Story
Let's start with a brief historical overview.
The oldest known system for removing wastewater outside the city was found during excavations in the Indian city of Mohenjo-Daro, built more than 4,600 years ago.
The second oldest and most famous project is the Great Cloaca in Ancient Rome, built at the turn of the 7th and 6th centuries BC. The scale of the structure is impressive: the canal, which served as a collector, is three meters wide and has a height of more than four meters.
It’s curious: the sewage system, built more than three thousand years ago, has not only survived to this day. It is still used to drain rainwater to this day.
The construction of a sewer system in the then huge Chinese city of Linzi dates back to approximately the same time.
What about enlightened Europe? Alas, there is nothing to boast about: until the 18th century, sewage was simply poured into the street or, at best, into leaky pits, contaminating groundwater. The result was quite natural epidemics, which in some years wiped out up to a third of the population.
Underground sewer channels of ancient times in Athens and Eretria.
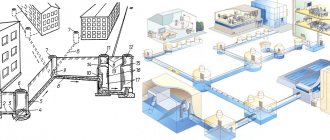
Connection to sewerage in a private house in the city
People are interested in how the sewage system works in the city and where the city sewerage drains. Sewage in the city is usually developed, starting with residential apartments and administrative buildings. All drains, except atmospheric ones, enter the outlets of the corresponding floors and, as a result, end up in a common riser. The riser at its lowest point is connected to an outlet pipe, which is connected to the first sewer well, installed in accordance with all the rules.
Pipes are connected to the wells to further purify the wastewater. If necessary, the wells can be turned off one by one, and the sewer system will continue to operate. Pipelines of standard designs are made from pipes of different diameters: for example, water drainage from plumbing can be carried out with 50 mm pipes, and when reaching the riser, the pipe diameter will be increased to 110 mm. In the future, the pipeline expands further, depending on the purpose and design features.
Everything written above gives some understanding of how the sewer system works in the city.
Classification
What types of sewerage systems can be distinguished in our time?
Classification is possible according to several criteria.
Location, functionality
- Internal sewerage collects domestic and industrial wastewater inside a residential building, industrial structure, warehouse, etc. and transports them beyond its borders.
- External transports wastewater from buildings to treatment plants.
- Finally, the treatment plants themselves transform contaminated wastewater into harmless solid waste, sludge (often used as fertilizer) and purified water, which can be discharged into any body of water or simply onto the terrain.
Drain type
The composition of the waste and its origin may also vary.
What options are possible?
- Household (fecal and household). This is, in fact, what drains into toilets, bathtubs and kitchen sinks in residential buildings.
- Industrial – liquid waste from enterprises.
- Finally, the contents of the storm drain are rain and melt water.
Storm water intake well.
Please note: in most cases, stormwater does not require treatment and is discharged into any local body of water. An exception is wastewater entering the storm system from the territory of enterprises, bus stations, gas stations and other heavily polluted areas.
Autonomy
Domestic and, less commonly, industrial waste systems can be divided according to one more characteristic:
- Centralized ones combine the flows of a large number of subscribers;
- Autonomous sewer systems are focused on one user. They are forced to provide not only transportation, but also disposal of products of economic activity.
It’s interesting: the most effective autonomous sewage systems, including deep biological treatment stations, can remove up to 98% of contaminants, which allows purified water to be discharged onto the ground surface or used for irrigation.
Pressure and gravity
The majority of urban sewerage systems are gravity-fed: they are laid with a constant slope towards treatment facilities. Alas, not everywhere the terrain allows for the required slope: in hilly areas, wastewater transportation is fully or partially provided by sewage pumps.
The corresponding scheme is called pressure.
Sewage pumping station.
Interaction of stormwater and domestic systems
A city or town is a territory in which it is necessary to solve the problem of drainage of both domestic and storm water. The tapping scheme can be implemented in three ways.
