- Work acceptance procedure
- Specifics of drawing up a test report
During testing of external sewerage using the spill method, the same document is drawn up as during testing of the internal sewage system. The form of the act itself is not a form of strict reporting and can be drawn up by the customer, contractor or subcontractor.
Also, during experiments on an external water drainage system, one of the forms of SNiP 3.05.04-85 can be used, which is a general form of document for acceptance of work performed when installing or repairing a drainage system.
Drawing up a test report for sewerage and drainage systems
Drawing up a report on testing sewerage and drainage systems is not a difficult task. All points are clear to masters. The header begins with the name of the system. Here, in comparison with the act of conducting a hydrostatic or pressure test for tightness, there can only be either a sewerage system or a drain. In the project, sewerage and drainage are also designated by letters, for example, sewerage system K1, drainage system KV1, etc.
Next, in the next line you need to write down the name of the object on which the system is mounted. Usually corresponds to the name PD or RD. If there is no such documentation, you can indicate the name of the premises, building or structure and the location address.
The place where the act is drawn up will be the place of installation of sewerage and/or drainage systems. The date of compilation almost always coincides with the date of testing of the systems.
What to check
Checking the functionality of the sewer system includes:
- testing of the internal sewerage system;
- checking the tightness of pipelines;
- determining the performance of wells;
- storm drain testing.
What applies to the internal sewerage system
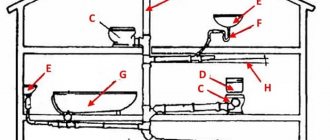
The internal sewer network includes:
- plumbing products, including household appliances that drain water;
- internal pipelines connected to a common sewer riser;
- central sewer riser equipped with a drain pipe.
What applies to the external sewerage system
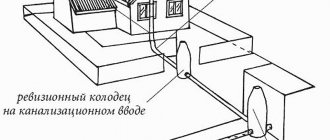
The external part of the sewer network includes:
- pipelines carrying wastewater from the house to the disposal site;
- wells that need to be installed at junctions, branching pipes or differences in network height;
- wastewater treatment plants;
- storm drains and storm water inlets.
- plumbing fixtures and their connections with outlet pipes;
- local sections of a horizontal pipeline with pipes flowing into it from plumbing fixtures;
- sewer risers;
- outgoing pipe.
Composition of the executive documentation for the section “Water supply and sewerage” (WK)
1. Register of as-built documentation 2. General work log and special work logs:
- General work log
- Welding work log (SNiP 3.03.01-87)
- Journal of anti-corrosion protection of welded joints
- Incoming quality control log
- Author's supervision journal (to be filled out by the responsible person from the design organization)
- As-built surveys of pipeline laying B1, B2, B4, T3, K1 (with marks)
- Executive diagram of the installation of trenches for sewerage outlets (with calculation of soil volumes)
- Executive diagram of the foundation for sewer outlets
- Laying pipelines under floors
- Thermal insulation of pipelines
- Installation of pipeline systems B1, B2, B4, T3, K1 and fastening to building structures
- Installation of passage of KhGSV pipelines through walls
- Anti-corrosion treatment of pipelines
- Construction of a natural foundation for sewer outlets (underground part)
- Construction of an incompressible base for sewer outlets (underground part)
- Installation of sewerage outlets (underground part)
- Thermal insulation device for sewerage outlets (underground part)
- Backfilling of storm sewer outlets (underground part)
- Installation of brackets for fastening fire water supply pipelines to the metal structures of the building frame
- Anti-corrosion protection of welded joints of fire-fighting water supply pipelines
- Installation of fire hydrants included
- Sealing of pipe passages through external walls
- Installation of treatment plants
5.Acceptance and testing certificates:
- Act on the flushing and disinfection of pipelines of KhGSV (with conclusion)
- Report of hydrostatic or manometric leak testing of pipelines B1, B2, B4, T4, K1
- Test report for the internal sewerage system and spillage drains
- Test report for internal fire water supply for water loss
- Certificates of individual testing of equipment (pumps, water heaters, etc.)
