substances of moderate degree of danger.
Conducting an analysis of enterprises includes special formulas and methods for calculating the presence of deviations from the norms. Diagnostics should be characterized by the frequency chosen by the organization conducting the inspection.
Composition of domestic wastewater
The standard for the composition of wastewater is determined by specific water disposal per 1 resident. This indicator takes into account the daily amount of water consumed recalculated to annual data.
Wastewater includes mineral and organic components, while organic ones are nitrogen-free and nitrogen-containing. Normally, each element should maintain its standard percentage content.
| Mineral components | Organic elements | |
| The mineral content must meet the following criteria: proportion of insoluble matter – 5%, · suspensions – 5%; · colloidal solutions – 2%; · completely dissolved substances – 30%. Mineral compounds include ammonium salts, phosphates, chlorides, and bicarbonates. | If you look at the organic part, their percentage content is different: · proportion of insoluble base – 15%; · suspensions – 15%, · intermediate dispersed systems – 8%; · homogeneously dissolved elements – 20%. | |
| Nitrogen-free inclusion | Nitrogen-containing particles | |
| · carbohydrates; · fats. | · proteins; · products of protein hydrolysis. | |
The biological component is separated separately - bacteria, viruses and other types of microorganisms. They pose a particular danger and become a source of epidemics if not properly cleaned.
Norms of maximum concentration limits for pollutants in wastewater discharged into sewers in cities.
| Ingradient | Units | Permissible concentration |
| Biochemical oxygen demand | ||
| Suspended solids | ||
| Ammonium salt nitrogen | ||
| Sulfates | ||
| Nitrate nitrogen | ||
| Petroleum products | ||
| Chrome general | ||
| General phosphorus |
Methods and methods for determining the content of pollutants in wastewater:
Biochemical oxygen consumption is measured by a BOD tester.
Suspended solids - determined by filtration through a membrane filter. Glass, quartz or porcelain, paper are not recommended due to hygroscopicity.
Nitrogen ammonium salts - the method is based on the interaction of ammonium ion with Nessler's reagent, resulting in the formation of mercury iodide - yellow ammonium:
NH 3 +2 (HgI 2 + 2 K) + 3 OH=3 HgI 2 + 7 KI + 3 H 2 O.
Sulfates - the method is based on the interaction of sulfate compounds with barium chloride, resulting in the formation of an insoluble precipitate, which is then weighed.
Nitrates - the method is based on the interaction of nitrates with sulfasalicylic acid to form a yellow complex compound at pH = 9.5-10.5. Measurements are carried out at 440 nm.
Petroleum products are determined by the gravimetric method, after pre-treating the test water with chloroform.
Chromium - the method is based on the interaction of chromate ions with diphenylcarbazide. As a result of the reaction, a purple compound is formed. Measurements are carried out at λ=540 nm.
Copper - the method is based on the interaction of Cu 2+ ions with sodium diethyldithiocarbonate in a weak ammonia solution with the formation of copper diethyldithiocarbonate, colored yellow-brown.
Nickel - the method is based on the formation of a complex compound of nickel ions with dimethylglyoxin, colored brownish-red. Measurements are carried out at λ=440 nm.
Zinc - the method is based (at pH = 7.0 - 7.3) on the compound of zinc with sulfarsazene, colored yellow-orange. Measurements are carried out at λ = 490 nm.
Lead - the method is based on the combination of lead with sulfarsazene, colored yellow-orange. Measurements are carried out at λ=490 nm.
Phosphorus - the method is based on the interaction of ammonium molybdate with phosphates. A solution of stannous chloride is used as an indicator. Measurements are carried out on KFK - 2 at λ = 690-720 nm.
Nitrites - the method is based on the interaction of nitrites with Griess reagent to form a yellow complex compound. Measurements are carried out at λ=440 nm.
Iron - the method is based on sulfasalicylic acid or its salts (sodium) form complex compounds with iron salts, and in a weakly acidic environment, sulfasalicylic acid reacts only with Fe +3 salts (red color), and in a weakly alkaline environment - with Fe +3 and Fe +2 salts ( yellow color).
Division by content and characteristics of particles
There are several ways to differentiate contaminants in wastewater. In one case, they are distinguished by the content of the main components (mineral, organic or biological), in the other - by the nature of the particles. In the second option, mixtures are obtained that can completely dissolve in water or form dispersed solutions.
| sand; clay; slag; salt and alkaline mixtures. | Vegetable | Animals | molds, yeasts; microorganisms; seaweed; bacteria. |
| waste of fruits, plants and vegetables; paper; vegetable oils. | physiological secretions; tissue fragments; sticky substances. |
Biological pollutants are often placed in a separate group because they can be a source of severe diseases and spreading infections. They enter drains from residential buildings and enterprises (meat processing plants, slaughterhouses).
Soluble
If the particle size in wastewater does not exceed 1.0 nm, then such pollutants form a homogeneous soluble structure in water.
Foams, suspensions and emulsions
If the particles fall in the range from 0.1 mm to 0.1 µm, then insoluble compounds such as foam, suspension or emulsion are formed.
Colloidal
Solutions that are intermediate in solubility are considered to be colloidal, where particles from 0.1 μm to 1.0 nm are present.
Insoluble
When the particle size in pollutants exceeds 0.1 mm, complete dissolution in a liquid medium does not occur. Such mixtures are classified as insoluble options.