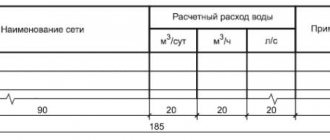
| Name | Description | Application |
| All-alloy | Domestic and storm drains are drained into a common network | A common sewage system is cost-effective primarily in small settlements. The design of the wastewater network as a whole is noticeably simplified; however, its capacity must be significantly higher than that required for the removal of domestic wastewater. |
| Separate | Domestic and storm water are collected and disposed of separately | The pattern is typical for all large cities. |
| Semi-separate | Domestic and storm water are collected by different networks, but are discharged into a common collector | Solution for areas with high levels of pollution. It is used where rain and melt water needs to be purified. |
One of the possible semi-separate schemes.
Introduction
If there is a main water supply, as a rule, there is a main sewerage system.
The material presented below will allow you to easily answer the question: “Sewerage for a private home. Which is correct?” Tapping into main sewer networks is similar to tapping into a water supply network. In this case, the depth of laying pipes on the external section of the pipeline from the main lines to the house is taken in accordance with the depth of soil freezing. Due to the close relationship between water supply and sewerage, their design is carried out jointly. Regarding sewerage, the project must contain text and graphic parts.
The text part includes:
- information about the designed sewerage systems;
- justification of the adopted systems for collection and disposal of wastewater, the volume of wastewater, methods of its preliminary treatment, reagents and equipment used;
- justification of the adopted procedure for waste collection and disposal;
- description of the sewer pipe laying scheme;
- information about the material of pipelines and wells;
- solutions for storm drainage and drainage water disposal.
The graphic part includes:
- schematic diagrams of sewerage and wastewater systems;
- plan for laying external networks of storm drains and drainage water;
- plans for sewerage and wastewater networks.
Elements and materials
Let's get acquainted with the main elements of sewerage and the materials used to create them.
Comb
In-apartment sewerage. It got its name for its shape, which is typical for compact apartments with adjacent bathrooms and kitchens: three outlets (for the washbasin, bathtub and sink) form something vaguely reminiscent of a comb.
Materials used:
- Until the 70-80s of the last century - cast iron. To seal socket joints, helix (tow with oil or resin impregnation) and, less commonly, molten sulfur were used.
Removing the cast iron comb.
Attention: dismantling joints filled with sulfur requires heating them with a blowtorch or hairdryer. When doing this work with your own hands, do not forget about respiratory protection: the fumes are so caustic that they can cause spasms of the respiratory tract.
- For the next 20 years, monolithic plastic combs were widely used. They were connected to cast iron tees sealed with the same cap.
- Finally, prefabricated polyvinyl chloride and polypropylene structures with rubber seals are now widely used.
Riser
A vertical pipe connecting the combs of several apartments. Opens to the roof, thereby providing ventilation.
According to the current SNiP, it is required to be supplied with several revisions (holes for cleaning):
- On the ground floor and/or in the basement;
- On the top floor of the building;
- If there are more than 5 floors, every three floors.
The photo shows cleaning the riser through inspection.
They are prefabricated, made from socketed plastic sewer pipes, and, less commonly, cast iron.
Useful: modern cast iron pipes are increasingly equipped with the same rubber seals as plastic ones. This somewhat simplifies installation, but does not add to the popularity of cast iron: its solid weight and three to four times higher price make it a dubious purchase.
Lezhnevka
A horizontal branch that connects several risers and ends with an outlet to the well. Supplied with revisions or cleanings on bends; laid with a constant slope, which is determined by the diameter of the pipe:
| Diameter, mm | Slope, cm/m. |
| 110 | 2 |
| 150 | 1 |
| 200 | 0,8 |
The materials are the same as in the case of risers. A caveat: when hanging plastic pipes, the maximum step between hangers should not exceed 10 diameters. The instructions are due to the fact that over large spans the plastic can sag under its own weight, creating counter-slopes.
Cast iron bench in a house built in the 70s.
