Drainage and storm sewerage are structures that are engineering structures that collect and discharge wastewater of various natures outside a specific area. Drainage is usually laid to reduce the groundwater level in the area, and storm drains are used to collect rainwater on the roof and then drain it away.
Drainage systems are necessary to remove excess moisture from the soil
Why are drainage and storm sewers needed?
Storm drainage is used to collect precipitation on the roof. Collecting rainwater and melted snow is necessary, since when moisture flows freely from the roof, it damages the foundation of the building, which can lead to the house being tilted. The main task of storm drainage is to collect and drain wastewater outside a specific area.
The sewerage drainage system performs the function of collecting excess water in the soil on the site. Its main task is to drain the area adjacent to the house. Arrangement of drainage is a necessary measure to avoid rising water levels in the soil.
Important! It is worth remembering that it is strictly forbidden to combine these two systems together. This is due to the fact that during heavy rainfall, the drainage system quickly overflows with water from the storm sewer and ceases to function.
The water collected by these systems is transported through pipes to special storage tanks, after which it is discharged outside the site. In some cases, moisture collected in storage containers is used for irrigation. Installation of drainage and storm sewerage is necessary on almost all soils and in all areas. To understand the issue, it is necessary to study the main characteristics, as well as the design features of drainage and storm sewers.
Storm drainage is needed to collect atmospheric moisture from the roof and drain it outside the site
Drainage ditch
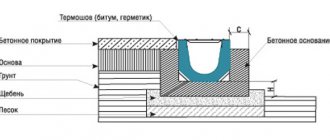
One of the simplest and most accessible devices that allows you to drain water from a site is a drainage ditch. It is best to do this if the area has a slope in one direction.
It comes off to a depth below the freezing level of the soil. It is important to maintain a slope along the entire length towards the water drainage. Its size should be up to 3-5 centimeters per meter of length. This slope allows water to flow slowly enough, taking with it particles of soil, otherwise rapid silting of the storm drain of a country house may occur. See the rules for laying sewer pipelines in the ground. Storm sewerage in a private house in its own way
At the bottom of the ditch, approximately a third of the depth, a layer of wild stones or concrete scrap is placed. Then you need to pour coarse gravel, sand and cover it all with geotextiles. It will prevent rapid silting of the drainage channel. Ideally, the drainage ditch is led into the nearest storm drainage well.
In modern conditions, pipes made of various materials are used as drainage systems - steel or plastic. For greater strength, products with a corrugated wall are used for conductors of the second option. This design increases the radial strength of the product.
Storm sewer drainage ditches on the site can also be open, which simplifies their operation.
They come in the following types:
- perimeter - come off along the perimeter of the area that needs to be protected from excess moisture;
- the main ones are essentially the main channel of the river, to which tributaries converge in the form of additional drains.
Types and design of drainage systems
Today, there are several types of drainage systems that differ in their design and installation method. Consider these varieties:
- horizontal drainages;
- vertical drains;
- combined (systems that include both horizontal and vertical sections).
Horizontal drainage structures, in turn, are divided into:
- open;
- closed;
- wall-mounted
To understand the structure of the drainage system, you need to study what elements it consists of. Let's consider the drainage device:
- drains (these are special perforated pipes that are equipped with holes that allow moisture to pass through);
- sand traps (filtration elements);
- pipelines that drain collected water outside the site;
- wells.
Pipes for drainage systems can be made of different materials. The selection of material is carried out depending on the characteristics of the site and other individual characteristics in a particular situation.
Today, pipes made of various polymers are often used for drainage systems and storm drains.
Let's look at the main materials from which drains are made:
- polymer;
- asbestos-cement;
- ceramic;
- non-perforated drains, which are made from modern porous materials (for example, expanded clay glass). A special feature of such pipes is the way water enters them. Water does not enter them through standard perforations, but seeps through the porous wall.
In addition, wells are divided into three main types:
- examination rooms;
- accumulative;
- differential.
Rules for installing a dual system
Proper installation of a combined system must be carried out according to a pre-created project, which specifies the nuances regarding connection to the site and synchronization of the operation of wells, so that both drainage and stormwater work properly both in normal mode and during overload.
When installing, the following nuances must be taken into account:
- Arranging a drainage system is quite an expensive pleasure. If something goes wrong and after a few years the drainage stops working, then you will have to spend no less money on its restoration than on installing a new one, especially considering that you will have to “pick apart” the landscape design. As a result, drainage installation should be done by professionals.