- Certificate of acceptance of the system and releases of internal sewerage
- Certificate of inspection of engineering support networks
- Water meter inspection report
- Certificate of completion of installation work
6. Welders’ certificates, welders’ certification protocols
7. Passports, quality certificates, fire certificates, sanitary and hygienic certificates for building materials, products and structures. For all building materials, products, structures and equipment arriving at the construction site, an incoming inspection report must be drawn up and then signed by the responsible persons.
8. A set of working drawings for the construction of the facility presented for acceptance, developed by design organizations, with inscriptions on the compliance of the work performed in kind with these drawings or changes made to them made by the persons responsible for the construction and installation work, agreed with the authors of the project.
9. Documents on approval of deviations from the project during construction
- Installation organization information sheet
- SRO of the installation organization
- Orders for responsible representatives
- Personnel certificates (welders, electrical personnel, etc.)
- Detailed documentation with the Customer’s stamp “In production of work”
- Work production project (title page and familiarization sheet)
*The presented composition of the executive documentation is approximate. Please check with the customer for the exact composition of the as-built documentation.
When the commission may not sign the act
According to the above regulations, the main feature lies in compliance with the mandatory requirements of the strait. According to this rule, it is implied that up to three-quarters of the total number of drain systems and openings in the house will be involved in the inspection. If the specified number is smaller, the test document cannot be called complete. The commission responsible for signing the act has the legal right to make a negative decision on the acceptance of the building, since the drainage system does not meet the requirements of construction standards.
It is important to remember that launching the sewage system on an ongoing basis can only be done in one case. After a comprehensive check of its performance and only after the moment when a test certificate for the internal sewerage system and drains for spillage is signed.
Work acceptance procedure
When accepting such work, the tests themselves are carried out first, which can be:
- Hydraulic - only non-pressure drainage systems are exposed to them, be it wastewater pipelines or storm sewers. testing is carried out in areas between wells by filling the system with process water. The tests are carried out in two stages - checking pipes and connections before filling the soil and checking the performance of the entire sewer system after filling the soil. Tests are carried out by pumping water into wells or receiving grids for 30 minutes; during the tests, the performance of the system is measured and the tightness of seams and joints is monitored. Tests may also be performed to determine the ability of pipes and connections to withstand the maximum allowable pressure throughout the entire drain.
- Pneumatic - during such tests, the ability of the waste system to withstand the design pressure is checked, according to GOST standards or design documentation. For such a series of studies, specialized organizations with the necessary equipment and licenses are involved; the process itself includes checking the pressure in the system or in its individual sections when supplying air under pressure.
If during the experiments the entire system met the standard indicators of SNIP 3.05.04-85, then an acceptance certificate for the work performed is drawn up, otherwise a defective statement and a drainage troubleshooting report are drawn up.
During periodic monitoring at enterprises with drinking water pipelines, external drainage systems are also tested during disinfection or treatment with special reagents.
Hydraulic testing of pipelines and commissioning
Testing of water supply, sanitation
The installed pipeline is subject to testing for strength and density (tightness) using a hydraulic method. The maximum length for testing a pipeline made of cast iron pipes in one step should be no more than 1 km, with longer lengths in sections of no more than 1 km.
The length of test sections of pipelines during hydraulic testing is allowed to exceed 1 km, provided that the permissible flow rate of pumped water should be determined as for a section 1 km long.
Pipeline testing should be carried out in 2 stages:
— preliminary testing for strength and tightness, performed after partial backfilling of the pipeline;
— final (acceptance) test for strength and tightness, performed after the pipeline is completely backfilled.
Both stages of the test must be performed before installing hydrants, plungers, and safety valves, in place of which flange plugs should be installed during the test.