Well
All external sewage systems are supplied with wells. The goal is periodic inspection and clearing of blockages.
Inspection wells are installed:
- On straight sections of sewerage with a step directly proportional to the diameter of the pipe.
- On all turns.
- At the junction of two or more branches.
Rotary well.
In addition, the well can compensate for the excessive slope of the terrain.
The traditional material for well walls is brick; Nowadays, reinforced concrete rings are widely used in the construction of wells. Fully sealed polyethylene and polypropylene structures are also gaining popularity.
Collector
Simply put, this is a large pipe that connects street and yard networks on the way to the treatment plant. Diameter – from 600 to 2400 or more millimeters. Materials - brick, reinforced concrete rings, monolithic reinforced concrete, polyethylene pipes.
Stages of as-built survey of sewer networks
The subject of the survey is constructed sewer pipelines, as well as other communication networks and engineering systems. Surveyors examine and record characteristic turns of pipes, points with a changing diameter (joints) and branching points. Work materials must reflect the application of new pipes with precise references to points of the state geodetic network and the nearest rigid contours. The coordinates of the linear object of construction work are checked for compliance with the project values.
Geodetic surveys of sewer networks at the construction site take place in three main stages.
The process begins with the preparatory collection of necessary documents and study of maps of the area with existing underground utilities. It is necessary to navigate the places where gas pipelines, water pipes, and water supply systems are laid. At the next stage, surveying is carried out using high-precision equipment with the creation of a plan-elevation justification
It is necessary to pay attention to pipe joints, variability of their diameter, emergency outlets, drain outlet heads, and turning points along the entire length of the network. Geodetic control is carried out before filling the trench with soil. The third stage is desk processing of the received data from control and geodetic work, comparing them with design values and drawing up as-built diagrams, drawings and other documentation.
For the performance of the sewerage system, the ability to cope with the load from the quantity and speed of incoming water is important. In order to control this factor, stormwater inlets and storm drains are subject to executive survey. The dimensions of pumping water supply and sewerage stations, including treatment facilities, must also be recorded.
The detailed location of each element of the trench system is important in the final placement of manholes and other sewerage structures on the site.
Final sewerage documentation and as-built drawing
Upon completion of the geodetic control survey, the information obtained is processed and drawn up in the form of an as-built drawing. It displays the routes of underground communications in the form of text and graphic information. Data must be updated and correspond to design values. The calculation part of the final document includes detailed calculations and measurements to search for deviations from the coordinates laid down during the design. Only maximum permissible values are possible, since construction and installation work during sewer installation is regulated by codes of practice and GOST.
Specialists
They not only carry out high-quality control surveys of sewer networks, but also monitor compliance with the norms and standards laid down in the project. Based on geodetic control materials, specialists create as-built diagrams of pits and utility systems.
Terms of use
The rules for using domestic sewage systems are, in general, quite obvious:
- They cannot be used for the disposal of insoluble and solid waste;
The consequences of a blockage on the first floor of an apartment building.
- It is prohibited to discharge toxic, volatile and flammable substances into the waste system;
- It is not recommended to discharge large volumes of hot water with a temperature of 80C or higher (in particular, when flushing heating systems). Local overheating can lead to leakage of connections and deformation of plastic pipes.
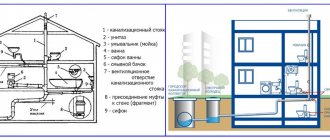
Internal sewage system
Sewerage inside a house is a system of devices that ensures the removal of wastewater from sanitary fixtures and equipment. The sewerage system is introduced into the house, as a rule, in the basement or first floor and is made of high-density polyethylene pipes. Risers and outlets from sanitary fixtures designed to collect wastewater can be steel or plastic.
Sewage diagram inside the house
The layout of sewer networks is:
- open - along the perimeter of walls and partitions;
- hidden - inside walls and partitions.