- During the flood period, each of the systems will be overloaded. Since they collect moisture from different sources, drains must be laid for each system separately. You can do this in the same trench, but at different depths. A common well can be used to collect water.
- When digging trenches for drains, you should definitely take into account that the bottom of the hole will be covered with crushed stone and sand. This means that if it is necessary to place a drain at a certain depth, the hole must be dug deeper to the thickness of the layers of sand and crushed stone.
The pit for the drainage system well must be deep enough Source besplatka.ua
- Typically, water is collected in a storage tank (pit or reservoir), from where it is used for technical needs or pumped into reservoirs or simply away from the site. If perforated pipes are used for drainage, the outlet pipes are always solid. When combining them vertically in one trench, the perforated ones are laid on the bottom, and the regular ones on top.
- If main and drain pipes are combined horizontally in a trench, then they are laid parallel, at a short distance from each other (so that if the main pipe is damaged, water from there does not enter the drainage system and overload it).
About the installation of a stormwater system and drainage in the following video:
Open drainage design
Such systems are installed on the surface of the earth, and water is drained into special containers or ditches. Surface drainage design is the most budget option, and its installation takes the least time. To implement such a system, you will need to dig ditches that must correspond to certain dimensions.
An important point when organizing drainage sewerage is the slope. The slope of such a system should go from the residential building to the sewers. Without an appropriate slope, water simply will not move through the trenches. You should also make sure that melt or rain water flowing from the roof falls into pre-organized trenches along the blind area and recesses along the paths.
The underground drainage system will not create inconvenience for residents of the site
The main disadvantage of such drainage is its unpresentable appearance. In addition, open trenches on the site can cause various kinds of inconvenience for the residents of the house. Therefore, experts recommend constructing drainage systems that contain prefabricated trays or constructing the structure underground.
What functions do drainage systems perform?
Without water there is no life, but if there is an excessive amount of it, this very life becomes much more complicated. Stagnation of water has a detrimental effect on the fertile layer, and any structures in contact with waterlogged soil fail much faster. And we’re not just talking about paths and other surfaces where puddles have been standing for months, but also about foundations.
Maria SukharevaSpecialist at Uponor
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of protecting the foundation of the house and surrounding areas from the negative effects of moisture, which affects both the characteristics of the building and the residents. A drainage system installed in the foundation area not only collects and drains water, but also prevents the groundwater level from rising.
Even capillary rise of moisture is fraught with dampening of the foundation and the appearance of mold, while freezing of wet soil under a building site can lead to deformation of the foundation. Not to mention the fact that ice crystals “tear” the most durable materials without any problems, and in the spring, instead of a monolith, it is quite possible to find its cracked likeness. The drainage system promptly removes all types of water from the foundation and plinth, thereby drying them and providing load-bearing structures with optimal operating conditions.
sartreekFORUMHOUSE Member
The soil is clayey, my water level is quite high - 30-40 cm, I want to make some kind of drainage around the house with drainage into a well with subsequent pumping. High water does not interfere with life at all, but in winter the foundation is a pity.
According to statistics, from the roof of an average-sized country house, from 50 to 150 m³ of wastewater, including melt and rainwater, is collected throughout the year. Draining such a volume of water onto a site, even with permeable soil, can cause stagnation, not to mention clay soils. To prevent this, there is a storm drain.
Maria Sukhareva
Storm drainage is designed to collect, filter and drain rain and melt water, as well as surface runoff during snowmelt or heavy rainfall. This prevents the flooding of buildings and the formation of puddles in the warm season and ice dams in the cold season.
Drainage and storm sewerage are different systems and must be differentiated.
Storyteller14FORUMHOUSE Member
Need advice on organizing a drainage system around the house and draining water from the roof. My house is located on the bank of a former river, now it has no flow, the groundwater level is very high, and in the spring water appeared in the basement before waterproofing was done. This summer I decided to make drainage and combined it with a storm drain. Drainage pipes (corrugated pipe 110 mm, perforated and in geotextile) led into the lake. Now I think that I should have combined it in vain: during heavy rain, it is not visible that water flows out of the drainage pipes, it simply soaks into the ground. Tell me, please, is it possible to do this or is it better not to put the storm drain into the drainage?
