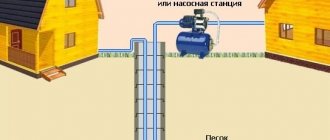
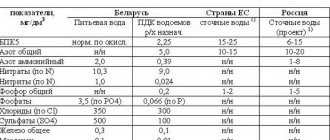
Wastewater is any water and precipitation that is discharged into reservoirs from the territory of enterprises and settlements, through sewerage systems or by gravity, the properties of which have been deteriorated as a result of human life and activity.
Centralized sewerage is a complex of engineering structures that receives surface wastewater for further removal outside populated areas and enterprises for the purpose of further disinfection.
Species by origin
Wastewater and its classification implies the following types.
This:
- Household, which comes from bathtubs, sinks and toilets. They are formed both in residential, public and industrial premises, in the process of human life.
- Industrial, formed in technological production processes using water.
- Rain or atmospheric, formed on the surfaces of roads, squares, roofs, etc., as a result of precipitation.
The classification of wastewater is determined by the sanitary standards that must be observed.
Wastewater, of all categories without exception, contains a small amount of contaminants of both organic and mineral origin.
Let's look at the composition of the contaminants:
- Domestic waters are considered more polluted, since they contain a huge amount of organic substances that are susceptible to decay . These include feces, urine and various bacteria. Among the bacteria, there may also be so-called “pathogenic” bacteria, that is, bacteria of the pathogenic group.
- Industrial wastewater is usually divided into contaminated and conditionally clean, used for cooling production units . All substances that pollute industrial wastewater are very diverse and completely depend on the production technology itself.
- As a result of prolonged heavy rains, wastewater enters the collector slightly polluted , therefore, in order to reduce the diameter of the sewer network pipes and reduce the volume of wastewater treatment facilities, several chambers are provided on the main collector, equipped with a storm drain and storm drainage system, thanks to which rainwater mixes with the rest of the wastewater , without treatment, are directly discharged into water bodies.
With a common sewage system, all water flows to treatment facilities, where they are further purified, after which clean water is released into the reservoir.
Settlements
The most well-known source of water pollution and the one that has traditionally received the most attention is domestic (or municipal) wastewater. Urban water consumption is usually estimated based on the average daily water consumption per person, which in the United States is approximately 750 liters and includes water for drinking, cooking and personal hygiene, for the operation of household plumbing fixtures, as well as for watering lawns and lawns, extinguishing fires, and washing streets and other urban needs
Almost all used water goes down the drain. Since a huge volume of feces enters wastewater every day, the main task of city services when processing domestic wastewater in the sewers of treatment plants is to remove pathogenic microorganisms. When insufficiently treated faecal waste is reused, the bacteria and viruses it contains can cause intestinal diseases (typhoid, cholera and dysentery), as well as hepatitis and polio.
Soap, synthetic washing powders, disinfectants, bleaches and other household chemicals are present in dissolved form in wastewater. Paper waste comes from residential buildings, including toilet paper and baby diapers, waste from plant and animal food. Rain and melt water flows from the streets into the sewer system, often with sand or salt used to accelerate the melting of snow and ice on the roadways and sidewalks.
Separate sewerage
R
The separate sewerage system is divided into:
- complete,
- separate,
- and incomplete separate.
A complete separate system involves the laying of two independent underground networks of pipes and canals, one of which is designed to drain water for domestic and industrial purposes, and the second network is necessary for draining relatively clean industrial and rainwater.
The first network is called household, and the second is called rain or drainage.
Through household networks, all wastewater is discharged to treatment plants, which, as a rule, are located outside populated areas.
In turn, rainwater is drained through another shortest network into the nearest water channels.
A complete separate household network system has a significantly smaller diameter of pipes and channels, in contrast to a storm sewer system. The estimated amount of rainwater is usually 20 - 50 times, sometimes more, higher than the estimated amount of all domestic water.
If, with separate sewerage, only a household network is laid, such a system is designated as incompletely separate.
Water disposal at ODN in 2021
Residents of apartment buildings are also required to pay for such expenses as general house needs. If a collective metering device for water disposal is installed in the house, then it is easy to measure the difference by its readings and the drainage of water from apartments supplied by individual metering devices.
If such a deviation is present, then this will be one. Needs are distributed to each apartment in proportion to its area in the total volume of premises of the house.
If a device that specifically takes into account water drainage is not installed in an apartment building, then residents are not required to pay for the ODN for this item. This is due to the fact that standards are not established here, and therefore there is no calculation procedure.
Semi-separate sewer
A semi-separate sewerage system is laid from two networks, one of which carries out the removal of domestic wastewater, contaminated industrial wastewater and the first flows of dirty rainwater, while the second one removes relatively clean rainwater and relatively clean industrial wastewater.
To organize the separation of rainwater, special chambers called “interceptors” are provided.
In turn, a combined sewerage system can be installed in certain areas of the city with different sewerage systems.
The most advanced sanitary system is the semi-separate sewage system. When using it, contaminated wastewater of absolutely all categories is removed far beyond populated areas and subsequently undergoes purification.
But interceptor cameras are not completely perfect, and the financial investment for the construction of two networks with special cameras at once is very large. That is why this type of sewerage systems is not currently being designed.
Internal sewerage division, depending on the composition of wastewater:
- domestic, used for the removal of domestic wastewater from buildings, into which industrial water is sometimes discharged, if its quantity and quality allow it to be discharged into this type of network;
- production, serving as a means of draining water from production premises and workshops;
- rainwater (internal drains), serves to drain accumulated rainwater on flat roofs of both residential and public buildings.