Work on installing water supply and sewerage systems consists of two main stages:
- installation of internal sewerage systems, cold and hot water supply, sealing of holes in ceilings and walls after laying pipes;
- installation of sanitary fixtures, connecting them to water supply and sewerage risers; installation of shut-off and mixing valves.
It is better to entrust the installation of water supply and sewerage to professionals. It is ideal if the sewer diagram has a visible design or design. This could be part of a whole house project or a sketch you did yourself. From the drawing it is easy to determine the length of the pipeline, and therefore calculate the required number of pipes.
Construction of a structure
The construction of a sewer collector is carried out at the stage of laying the foundation in a private house. At the same stage, a drain outlet is installed. This saves money and effort. In the finished building, holes for the pipeline are punched with a hammer drill.
The organization of a sewer collector has several stages:
- Carrying out earthworks (at this stage, trenches are dug for laying the pipeline, cesspools and pits are made for storage tanks);
- Pipeline installation (bends and tees allow wiring);
- Equipment and installation of treatment facilities (cesspool, septic tank).
To avoid freezing of the pipeline, the sewer outlet is insulated - the boundary part between the external and internal parts of the sewer. Glass wool, basalt fiber, polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene are used to insulate pipes. In some cases, pipelines are insulated with a heating cable.
Moscow Central Sewage Pumping Station
| Comments: | |
| (Link) |
is this really about this station? As a child, we almost climbed inside, but the kind security dissuaded us :) they really didn’t let us on the excursion. I always thought that it was from the flooding of Zamoskvorechye or is it something else? (no subject) – simsun
Expand(no subject) –
alex_avr2
Expand
| From: mitia_baban 2016-07-08 04:17 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
Well, why are you doing this with the nameplate, now you need to wash the monitor... =) and so - it’s too much...
I’d like to look at the cross-section of the pump, at the real one, that’s interesting...
(no subject) – mitia_baban
Expand(no subject) –
iime
Expand
| From: undergroundfoto 2016-07-08 04:37 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
Interesting) Especially about the days of peak flows... one can see the tendency of people to wash before New Year and September 1
| From: alex_avr2 2016-07-08 04:52 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
Well, the head of the sewerage department said that he calls August 31st the day for washing children before school :) Like everyone is preparing for September 1st, they come from their dachas on vacation, etc. But only if September 1st is a working day. And December 31st, if it’s a working day, then everyone comes home in the evening and starts being active, and then it’s very difficult. And if it’s a day off, then they start in the morning and it’s fine
And the day with the least consumption is the day of Russia, suddenly
(Parent) (Thread) (Expand)(no subject) – wazawai_n2
Expand
| From: simsun 2016-07-08 04:41 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
By the way, not all the stations are on panels, offhand I immediately remembered, far from there: Runovskaya, I wouldn’t have known about her if it weren’t for the very strong smell nearby (no subject) – simsun
Expand(no subject) –
alex_avr2
Expand
| From: der_wilde_hund 2016-07-08 05:04 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
Thank you, very interesting material!
It would be great to see the consumption statistics. Look for non-trivial correlations. True, everything is probably very secret.
| From: wazawai_n2 2016-07-09 05:46 am (UTC) | (Link) |
“The pumps are driven by huge motors, each with a power of 1.6 MW. For comparison, this power is comparable to the power of one metro train or approximately 160 apartments.” Not the best comparison. The pump has operating mode S1 - its installed power is close to the consumed one. This is not the case with apartments and even electric trains. “The station has an impressively sized switchgear (integrated switchgear).”
Complete.
| From: drink_drunk_roo 2016-07-09 08:26 am (UTC) | (Link) |
Yeah, it turns out that an apartment uses 10 kW, but in my house, according to the standards, it’s 4 times less, so that’s already 640 apartments
| From: drink_drunk_roo 2016-07-09 08:32 am (UTC) | (Link) |
Cool! I love posts like this. At work, I came across 10 MVA synchronous motors that drive VOD-40 two-stage axial fans (sorry, I didn’t take a photo of the nameplate). Surprisingly, they are approximately the same in size as here in your photos, 1.6 MV, although I always believed that power and size are directly related.