Maria Sukhareva
The system of deep drainage and storm sewer perform related, however, different tasks. Drainage collects water contained in the soil and removes it from the foundation of the house. If necessary, drainage also prevents groundwater from rising to the level of the lower foundation of the building. Storm drains drain rainwater from the roof of a building to avoid deep puddles in the yard, which can increase moisture in the foundation and basement.
It is not recommended to discharge rainwater into the drainage system. If this happens, then during heavy rainfall the drainage pipes overflow with water, which puts pressure on the foundation structures. Thus, the drainage system has the opposite effect, which is what happens in this case. The shape of the drain pipe or the location of the holes also does not improve the drainage system's ability to protect itself from excess rainwater.
Water coming from the drainage and storm sewer system accumulates in the main drainage well. At the connection point of the drainage pipe inside the well, it is recommended to install a check valve, which, even in the event of a flood, will prevent the reverse flow of water through the drainage system to the foundation of the building.
- Storm water inlet.
- Storm sewer pipe.
- Drainage pipe.
- Drainage well.
- Rainwater funnel.
- Flexible socket tee.
- Flexible socket outlet.
- Manifold well (solid cast iron cover and ball check valve).
- Collector well (grid cast iron cover).
Closed drainage design
Closed sewer drainage consists of ditches with drainage elements located at the bottom. The closed type stipulates that such ditches must be filled with earth.
There are several types of closed drainage structures. Let's look at them:
- simple closed systems;
- systems that contain special water collectors (trays);
- systems equipped with drainage mats.
Note! The first two types of systems are installed in order to remove water linearly or contour. The last option, which uses drainage mats, does not take this into account.
1. Simple closed drains. To lay such communications, it is necessary to dig appropriate trenches around the perimeter of a specific area. Then the ditch is backfilled with waterproof materials. Backfilling is carried out in several layers and mainly sand and crushed stone are used for these purposes. At the end, the trenches are filled with earth and compacted.
To install drains, it is necessary to prepare trenches into which a layer of geotextile is laid and crushed stone is filled
This drainage system has some operational disadvantages. For example, when organizing such a system, the possibility of monitoring the condition of the drains is excluded. Based on this, over time, the effectiveness of drainage will gradually decrease. In order to increase the efficiency of drainage and extend the service life of such a structure, it is recommended to use drains.
2. Closed structures, which include special trays. To organize a closed system with trays, one important point must be taken into account - for the installation of such a system, a scheme must be used that takes into account free passage or passage. To install the tray system, two types of trays are used. Let's look at them:
- perforated (such trays collect water from the adjacent land);
- non-perforated (for water condensation on the surface).
In addition, all trays are equipped with gratings on top. Grilles not only affect the overall aesthetics, but also perform a protective function, preventing various debris (for example, branches) from entering the system. The materials from which such gratings are made can be very different, but cast iron products are usually used.
Basic elements of classic sewerage
Storm drainage can be point or linear. The first option involves collecting water from surfaces that do not absorb moisture, such as the roof, hard surface areas. The wastewater then flows into receiving tanks, and then enters the drainage system.
With the linear method of drainage, water is drained into trays located near paths and platforms. A simplified version of a storm drain consists of the following elements:
- a central pipe laid under a layer of earth and finishing coating and carrying collected water to the extreme point of the scheme;
- trays - the main part of the system that transports excess water to sand traps; the efficiency of drainage largely depends on them;
- a storm inlet located under a pipe or low point in the yard to collect liquid;
- filters and distributors - invisible, but extremely important components.
All elements included in the system are equally important. If any of them fails, the efficiency of the entire structure decreases.
Image gallery
Photo from
Point type storm water inlet
Connection to drainage system
The principle of point sewerage
Paving a storm drain area
Types of storm water inlets for sewerage
The purpose of a rainwater inlet is to collect moisture coming from pipes and yard coverings. This element is the first to absorb the entire volume of water coming from the drainpipes. When choosing a rainwater inlet, we are guided by such data as the average volume of precipitation, its intensity, topography, and the area occupied by the storm drain.
Image gallery
Photo from
Storm drain with linear water inlet
Point rainwater system
Installation of storm drainage trays
Protective decorative grille
You can buy a cast iron or plastic storm inlet. The former are preferable in case of heavy loads, while the latter are attractive due to their moderate cost, low weight, simplifying installation. A cheaper option is to make a rainwater well for storm drainage at your dacha yourself from brick.