The values of the internal design pressure Рр and test pressure Risp for carrying out preliminary and acceptance tests of the pressure pipeline for strength must be determined by the project and indicated in the working documentation.
Before starting the hydrotest, you should check and make sure that the air has been completely removed from the pipeline presented for testing. It is recommended to fill the pipeline with water from the lower side of the site. When testing a pipeline for strength, the following operations are performed:
— gradual increase in pressure in the pipeline (3-5 kgf/cm2) with holding the pressure at each stage for at least 5 minutes and inspecting the pipes and butt joints;
— if a leak is detected during an increase in pressure, it is necessary to establish the cause of the leakage and take measures to eliminate it; Elimination of detected defects in the pipeline can be carried out after reducing the pressure in it to atmospheric pressure;
— it is strictly prohibited to walk along the pipeline being tested, tapping, tightening bolted joints, or having workers in the trench;
— when the pipeline reaches test pressure Rsp for at least 10 minutes, do not allow the pressure to drop by more than 1 kgf/cm2, performing additional pumping of water to Rsp.
The pipeline is considered to have passed the strength test if, when the test pressure is reached, no pipe rupture occurs in it, butt joints are not broken, and no water leaks are detected during inspection of the pipeline.
Composition of as-built documentation for external water supply and sewerage networks
A19. List of contents of the executive order for the object: “Installation of external water supply and sewerage networks.”
A19.1 Download the general work log.
A19.2 Download the welding work log.
A19.3 Author's supervision journal download.
A19.4 Download incoming quality control log.
A19.5 Download the act for laying out the route with the executive layout diagram.
A19.6 Executive diagram of the trench for laying pipelines.
A19.7 As-built survey of the plan and longitudinal profile of underground networks download.
A19.8 Download diagram of welded joints with distances indicated on it.
A19.9 Conclusion on the quality of welds from the pump.
A19.10 Download the report on hydraulic testing of the pressure pipeline for strength and tightness.
A19.11 Download the report on conducting a hydraulic test of a gravity pipeline for leaks.
A19.12 Download the pipeline flushing (disinfection) report.
A19.13 Conclusion of the sanitary-epidemiological service.
A19.14 Download the test report for the external fire-fighting water supply system for water yield and operability of fire hydrants.
A19.15 Certificate for checking the laying of non-pressure pipelines by looking at the light.
A19.16 Download the certificate of inspection of engineering support networks.
A19.17 Download the act of hidden work for the development of a trench for laying pipelines.
A19.18 Download the act of hidden work to prepare the foundation for pipelines.
A19.19 Download the act of hidden work for laying pipelines.
A19.20 Act of hidden work on pipeline insulation download form.
A19.21 Act of hidden work on the construction of wells and cameras download.
A19.22 Download the act of hidden work for backfilling.
A19.23 Download the act of hidden work for inspection and testing of fittings.
A19.24 Act of hidden work to seal passages through the walls of wells and chambers.
A19.25 Certificates of certification of welding technology, welding equipment, welding materials.
A19.26 Documents on certification of the laboratory for quality control of welded joints.
A19.27 Certificates and certification protocols for welders.
A19.28 Certificates and passports for the materials and equipment used, sanitary and epidemiological reports, fire safety certificates (can be downloaded here).
A19.29 A set of working drawings for the construction of an object presented for acceptance, developed by design organizations, with inscriptions on the compliance of the work performed in kind with these drawings or changes made to them made by the persons responsible for the construction and installation work, agreed with the authors of the project.
See executive examples in the section: “Executive Examples”
See the composition of the executive in the section: “Composition of the executive”
Download acts, protocols and more in the section: “Acts and other”
Download useful books, GOSTs, SNIPs in the section: “GOSTs and books“
Verification stages
To identify defects in the operation of the sewerage system, a series of tests are carried out, which includes:
- Checking the operation of the internal part of the communication using the spill method;
- Full check of the tightness of all pipeline joints along its entire length;
- Identification of possible defects in the operation of all sewerage wells (inspection, rotary, inspection, etc.);
- Storm sewer testing.
in Ivanovo
About the company+7 Pumping out sludge, cleaning car washes, pumping out wells, septic tanks and cesspools.
