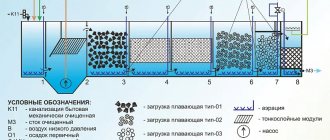
Design and purpose of flotators
Design of an industrial flotator
Liquid purification is carried out using flotation block units. The main components of the devices are:
- a container with a pump that mixes oxygen with liquid and reagents;
- flotation tank with a valve to eliminate excess air;
- degasser to remove residual oxygen.
Flotation blocks are not used as independent purification tools. They are used in combination in treatment plants of industrial enterprises and car washes, since they require preparation - mechanical treatment of sewage.
Who does the production?
Before purchasing flotation machines, you need to clearly define the parameters.
The parameters are selected based on the following conditions:
- Composition and nature of sewage waste.
- Temperature and uniformity of water supply.
- Where is treated water discharged?
In Moscow and St. Petersburg, quite a few companies are engaged in the implementation of installations:
- — TR brand flotators, cost from 313,500 rubles.
- Trading house "Water treatment equipment" - pressure units of the DAF brand.
- Rosintereko LLC - flotators and two-stage units of the Angara brand.
Important. It is necessary to take into account the requirements for processing and removal of sediment, the degree of disinfection.
Action diagram
The operating principle of a flotation unit is quite simple:
- The wastewater enters the working tank, where it is enriched with fine air.
- The mixture enters the flotation chamber, where hydrophobic debris interacts with gas bubbles.
- Gradually, the layer separating hydrophobic particles and air bubbles decreases and ruptures. This is explained by a change in the surface tension of water.
As a result, dirty foam appears on the surface of the liquid. Its removal occurs using special rake devices.
Flotation in devices is a forced process when the density of waste particles is artificially reduced.
Why do you need to purify water?
Of the total supply of the World Ocean, only 3% is fresh water, of which 68% is glaciers (not suitable for drinking), 30% is underground sources (often polluted from soils) and only 2% is land-based water supplies. From the global picture of the world it is clear that the availability of clean fresh water is not just a necessity, but sometimes a luxury.
Wastewater generated during the economic activities of enterprises contains a large amount of pollutants in concentrations exceeding permissible and regulatory standards. As a rule, we are talking about heavy metals (iron, nickel, copper, lead, mercury, cadmium, etc.), petroleum products, suspended solids, aluminum, surfactants (synthetic surfactants, for the average person this is everything that foams). When these substances enter water bodies, they disrupt the normal functioning of aquatic biogeocenoses, poison the soil, provoke the growth of blue-green algae, and are toxic to animals. These pollutants are also toxic to humans.
Human economic activity in residential apartment buildings and private buildings also produces a large amount of pollutants. These are mainly surfactants and organic waste, but metal salts also end up in the sewer system.
Flotation techniques
Flotators are classified according to the method of formation of gas bubbles. The most commonly used flotation methods are:
- mechanical;
- pressure;
- vacuum;
- biological;
- electrochemical.
Pressure flotation is a simple method of wastewater treatment when reagents are added to the liquid and oxygen is supplied under high pressure using a pump. Bubbles form throughout the entire volume of sewage. This method is often used to purify liquid from activated sludge. The technology requires the presence of a saturation chamber.
Electroflotators do not have this unit. The technique does not require electroflotation or reagents. It involves removing suspended matter from a liquid using an electric current. The electrolysis process is carried out in the electroflotator: hydrogen is released at the cathode, and oxygen is released at the anode.
The principle of operation of a vacuum device is to reduce the pressure below atmospheric pressure in the flotation tank. This releases air dissolved in water.
Biological flotation is heating the sediment after primary purification using steam and allowing it to settle for several days. The resulting bacteria release gas bubbles. Thanks to them, sludge particles are flotated into a foam layer, where they are compacted and dewatered. Within five days, the moisture content can be reduced to 80 percent, making subsequent processing easier.
Chemical additives
Reagents for flotation purification of liquids significantly increase the efficiency of equipment.
Flotation reagents are classified into three main groups:
Collectors – designed to remove a water film from the surface of suspended particles. This ensures the possibility of combining suspensions with gas bubbles.- Foaming agents – form a dense shell of gas capsules. They also regulate the size of the bubbles, preventing them from increasing.