The walls of the pit are lined with brick, leaving a hole for the pipe, then plastered from the inside. Better yet, leave a gap between the soil wall and the cover and fill it with concrete. The bottom of the rainwater inlet must be concreted.
No storm drain can do without a rainwater inlet. It preserves both the foundation of the building and the covering around it. If you try to save money on its installation, then water falling on the foundation will lead to shrinkage and cracks on the walls of the building
This important element is also made from concrete rings. Then the bottom ring can be purchased with a finished bottom and you won’t have to fill the slab. Sometimes factory rain inlets go on sale complete with a basket, siphon, and decorative grille.
Most often used for private construction, rainwater inlets made of plastic or composite materials are produced in the shape of a cube, each side of which is 30-40 cm. There are adapters for inserting pipes from below and on all sides of the product.
Storm drain grates vary in quality and cost. You should always take into account the expected loads on them during operation
In order not to clog the pipes with debris falling through the grid cells, rainwater inlets are equipped with baskets. Once they are full, they are removed and cleaned, then returned to their place.
The design of the factory rainwater inlet includes partitions that divide its internal space into compartments and create a water seal. As a result, the unpleasant odor from decaying organic matter does not penetrate outside.
The efficiency of a point storm drain depends not only on its volume, but also on the installation location. It should be located under a drain or in a place where moisture constantly collects. If it is installed under a pipe, then the jets must accurately hit the center of the grate, otherwise some of the water will fall on the foundation or yard surface in the form of splashes.
Why are sand traps needed?
Rain and melt water in any case contains a certain percentage of insoluble particles. If sand traps are not included in the scheme, dirt will settle in the sewer and it will cease to function fully. Flushing the system is expensive.
A sand trap is a chamber installed behind point receivers in places where water is discharged into underground pipes. It is designed in such a way that the flow of water entering it reduces its speed.
As a result, under the influence of gravity, suspended particles sink to the bottom, and the liquid released from them leaves through a special hole. The shape of the sand catcher is a trap with many chambers located horizontally or a chamber in a vertical design.
Image gallery
Photo from
The sand trap is built into the rain inlet
Sand traps in combined systems
Sand catcher for public storm drainage
Trap device for household system
What are drainage channels?
If the blind area around the house has already been completed, but the drainage system has not been taken care of, drainage gutters, which are also called linear rainwater inlets, can be used as a way out of the situation. Channels made of concrete or plastic are laid outside the blind area parallel to the paths and roof overhangs with a certain slope.
Linear drainage channels receive water from roof gutters and from the entire yard covered with asphalt or slabs. Such a sewer can cover much more objects than a point one. When purchasing ready-made trays, you need to pay attention to such important parameters as permissible load class and mechanical strength limit.
The tray, at first glance, is a very simple product, but if the calculation is done incorrectly, the system will not work fully. It is necessary to take into account the throughput of the storm drain, the type of coating, and the degree of contamination of the drained water.
The weakest products are marked A15. This means that their use is permissible with a maximum load of up to 1.5 tons. They are installed around the perimeter of the house, in pedestrian and bicycle areas. Trays of class B125 can handle loads of up to 12.5 tons without compromising their integrity. They will not be damaged under the weight of a passenger car, so they are appropriate in the garage area.
For private construction, you should not buy massive concrete gutters; plastic trays are quite suitable here. They have strength classes A, B, C. The material for their manufacture is polyethylene or polypropylene.
An important parameter when selecting trays is the hydraulic section, denoted by the abbreviation DN. It must correspond to the diameter of the pipes supplied to these elements. For plastic gutters, the DN value ranges from 70 to 300.
The length of a standard tray is 1 m. The products are equipped with a locking system, with its help the gutters can be lined up in one line, connected to pipes or branches can be made. A rational choice for a summer house, private home - models from DN100 to DN200.
Image gallery
Photo from
Trays with different capacities
Construction of a storm drain from steel parts
Concrete gutters
Practical plastic option
How to choose pipes?
For storm sewerage, according to SNiP, pipes made of metal, asbestos or plastic can be used. Most often, for private homes and cottages, the choice is made of plastic pipes. They are lightweight, decorative, do not corrode, their installation is simple, but the mechanical strength of the material is low compared to metal.
Having chosen the material, you need to decide on the diameter of the pipes.