(no subject) – drink_drunk_roo
Expand(no subject) –
alex_avr2
Expand(no subject) –
drink_drunk_roo
Expand(no subject) –
dimon_w
Expand(no subject) –
drink_drunk_roo
Expand
| From: snarkfog 2016-07-15 07:45 am (UTC) | (Link) |
Interesting. I have been to KNS, but much smaller ones. Are the grates not cleaned by hand here? And then at one of the stations I watched the work of a rake man, who every half hour went down and manually cleaned the grates with a rake.
Work is daily, in shifts. The salary was meager, but he worked there purely for the sake of his pension, because a year was counted as two years, and he had a couple of years left before retirement.
He says that it’s not so easy to get a job as a robber, there is a real competition among people of pre-retirement age :)
| From: vmulder 2017-09-14 05:46 pm (UTC) | (Link) |
Just a bomb! How I love this
Determining the location of the blockage
A clogged sewer is not a problem, you just need to determine the root cause. As a rule, these are errors during installation work in the house or uncharacteristic slope of the pipes, the appearance of a large amount of corrosion or icing and, as a result, a decrease in the effective diameter of the pipes in winter. A harbinger of impending danger is a rather unpleasant smell that appears from communications. Therefore, if you smell an unpleasant odor, you should try to take all possible measures.
If the drain is clogged, what should you do? You need to try to find out the extent and cause of the blockage as early as possible. The blockage usually occurs in the house, local communications, but sometimes external pipes become clogged. To clean, you need to disconnect the sewer pipe that enters a private house or apartment, for which you should do the following simple operations:
- We place any free container (basin or bucket) under the pipe;
- We disconnect the pipe with a special wrench, that is, you need to pull the inner pipe out of the outer sewer pipe. If there is a threaded connection, then first we knock out the seal;
- We collect all garbage and leaking sewage in a separate container;
- We open the mixer to supply water in the right place and visually observe whether water flows from there or not;
- If the water does not pass, or the water pressure is much less than expected, then turn off the water and look for the blockage locally. If there are no problems in this area, then you need to look for blockages in external communications.
Functionality
The map is located on the server, and specialists from various workplaces have access to it.
The map program provides convenient means of quickly searching for an object by address or name, and printing a map. The card is used in various complexes and systems that provide specific functions for each enterprise management department: Modeling of outages due to an accident
When an emergency facility is indicated on the map, a list of shut-off devices, lists of disconnected consumers, hydrants and other facilities are automatically determined. The list of disconnections is used in the Dispatcher system to generate the text of the telephone message.
Displaying current outages on a map
During the period of work related to shutdown, disconnected objects and sections of networks are highlighted in color on the map. Current shutdowns are also displayed in the form of a tree of objects linked to a map. Shutdown diagrams are stored in an archive and are available for subsequent viewing and analysis.
Displaying service areas (circuits) of boiler houses
The outlines of each boiler room are highlighted in a different color. To change the contours, it is enough to indicate the switchable valves on the map, after which the boiler room contours are recalculated, and the map displays the actual states of the switching valves and pipelines. Switching diagrams are saved in the archive. You can select a diagram from the archive and make it current, which will generate a list of shut-off valves that need to be switched.
- Network passport - complete inventory accounting of all network objects;
- highlighting network objects on the map by accession numbers;
- thematic coloring of the card according to the conditions (year of commissioning, diameter, material, etc.);
- viewing digitized as-built documentation for utility networks linked to a map.
- electronic directory of consumer enterprises linked to a map;
- displaying the current location of vehicles on the map according to GPS navigator data;
- display of current values of main technological parameters on the map;
Installation rules
When assembling and installing sewers with random drainage of household waste, the following rules must be observed:
- The sockets must be installed against the flow of wastewater.