- Modifiers or regulators - affect the number of molecules that adhere to molecular suspensions. In addition, the degree of consolidation of the connection depends on them.
The selection of reagents is carried out depending on the type of equipment and the composition of the liquid being purified.
Features of mechanical flotation
The principle of operation of the flotator
There are several flotation methods for mechanical wastewater treatment:
- The liquid is mixed by a special impeller with blades. This purification method is performed without pressure and is well suited for removing coarse and fibrous impurities from water - hair, threads, wool.
- The wastewater is discharged into a centrifuge (impeller). There they mix, acquiring a homogeneous structure. As the contaminated water moves, it becomes enriched with oxygen and small bubbles form. They are able to attract even the remains of petroleum products.
- The wastewater is enriched with air using special pipes located at the bottom of the receiving chamber. The method is called pneumatic. It is used when it is necessary to purify wastewater that is aggressive for processing in an impeller or free-flow installation.
During pressure treatment, the level of purification depends on the rotation speed of the impellers - the higher it is, the better. But you need to calculate the exact acceleration. At a certain stage, flow turbulence increases and debris flakes may collapse, which reduces the efficiency of the process.
Purification of sewer liquids in mechanical flotation units is used when the liquid contains light hydrophobic impurities - fats, oil residues, oils.
If the wastewater contains impurities that require aggregation, a different method should be preferred. Due to significant turbulence, contaminant molecules are destroyed, and the quality of purification sharply decreases.
A compromise between the mechanical and pressure methods is the saturation of water with oxygen using a porous material. The direction of air flow here occurs through special plates with slots. The thinner the slot holes in the plate, the smaller the air bubbles and the better the cleaning.
Types of structures
The table describes the equipment that is used at different stages of wastewater treatment.
For the mechanical stage:
| Installation | What is | Principle of operation |
| Sand traps | Horizontal or vertical installations of oblong shape. | Water moves through the equipment at a speed of 0.15-0.3 m/s. At this rate, mineral impurities with a diameter of 0.25 mm or more settle to the bottom, and small particles of organic matter remain in the water. |
| Septic tanks | Reservoirs where water stands still or moves very slowly. | Mechanical impurities settle to the bottom under the force of gravity. |
| Lattices | A filter cloth made of metal rods, which are located at a distance of 2-8 mm from each other. | Water passes through the rods and large debris is retained. |
| Oil traps and oil sand traps | 3-4 separate chambers connected to each other. | In the chambers, the wastewater settles, passes through a grate and a coalescence filter, and sorption materials. |
For the physico-chemical stage:
| Installation | What is | Principle of operation |
| Flotators | Reservoirs in which gas bubbles form. They are generated by an electric pump / electrolysis process / rotating turbines. | Gas bubbles rise and take with them fine particles. |
| Flocculators | A system of pipes in which the coagulant is mixed with wastewater and a chemical reaction occurs. | Coagulants combine with contaminants, form large flakes and precipitate. |
For the biological stage:
| Installation | What is | Principle of operation |
| Aero tanks | A rectangular tank through which wastewater mixed with activated sludge flows. | Aerobic bacteria break down organic matter in the presence of oxygen. O2 is supplied by mechanical or pneumatic aerators. |
| Membrane bioreactors | An aeration tank with a membrane that retains activated sludge after processing organic matter. | Aerobic bacteria break down organic matter in the presence of oxygen. O2 is supplied by mechanical or pneumatic aerators. |
| Biofilters | A reservoir with loading material on the surface of which a film of microorganisms forms. | The water passes through a porous filter media. The biological film on the granules breaks down contaminants. |
| Installation | What is | Principle of operation |
| Fixed partitions | Installations with filter fabric of different porosity. | The water passes through the filters and the contaminants remain behind the separating sheet. |
| Grain filters | Granular porous materials that are poured into pipes, tanks, flasks. | Water passes through the absorbent material granules and contaminants accumulate on their surface. |
| Ultrafiltration systems | Filters equipped with membranes - materials with a pore size of up to 0.2 microns. | The membranes allow water to pass through, but retain high-molecular contaminants (99.9% of impurities). |
Disinfection equipment:
| Installation | What is | Principle of operation |
| Ozonizers | Electrical installations with long hoses. The devices generate ozone, which penetrates into the water through tubes. | Ozone oxidizes lipids and lipoproteins of the bacterial cell wall. This leads to structural changes that are incompatible with cell life. |
| UV disinfectants | Devices equipped with several lamps. They are immersed in water and there they emit UV rays. | The lamps generate waves with a length of 200-280 nm. They destroy the genetic apparatus of harmful bacteria and viruses, which prevents them from reproducing. |
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of flotation devices has both advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include:
- ease of machine maintenance;
- low cost of most methods;
- high quality and speed of wastewater treatment.