The initial value is the largest volume of drained rain and melt water. This parameter is determined by the formula:
Q=q20×F×Ψ
Here: Q is the required volume, q20 is the coefficient characterizing the intensity of precipitation within 20 seconds. (l per second per 1 ha). F is the area of the farmstead in hectares, if the roof is pitched, the area is calculated on the horizontal plane. Ψ is the absorption coefficient.
Different surfaces have their own absorption coefficient. To perform independent calculations, its value can be taken from the table
Based on the calculated value and using the Lukin tables, not only the diameter but also the slope of the system is found.
Most often, home storm drainage is performed using pipes with a diameter of 100 mm. The optimal slope of the drains can be taken from this table
With the correct selection of pipe diameters, storm sewers will cope with the task even during moments of the heaviest rainfall. If flows from several gutters enter the pipe, they are all summed up. Professional practitioners for pipes with a cross-section of 110 mm and gutters of the same diameter usually use a slope of 20 mm/linear. M.
If the pipe is connected to a storm inlet, the slope value is slightly increased to avoid stagnation of liquid, and when entering the sand trap, the slope is reduced. This slows down the flow of water, and suspended particles settle to the bottom in greater quantities.
Water in a sewer system of this type drains by gravity, which occurs due to the formed slope of the drainage pipe. There are no pressure pumps here, so you don’t have to look for a team of professionals to install a storm drain at your dacha or country yard.
The owner can do all the work himself. Details about the calculations for organizing storm drainage are written in the article, the contents of which we recommend that you familiarize yourself with.
Where do you need a well and a collector?
As in any system consisting of underground pipes, there must be a well in the storm sewer.
Its installation is advisable in the following circumstances:
- if 2 or more flows converge;
- when it is necessary to radically change the height, direction of the pipeline or its slope;
- if there is a need to switch to a larger pipe diameter.
Wells are also provided at established intervals of straight sections of the system. If the diameter of the well does not exceed 150 mm, then the next one is located at a distance of 30 to 35 m. With a diameter of 200 mm - from 45 to 50 m, and if the diameter is 0.5 m, the interval is increased to 70-75 m.
The diameter of a well in a private house does not exceed 1 m. The deeper the well, the larger its diameter should be.
Some owners lay out wells the old fashioned way from brick or reinforced concrete rings. Others prefer more advanced materials - plastic and fiberglass. According to their design, wells are either collapsible or solid.
They have the shape of a cylinder with a completely sealed bottom and a hole at the top. There are nozzles for connecting pipes. Several assembled storm water inlets are also used as wells.
All fluid flows are redirected to the collector after combining them into one. The choice of material for this storm drainage element is individual and depends on the preferences and capabilities of the owner
To redirect the collected water to ground treatment facilities or to a sewer, a collector is included in the system. Sometimes its role is played by a large plastic well. It is converted into a storage tank by hermetically sealing the outlet pipes. To use water, a submersible pump is used.
Large cross-section pipes are also used for the collector - reinforced concrete or plastic with all pipelines connected to them. On the construction market you can also purchase ready-made containers for underground use. There are multi-chamber tanks where rain and melt water are treated according to the same principle as in septic tanks.
Image gallery
Photo from
Collector well for redirecting water
Absorption well made of perforated rings
Budget option for an absorption well
Discharging rainwater into a drain
Wall drains
Wall drainage structures are organized near the foundation. The main feature of such communication is that it contains waterproofing materials. A ditch is dug along the entire foundation. The depth of such a ditch should correspond to the depth of laying the foundation or exceed it.
Wall drainage is done in order to remove moisture from the foundation of the building
The necessary waterproofing is installed on the foundation walls, and the pre-dug ditch is filled with drainage materials. In this case, it is allowed to use special drainage mats, the filter of which is made of geotextile. Such mats are usually waterproofed with polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Note! Pipes can be laid in the trench to drain rainwater collected from the roof. In this case, it is recommended to use plastic pipes without perforation. With the help of such pipes, water is removed from the tray structures into a special well.
Rainwater must not be discharged into the drainage system, as this may lead to overflow of the structure. If the drainage structure overflows, the water will rise into the foundation of the building, which is fraught with unpleasant consequences.
Care and instructions for use
Both systems require regular inspection and cleaning of silt, sand, clay and other debris. Seasonal inspections are required - in late fall when the rainy season ends and at the end of winter to ensure that the drainage capacity is not compromised. Despite various filters, sand traps and debris nets, dirt still gets inside. They are found everywhere: in pipes, gutters and wells. If left unattended, the system will simply become clogged and stop functioning.