- To check the slope of the incoming sewer pipe, use a building level.
- The pipeline must contain a minimum number of turning sections.
- Slanting tees should be used in areas where internal risers transition to the main line.
- Installation of a fan riser is encouraged.
- The highway must have a minimum length.
- A sealed connection is obtained by installing rubber O-rings.
- Regular inspection of the pipeline requires the installation of inspection wells or inspection hatches.
Gravity sewerage is a system option that creates comfort in a private country house for residents.
How does a filtration well work?
A filtration well is the simplest and most compact of all filter structures that you can build yourself. Almost all owners of private houses would prefer a filtration well when installing a sewer system, but their installation is limited by a number of conditions:
- — moderate volume of wastewater (less than 1 cubic meter per day);
- — good filtering ability of the soil (For stable operation of the system, sand and sandy loam are needed; even black soil and loam are suitable, but with a predominance of sand). But the lighter the soil, the slower the well will silt up!
- — low groundwater level (below 3.5 m).
The FC can be made from available materials, from tires and bricks to large-diameter concrete rings, the main thing is that holes with a diameter of up to 50 mm are evenly made in the walls of the well. The total area of the holes is 10% of the total area of the well walls.
Unlike a septic tank, which must have a bottom, the FC does not have a bottom; it is placed on a gravel-crushed stone base with a height of at least 30 centimeters. The lower part of the well is covered with coarse river sand and gravel, and the height of the filter depends on the soil: if there is sand, then 25-30 cm, and if there is loam, then up to a meter. The size of the backfill fraction also depends on this: from 40 mm on sandy soils to 3-10 mm in loams.
The FC is buried to a depth of 2.5 - 3 meters, and the outside is also covered with a layer of gravel and crushed stone, the width of the layer is 30 cm, the height is up to the pipe that comes out of the septic tank. The outer backfill is covered with a geomembrane and covered with earth. The well must be covered with a lid with a built-in hatch.
.How this system works: the septic tank retains and partially dissolves “undissolved contaminants” from the toilet, feces, etc., and passes the rest into the filtration well. The liquid in the well slowly passes through the filter base and is absorbed into the soil; the organic matter that it contained is dissolved and processed by bacteria, “dying peacefully in a few weeks.”
AlexeyL Member of FORUMHOUSE
In addition to the septic tank itself, a “soil filter” is required, a structure that will take the clarified runoff below the freezing depth of the soil and distribute it over an area sufficient for absorption into the soil. Sometimes it is made in the form of 1-2 rings with a lid; The cross-sectional area of the ring works, but not on all soils this is enough for water to escape into the soil. It is advisable to do a soil absorption test before construction.
LadomirModerator FORUMHOUSE
The main thing is that the soil around the well is capable of receiving the amount of runoff you need.
The foundation pit is dug manually, and in order not to harm the filtering capacity of the future well, it is not raining and “trampling” on the bottom of the pit. If necessary, several filtration wells are installed in the autonomous sewage system.
Literature
- Sewerage // Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron: in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - St. Petersburg, 1890-1907.
- Sewerage // : / ch. ed. A. M. Prokhorov. — 3rd ed. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1969-1978.
- Water Dictionary. - M., 1974
- SNiP 2.04.01-85* - Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings;
- SNiP 2.04.02-84 - Water supply. External networks and structures;
- SNiP 2.04.03-85 - Sewerage. External networks and structures;
- STO 02494733 5.2-01-2006 - Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings;
- S. V. Yakovlev, Yu. M. Laskov.
Sewerage (water disposal and wastewater treatment). 7th ed. - M.: Stroyizdat, 1987. - G. S. Safarov, V. F. Veklich, A. P. Medved, I. D. Yudovsky
New technology in housing and communal services - Kiev: Budivelnik, 1988. - 128, p. : il; 17 cm. - Bibliography: p. 124-129 (68 titles). — 3000 copies. — ISBN 5-7705-0097-2