Using the technique, you can remove most of the fine impurities, but not all. Disadvantages also include the need for additional use of reagents to increase the degree of hydrophobicity of mud particles. When using an electric flotator, it is necessary to fine-tune the device to create bubbles of the required diameter.
What it is?
A flotator is a device for removing suspended particles and organic matter from water by a combination of physical and chemical processes.
Using flotation, wastewater is purified from:
- oils;
- fatty contaminants;
- petroleum products;
- surfactants;
- organic impurities.
Reference. Depending on the type of contamination, the type of installation is selected.
Operating principles
An air mixture is supplied to the wastewater that is being purified in a variety of ways. Undissolved particles are attached to capsules of gas passing through the liquid medium. Then the containers float to the top in a state of foam (photosludge).
It is collected from the surface of the wastewater mechanically using special scrapers. Purified water is removed from the flotation chamber.
There are several ways to saturate liquid with gas capsules:
- mechanically;
- pressure;
- vacuum.
Mechanized filling of contaminated liquid with gaseous mixtures is carried out in the following steps:
- In centrifuges, wastewater is mixed until uniform. At the same time, the mass is filled with gases. The resulting capsules attract and bring polluting particles to the surface.
- Thoroughly churning the effluent in a tank equipped with paddles attached to wheels.
- An aeration option is to fill the drains with a water-air mixture through pipes located in the lower part of the tank.
When using the pressure method, oxygen is pumped into the contaminated liquid using pressure. The use of a vacuum option - sewage is saturated with air molecules in special containers.
In order for the air capsules to have the required volume, they are crushed using:
- turbines;
- nozzles;
- porous plates;
- gratings.
Interesting. In order to increase the efficiency of collecting finely dispersed contaminants in flotation plants, special reagents are often used. They increase the degree of adhesion of suspensions with air molecules.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of using flotation units:
- The device is highly effective for removing many types of fine substances.
- Flotation copes quite quickly with the purification of waste liquids.
- The work of purifying purification is carried out continuously.
- All equipment has a simple design.
- Maintenance work on flotators does not involve large expenses.
- The price of the equipment is quite low.
At the same time, there are certain disadvantages of flotation cleaning:
- This option does not allow removing all types of suspensions from a liquid medium.
- Some processes use reagents, which increases the cost of purification.
- It is necessary to constantly monitor the parameters of the supplied gases. Otherwise, the effectiveness of cleansing will be significantly reduced.
effective in combination with other settling tank options Important. After treatment with a flotator, disinfection and subsequent passing of water through special filters is necessary.
- The greater the amount of suspended matter in sewage, the higher the productivity of the flotation unit.
- The effectiveness of purification is largely determined by the volume of gas capsules. A bubble that is not large enough will not have time to rise to the surface. They will dissolve on the way up. Large bubbles will rise very quickly. Therefore, they will not collect a lot of suspended matter.
The principle of operation of the flotator
The efficiency of operation also depends on:
- flotator type;
- its performance;
- degree of automation of the process.
Application area
Flotators are used mainly in purification systems in industries:
- municipal wastewater treatment plants;
- meat and dairy plants;
- poultry farms;
- canneries;
- oil factories and fat production;
- oil and gas industry.
In mining operations, this method is often used to enrich rock.
Reagents used
To increase the efficiency of purification, chemical collectors are used:
- coagulants - reagents that promote the formation of flakes and are iron and aluminum salts;
- flocculants (polyacrylamide compounds) – substances that create larger and more stable flakes (flocs);
- acid and alkaline reagents that allow you to adjust pH. They are added to water to ensure normal operating conditions for the two previous types of reagents.