Timely cleaning of the pipes of the drainage and storm water disposal system at the dacha will avoid many problems Source dp32.ru
To clean the pipe, just turn on the pump at maximum power and run ordinary water from a hose through the pipes; it will collect all the dirt and bring it into the well. You can pour water into the gutters and it will also collect all the dirt and then flow through the vertical pipes. The stronger the pressure, the more dirt and debris will come out.
Already in the pump, all the water is pumped out with an even more powerful pump or suction pump; when all the water runs out, it will be necessary to clean the walls. Most often, this ends with flushing, but if the system has not been looked after for a long time, it happens that you have to manually clean the walls and bottom of the well using a scraper. Therefore, regular cleaning is necessary to ensure that both systems operate reliably.
Vertical type drains
Such structures are represented by a well in which pumping equipment is located (pumps are used to pump out wells). As a rule, such drainages are used in the agricultural industry, and they are also actively used to drain land during the construction of highways.
When laying this system, wells and trays are used, which, as a rule, are located on a waterproof layer. In addition, such a system must be equipped with deep-well pumping elements. This drainage system is considered the most effective. And if the land on the territory of a particular site has a high coefficient of water resistance, then such a structure will not only be effective, but also quite economical.
A vertical drainage system requires a pump to pump water from wells
The depth of laying vertical drains can be different, since everything in this case depends on the level at which the groundwater is located. It can be 20 or 150 meters, depending on the characteristics of the soil on which the site is located.
Helpful information! The vertical design is represented by different types of pipes: conventional and perforated. Regular ones are located at the top of the structure, and perforated ones are located at the bottom. It is also worth noting that the holes of perforated pipes can be of different shapes.
Such borehole drainages can operate in various modes (the choice of mode is carried out based on the time of year). Do not also forget that such systems require periodic preventive inspections and cleaning of the filter, which consists of sand and gravel.
What does a storm drain consist of and how does it work?
Storm drainage is a system of channels connected at intersection points by catch basins. This system can be either open or closed and consists of storm water inlets, inspection wells, filters, sand traps, catch basins and the canals themselves.
Storm water inlets are polypropylene or polymer concrete containers with baskets for catching fallen leaves and debris. Storm water inlets collect water from drainage systems and redirect this water into channels equipped with sand catchers and filters. The water then flows through an underground channel or above-ground gutter into the catchment tank. Inspection wells are necessary for inspecting and cleaning stormwater drainage channels if they are clogged and are located in areas with turns and at pipe joints.
There are two types of storm drains: closed and open.
Types of storm sewer system
Storm sewerage, as mentioned above, performs the function of collecting melt and rainwater, as well as draining it outside a specific territory. There are several types of storm sewer systems that you need to pay attention to:
- Spot. This system performs the function of collecting water on the roof and is a structure of rain inlets that are installed under each roof drain. In addition, this system includes pipes that are laid in the soil at a certain slope to effectively drain wastewater. Such pipes are connected to the main collector (a well that drains water outside the site).
- Linear. A structure that collects moisture from roads, as well as concrete and other paths. It is carried out in the form of special channels at a certain slope. Such a system, like a point system, transports water to the main collector.
- Combined. Such a system includes both point and linear storm drainage. The combined system also includes various auxiliary elements (for example, pallets).
Installing any of the above systems is a rather complex process that is best left to specialists with experience in this field. The preliminary design should take into account such items as: site features (topography), the volume of collected water, as well as the place where this water will be discharged.
Installation rules for both systems
Unprepared people often have problems at the design stage. If drainage is needed for sewerage, how to properly make and place all the components?
Installation of systems is carried out according to general methods. The work is being carried out in stages:
- a diagram is created on which the routes for laying pipelines of both networks are marked;
- Excavation work is being carried out. The depth of the trenches should be increased by the height of the ASG backfill layer. At the same time, they dig holes for tanks and wells;
- the bottom of trenches and containers is filled with a layer of ASG;
- pipes are laid, the angle of inclination is constantly monitored;
- leak tests are carried out;
- the trenches and cavities of the nests under the containers are filled with excavated soil, and the systems are put into operation.
The installation process is simple, since connecting all the elements is not difficult. However, large volumes of excavation work complicate the work and require the use of construction equipment. If the area of the site is large, hire a tractor or excavator. This allows you to speed up the process in order to complete the installation during the warm season.