21 May '19
Guarantee of the best price for new MTKs in stock* Economy from RUB 14,000.
(incl. VAT) | Standard from 17,000 rub. (including VAT) Rental of dry toilets Short-term and long-term rental of dry toilet cabins Liquids for dry closets Universal environmentally friendly products for dry closets Sewage pumping Pumping of septic tanks and toilets, removal of reinforced waste by sewage truck from 800 rubles Any type of rental and maintenance of toilet cabins in Ivanovo and region B The cost of short-term rental includes: delivery and installation, unloading and loading, special refueling. liquid and toilet paper, waste removal for disposal.
from 13,900 rubles Sale of mobile toilet cabins in Ivanovo and Ivanovo region Sale of mobile toilet cabins with delivery and the possibility of further maintenance, as well as sale of shower cabins and portable washbasins.
from 300 rubles Portable dry toilets and consumables for them Portable dry closets for country holidays, as well as a wide range of consumables
from 400 rubles per 1 m3 Sewage disposal: pumping out cesspools, septic tanks and settling tanks We have a license for the collection and transportation of liquid household and industrial waste of hazard class 4, we enter into contracts with organizations for the removal and disposal of solid waste.
RUR 15,000/month Autonomous wheel washers for construction sites The installation allows for recycling water supply for wheel washing without polluting the natural environment and does not require connection to a water supply.
Persons - members of the commission
In a separate paragraph in the inspection report for external or internal sewerage, it is necessary to record all the data about the members of the commission. These are:
- Representatives from the customer organization.
- Representatives from the general contractor. These persons are responsible for the correct installation of drains in case they do not comply with technical and operational standards during a spill.
- Members of the design organization who were involved in the development of the communication project being tested.
- A representative of a company or organization that was engaged in soil research at the site for the installation of external or internal communications. This office bears full responsibility for the inconsistency of the data received on the site regarding environmental and climatic conditions for the construction of sewer communications.
Thus, in the paragraph of the test acceptance certificate, it is necessary to include all the initials and surnames of the commission members with their signatures.
Who is on the commission?
As noted earlier, the act for draining internal sewerage must be endorsed by officials. The role of a commission member who is not responsible for drawing up the act can be played by:
- Representative of the customer, whether an individual or a legal entity.
- A representative of the general contractor, since it is this structure that is personally responsible for performing all installation work at the site. If problems are identified during the inspection stage, the contractor will correct the defects.
- Representative of the company developing the project.
- A representative of the company responsible for work on the land plot, as well as for the condition of the soil in which utilities were laid.
When filling out the document, all personal information about the members of the commission must be entered in legible handwriting. It is important to indicate the full last name, first name and patronymic and certify the information with the personal signature of each official.
What to do if an error is found in the act
Often, when drawing up documents, factual errors are made; for example, the person filling out the document may enter the wrong date or some indicator. In such cases, use the standard algorithm to correct the error:
- The misspelled word or number must be carefully crossed out.
- The correct option is written next to or above.
- At the bottom of the sheet or next to the correction (if there is space) they write: “Believe the correction.”
- Corrections are endorsed with your signature and date.
All members of the commission must be notified of corrections made to the document.
Nuances during testing
Often, the stage of checking the sewer system is carried out at a time when the object is not completely ready for delivery. For this reason, hydraulic tests of free-flow sewer pipelines should begin by clearing all sanitary points from possible accumulation of construction or household waste. It is important to follow these recommendations:
- All auxiliary points and nodes must be straight, which means the absence of deflections and other types of technological shortcomings.
- In some situations, it is difficult to use spill technology for testing. In this case, you can bleed the system with air.
- Control procedures must be carried out exclusively at positive air temperatures (the minimum threshold for testing is +5 C).