To stabilize foam formation, pine oil, phenols, and cresol are also used. They help protect air bubbles from destruction, making them elastic. This helps remove more contaminants from the sewer.
The use of chemical reagents to improve the process requires precise dosage selection, which can only be achieved experimentally.
Flotation reagents
There are several types of flotation reagents, differing in their operating principles:
- Collectors
are reagents that selectively adsorb on the surface of the mineral that needs to be converted into foam and impart hydrophobic properties to the particles.
Substances whose molecules have a diphilic structure are used as collectors: a hydrophilic polar group, which is fixed on the surface of the particles, and a hydrophobic hydrocarbon radical. Most often, collectors are ionic compounds; Depending on which ion is active, collectors of anionic
and
cationic
types are distinguished. Less commonly used are collectors that are nonpolar compounds that are not capable of dissociation. Typical collectors are: xanthates and dithiophosphates for sulfide minerals, sodium soaps and amines for non-sulfide minerals, kerosene for coal preparation. Gatherers' consumption amounts to hundreds of grams per ton of ore; - Regulators
are reagents, as a result of their selective sorption on the surface of a mineral, the latter becomes hydrophilic and incapable of flotation. Salts of inorganic acids and some polymers are used as regulators; - Foaming agents
- designed to improve air dispersion and impart stability to mineralized foams. Foaming agents are weak surfactants. The consumption of foaming agents is tens of grams per ton of ore. - Activator reagents
are reagents that create conditions favorable to the fixation of collectors on the surface of minerals. - Depressant reagents
are reagents used to prevent collectors from hydrophobizing minerals. They are designed to increase the selectivity of flotation when separating minerals with similar flotation properties.
What determines the quality of cleansing?
The effectiveness of the technique is influenced by the following factors:
- resistance of air bubbles to destruction;
- uniformity of foam formation;
- the degree of hydrophobicity of the particles - the higher this indicator, the more actively they interact with air bubbles.
The size of the bubbles is also important. Large ones float up quickly and do not have time to capture impurity molecules, while small ones are less durable.
The use of flotation techniques is indispensable for purifying wastewater from fats, fibrous inclusions, petroleum products, and other contaminants that cannot be settled. This method is used for sewer cleaning and mineral processing.
Possible problems
They want to equate the standards for the content of pollutants in treated wastewater to the world standards, and the majority of Russian enterprises use physically outdated equipment.
Purification using technologies developed in the last century does not reduce the level of impurities to the required levels.
Modern equipment is expensive. For example, UV disinfectants are installed only in the capital and several large cities. In most populated areas, the equipment has become so outdated that wastewater is often discharged into water bodies without treatment.
Some private entrepreneurs do not want to invest in the construction of treatment facilities. They dump polluted water into rivers.
- Selection of an ineffective technological scheme;
- Inability to dispose or bury waste, pollution, and by-products;
- Lack of money for electricity, equipment maintenance and repair, and transportation costs.
Existing problems can only be solved at the legislative level: increase fines for violations, finance city wastewater treatment plants and control the expenditure of money, encourage private owners to introduce new technologies, offering them various discounts and benefits.
Honest inspections should be carried out more often, which can be spontaneous - without warning.
Ore beneficiation
The flotation process is successfully used in the primary processing of all kinds of ores, making it possible to separate a valuable fraction with a high content of metal or its compounds. It is based on differences in the surface properties of the separated minerals.
Ore flotation is a three-phase process:
- the solid phase is a crushed mineral;
- the liquid phase is the pulp;
- the gas phase is formed by air bubbles passed through the pulp.
Flotation can be foam, film or oil, depending on the form of the product formed on the surface of the liquid phase.
Why choose EKOVODSTROYTECH® technological solutions:
- technological processes occur autonomously without operator assistance, they are fully automated;
- the equipment is easily integrated into wastewater treatment plant systems;
- an expanded model line allows you to choose the best option for any object;
- comprehensive wastewater treatment from inorganic impurities;
- high degree of purification in accordance with the standards established in the territory of the countries of the Customs Union;
- the equipment is compact and requires a small area for placement;
- the flotation unit can be located either in close proximity to the source of wastewater or at a considerable distance;
- ease of operation and maintenance;
- the ability to purify wastewater, recover and selectively isolate impurities;
- the equipment is immune to salvo discharges.