MPC
For surface water bodies, the following maximum permissible concentrations of pollutants in the waters of water bodies are used:
| No. | Analyzed indicators | Hazard class (Order of Rosrybolovstvo dated January 18, 2010 No. 20 and SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00) | MPC of water bodies of fishery importance (Order of the Federal Agency for Fisheries dated August 4, 2009 N 695 On approval of guidelines for the development of water quality standards in water bodies of fishery importance, including standards for MPC of harmful substances in waters of water bodies of fishery importance | MPC of water bodies of fishery importance (Order of Rosrybolovstvo dated January 18, 2010 No. 20) | Maximum permissible concentrations of water bodies for drinking, domestic and recreational water use (GN 2.1.5.1315-03 as amended by GN 2.1.5.2280-07 and SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00) |
| water use category | water use category | ||||
| highest and first | second | For drinking and domestic water use, as well as for water supply to food enterprises (first category) | For recreational water use, as well as within populated areas (second category) | ||
| 1 | Transparency, cm | not lower than 20 | |||
| 2 | Suspended substances, mg/dm3 | the content of suspended substances at the control site (point) should not increase compared to natural conditions by more than: | Within populated areas, when discharging wastewater, carrying out work on a water body and in the coastal zone, the content of suspended substances at the control site (point) should not increase compared to natural conditions by more than 0.75 mg/m3. dm | ||
| 0.25 mg/dm3 | 0.75 mg/dm3 | ||||
| 3 | Water mineralization, mg/l | no more than 1000 (at the control point) | |||
| 4 | Hydrogen value (pH) | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | |
| 5 | Total BOD, mg O2/l (at a temperature of 20 °C should not exceed in water of water bodies) | 3,0 | 3,0 | ||
| 6 | BOD5, mgO2/l (should not exceed at a temperature of 20 degrees C) | 2 (at the control point) | 4 (at the control point) | ||
| 7 | COD, mgO/l | 30 (at the control point) | |||
| 8 | Dissolved oxygen O2, mg/dm3 | During the winter (under the ice) period there should be at least | At least 4 | ||
| 6 | 4 | ||||
| In the summer (open) period, all water bodies must have at least 6 | |||||
| 9 | Chloride anion Cl-, mg/l | 300 | 350 | ||
| 10 | Sulfate anion, SO4, mg/l | 100 | 500 | ||
| 11 | Phosphates (polyphosphates) Men(PO3)n, Men+2PnO3n+1, MenH2PnO3n+1, mg/l | 0.05 (oligotrophic water bodies) for phosphorus 0.15 (mesotrophic water bodies) for phosphorus 0.2 (for eutrophic water bodies) for phosphorus | 3.5 (1.14 for phosphorus) | ||
| 12 | Ammonium ion NH4+, mg/l | 0.5 (0.4 nitrogen) m | 1.93 (1.5 for nitrogen) | ||
| 13 | Nitrite anion NO2-, mg/l | 0.08 (0.02 for nitrogen) | 3.3 (1 for nitrogen) | ||
| 14 | Nitrate anion NO3-, mg/l | 40 (9 for nitrogen) | 45 (10.16 for nitrogen) | ||
| 15 | Iron Fe, mg/l | 0,1 | 0,3 | ||
| 16 | Divalent manganese Mn2+, mg/l | 0,01 | 0,1 | ||
| 17 | Copper Cu, mg/l | 3 | 0,001 | 1 | |
| 18 | Zinc Zn, mg/l | 3 | 0,01 | 1 | |
| 19 | Lead Pb, mg/l | 2 | 0,006 | 0,01 | |
| 20 | Chromium3+ Cr, mg/l | 3 | 0,07 | ||
| 21 | Chromium6+ Cr, mg/l | 3 | 0,02 | 0,05 | |
| 22 | Chromium total Cr, mg/l | 0,05 | |||
| 23 | Aluminum Al, mg/l | 4 | 0,04 | 0,2 | |
| 24 | Nickel Ni, mg/l | 3 | 0,01 | 0,02 | |
| 25 | Cadmium Cd, mg/l | 2 | 0,005 | 0,001 | |
| 26 | Cobalt Co, mg/l | 3 | 0,01 | 0,1 | |
| 27 | Sulfides, mg/l | 0.005 For oligotrophic reservoirs 0.0005 | 0,05 | ||
| 28 | Surfactant (sodium dodecyl sulfate), mg/l | 4 | 0,5 | ||
| 29 | Petroleum products, mg/l | 3 | 0,05 | 0,3 | |
| 30 | Phenol (another name is hydroxybenzene or carbolic acid) C6H5OH, mg/l | 3 | 0,001 | 0,001* | |
| 31 | Formaldehyde, mg/l | 4 | 0,1 | 0,05 | |
| 32 | Arsenic | 0,05 | 0,01 | ||
| 33 | Calcium | 4 | 180 | ||
| 34 | Magnesium | 4 | 40 | 50 | |
| 35 | Potassium | 4 | 50 (10 for reservoirs with mineralization up to 100 mg/l) | ||
| 36 | Selenium | 2 | 0,002 | 0,01 | |
| 37 | Fluoride anion | 3 | 0.05 (in addition to the background fluoride content, but not higher than their total content of 0.75 mg/l) | ||
| 38 | Sodium | 4 | 120 | 200 | |
| 39 | Molybdenum | 2 | 0,001 | 0,07 | |
| *from GN 2.1.5.1315-03: MPC of phenol - 0.001 mg/l - is indicated for the amount of volatile phenols that give water a chlorophenolic odor during chlorination (test chlorination method). This maximum permissible concentration applies to water bodies for domestic and drinking water use, subject to the use of chlorine for water disinfection during its purification at water supply facilities or when determining the conditions for the discharge of wastewater subjected to disinfection with chlorine. In other cases, the content of the amount of volatile phenols in the water of water bodies is allowed in concentrations of 0.1 mg/l. |