In addition to the above recommendations, it is important to check the drainage floor by floor. Such work will allow us to determine with maximum accuracy the location of the defect. All identified malfunctions must be included in the working documentation, on the basis of which a report is drawn up with the subsequent sequence of work.
The sewer system should be checked before the trenches with pipes are filled up. If the commission members make a positive verdict on allowing the system to operate, the trenches can be backfilled and compacted in accordance with the requirements of the excavation work.
Everything useful about sewerage - gidkanal.ru
GidKanal | Yandex Zen
Paper rules
Based on the general requirements of the current regulations, each paragraph of the act must be completed. As soon as the final list of responsible persons is formed and filled out, you can begin to draw up the remaining points of the document.
Act
In order to avoid mistakes and omissions in the act, it is worth remembering all the details in each paragraph:
- First point. This part of the paper contains information about the name of the company that developed and approved the house project. The document compliance code is also written down here, and the serial numbers of the revision of all components of the drainage system based on the working design are listed. In addition, it is necessary to list the working numbers of the drawings used for the drainage system in a specific type of building.
- Second point. This part of the document contains exact values for the number of all simultaneously open visible sanitary points. The time periods during which the checks were carried out are listed. Sanitary points can be all plumbing fixtures that a person uses in everyday activities (toilet, sink, shower, bidet, and so on). It is important to remember that filling out the second paragraph implies hydraulic testing of the sewer system when working at least three quarters of the total number of sanitary points.
- Third point. The violations and inconsistencies identified during the inspection stage are listed. Here it is important to indicate all the comments that the commission had during the testing process with a detailed description of the problem. If there are no deficiencies, “not identified” is written in the column.
- Conclusion. This part of the act contains the final decision of the commission and the recommendatory part to eliminate the identified shortcomings. The last sentence must indicate whether the system is permitted for operation.
You may also like: All about hydrodynamic drain cleaning
Filling out a report on hidden work in the sewer system
After the free-flow sewer system and water supply system have been completely installed and have been tested for sealing by pouring the system, it is also necessary to inspect the communications before closing the entire system. Such work is called hidden and is carried out inside the sewer network. The documented inspection is certified through an inspection report of the sewer pipes before closing.
Such a test (research) is carried out for external pipelines of water supply and free-flow sewerage in order to identify the slightest defects that could ultimately lead to depressurization of the sewerage system and subsequent environmental disaster on a district/city/region scale.
Important: an inspection of the sewerage/water supply system for the purpose of its final commissioning must be carried out as part of a full commission. About who should participate in the inspection and how exactly the sewer network inspection report is filled out, see our material below.
For a detailed explanation, attached is a sample form for an inspection report of the wastewater system after a major pipeline spill to identify violations in the sealing of the system.
Drawing up an inspection report for the water supply system
Water supply, drainage and air conditioning systems need regular inspection. The intensity of its implementation is determined by operating conditions. The higher the load, the more often the user delves into technical nuances.
After receiving the act, you should check whether all signatures have been placed
The use of pneumatic technology for conducting exhaust tests is appropriate when the temperature in the system is below +5 C. If it is higher, then hydraulic flow is used.
In addition, engineers advise taking into account the following recommendations:
- Communications at each stage are checked separately and then in the context of the entire system;
- The water supply system on each floor is temporarily equipped with plugs for inspection;
- Before all trenches on the site are buried, all tests must be completed and a report must be filled out.
The report is filled out based on data obtained as a result of a detailed examination of the system. This is done on the basis of the approved procedure prescribed in GOST.
Only people whose list is approved by the current regulatory framework are allowed to work. The task of the assembled commission is to assess not only the current state of the system, but also the degree of responsibility of the operating organization. If obvious signs of negligence are identified, the materials are transferred to the appropriate structures for an in-depth analysis.
External sewerage test report for spillage + sample
During testing of external sewerage using the spill method, the same document is drawn up as during testing of the internal sewage system. The form of the act itself is not a form of strict reporting and can be drawn up by the customer, contractor or subcontractor.
Also, during experiments on an external water drainage system, one of the forms of SNiP 3.05.04-85 can be used, which is a general form of document for acceptance of work performed when installing or repairing a drainage system.
Proof test stages
Before you start filling out the document, you should go through each stage of verification, which includes mandatory requirements for installation work:
- A comprehensive check of the internal structure of system parts, carried out by performing a forced spill.
- Checking the connection points of the drainage parts along the entire length of the system for compliance with the tightness parameters (the requirement also applies to closed areas).
- Determination of damage to inspection wells.
- Conduct an inspection and issue a test report for a storm sewer installed at a common drainage unit.
An entry corresponding to the first specified paragraph must be included in the sewer spill act without changing the meaning. Accordingly, the official must prescribe the type of sewer system to be audited.
In addition, the inspector is required to indicate the full name of the construction project. Also, the physical address of the building is included in the test report for internal sewerage and drains. All necessary information is taken from the general documentation and the design of the building on which the sewerage inspection is being carried out. The document must contain the date when control tests of internal sewerage and drainage systems were carried out, or information about the time period when the wastewater system was accepted.
Methods for testing sections of internal sewerage
What and how is checked when checking the compliance of the internal network with the project and established standards is described in SNiP “Sewerage. Internal and external networks and structures." According to this fundamental construction document, the following parameters of the sewer system are subject to inspection inside the building and then reflected in the final document (inspection report):
- testing network pipes for strength and their connections for tightness;
- compliance of the location of installed instruments and elements of the outlet pipeline with the design documentation;
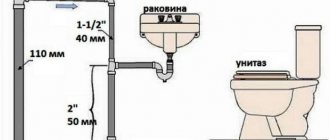
- correct installation of plumbing fixtures in relation to the floor surface (the distance from the floor to the upper edge of the receiver of each plumbing fixture is specified in the above-mentioned SNiP);
- the presence of a slope in the horizontal sections of the pipe and the degree of verticality of the risers.
Testing of pipes and connections for leaks in a gravity system, regardless of the material of the pipeline and fittings, is carried out using the spill method. The essence of the technique is that part of the main pipeline (bed) is fenced off in a certain area from the rest of the system. This is done with special plugs through inspection holes. The separated area is checked by filling it with water through the pipes of plumbing fixtures. According to SNiP, the results of a spill deserve attention if the pipeline was filled with the participation of at least ¾ (or 75%) of all devices connected in a given isolated section. Testing of the pipeline using the spill method is considered positive if the connections after filling the system did not give the slightest leak within 10-15 minutes (depending on the volume of the area filled with water).
According to the regulatory documentation, a spill, that is, testing a sewer system by filling it with water, is informative when the air t˚ is above 5˚. If the temperature is lower, a pneumatic leak test of pipes and connections is carried out (compressed air). The integrity of the riser, sometimes of external sections of the pipeline, is also determined by air. We will use the pneumatic testing method to assess the performance of a pressure sewerage system, when wastewater is forced out, under pressure created by pumping equipment.
The location of installed plumbing fixtures and its compliance with project documentation is determined visually. The height of the receiver of each device, the correct connection of the toilet drain, siphons of the washbasin, bathtub, sink, etc. are objectively assessed and reflected in the report. The condition of the plumbing fixtures themselves is also visually assessed. They must be free of visible dirt and mechanical damage.
The correct slope of the pipes inside and outside the building is controlled using a building bubble level. If the slope of the internal sewer network is allowed to be at least 1 cm per linear meter, then on the outside this figure must be increased to 2 cm per meter.
The installation position of the riser (this data is also reflected in the final report) is checked with a plumb line. A deviation from the vertical of 3˚ is allowed. A water tightness test of the riser is also carried out. The pressure should be about 0.8 MPa.