Internal domestic sewerage must consist of wastewater receivers: toilets, sinks, bathtubs; sewerage distribution in a private house to risers; risers equipped with inspections; highways to which risers and outlets are connected. In turn, the risers end in a ventilation pipe with the obligatory presence of a deflector.
[edit] Indicators
[edit] Sewer networks
The total length of the Moscow sewer network is 8354 km.[56]
The total length of pipelines for the wastewater collection and transportation system in Moscow (excluding Zelenograd and TiNAO) as of 2015 is ≈7.58 thousand km, they have a laying depth of up to 50 m and consist of gravity networks with a length of ≈6.93 thousand km, of which: yard (≈4.03 thousand km) and city street (≈1.67 thousand km) networks with a diameter from 125 mm to 600 mm, channels and collectors with a diameter from 600 mm to 4500 mm (≈ 1.13 thousand km), siphons and emergency outlets (≈0.10 thousand km); as well as pressure pipelines with a diameter of 100 mm to 3000 mm with a length of 0.65 thousand km. As of January 1, 2015, 5,370.18 km of gravity and pressure sewer pipelines (70.81% of the total length) were fully depreciated.[57]
The length of sewer networks within the Boulevard Ring is 124 km.[58]
[edit] Wastewater volume
The volume of wastewater entering the centralized sewerage system of Moscow in 2014 amounted to 3,627 thousand cubic meters. m per day. Including the flow of wastewater from the territory of Moscow amounted to 3,158 thousand cubic meters. m per day, from the territory of the near Moscow region - 469 thousand cubic meters. m per day.[59]
[edit] Number of clients
The number of customers served by the Moscow sewer system is 13 million people.[60]
[edit] Housing equipment with sewerage
Share of total housing area in Moscow equipped with sewerage:
- 2013: 98.6%[61]
- 2014: 98.6%[62]
- 2015: 98.6%[63]
- 2016: 98.6%[64]
- 2017: 98.3%[65]
[edit] Storm drainage
During 2010–2017, about 1 thousand km of storm sewerage were built in Moscow, including about 440 km in 2015–2017.[66]
Rules for receiving wastewater
The rules for receiving wastewater into the city sewer are strictly defined by sanitary norms and rules.
That is why, without exception, all wastewater receivers must be equipped with the necessary hydraulic seals to prevent polluted air from entering the premises from the sewer network.
Advice! To clean the sewer network, mandatory installation of inspections is provided. Due to the process of decomposition of organic substances found in wastewater, the street sewer network must be ventilated through internal sewer risers.
Water disposal and wastewater treatment through the general internal industrial sewerage network depends on the production technology itself, the design features of the installed equipment, the amount and degree of contamination of wastewater generated during the production process.
Composition of internal and external sewerage networks
Sewage network diagram
Internal drains include drain funnels that receive water from the roofs, outlet pipes connecting the funnels to the risers, risers and internal collection trays that receive water from the risers. In addition, in order to ensure normal operation of the network, audits and wells are provided on it.
As a rule, yard sewer networks include intra-block and street networks. This type of network is intended for receiving wastewater through internal sewerage networks and its further disposal.
Only in exceptional cases, with a permit for wastewater discharge issued by the State Sanitary Inspectorate, is it possible to organize sewerage systems without installing treatment facilities.
Content
- 1 Sewage operation diagram
- 2 Infrastructure 2.1 Pumping stations
- 2.2 Treatment plants
- 2.3 Emergency control tanks
- 2.4 Snow rafting points
- 5.1 Basin of the Kuryanovskiy wastewater treatment plant
- 8.1 Zelenograd
- 10.1 Sewer networks
Flocculation in wastewater treatment processes
Flocculation is a certain kind of transport stage that leads to the collision of stable particles with each other, tending to form larger particles (aggregates), which can subsequently be quite easily removed from the total amount of wastewater to be treated by filtration, sedimentation, or flotation methods .
Flocculation became widespread in water treatment technologies already in the 30s. At the moment, flocculation is quite widely used in the treatment of wastewater of both industrial and domestic origin.
The mechanism of action of flocculants itself is mainly based on the adsorption of flocculant molecules on the entire surface of colloidal particles, the further formation of a network in the structure of the flocculant molecules, and the adhesion of all colloidal particles due to van der Waals forces.
Flocculants for wastewater treatment form three-dimensional structures between colloidal particles that are capable of more complete and fairly rapid separation of the liquid phase.
The main reason for the appearance of this type of structure is the adsorption of macromolecules of flocculants on some particles with the further formation of special “polymer bridges” between them.
What are the consequences of not paying for sewerage?
Some people unknowingly decide that it is not necessary to pay for something that is not entirely clear. This leads to the fact that the generally small amount increases every month. Naturally, you will not be disconnected from the sewer pipe, but you are unlikely to be happy with the consequences. The management company has the right:
- charge a penalty for non-payment;
- to forcefully collect a debt through court. Most likely, the court will decide to collect the debt. The decision is transferred to the executive service, and then the executors will either describe personal property, the sale of which will cover the amount of the debt, or through the accounting department they will write off wages;
- impose a ban on traveling abroad.
As you can see, failure to pay for sewerage can have quite unpleasant consequences.
Cleaning stations
LIOS station
Stations where stormwater is treated are abbreviated as LIOS.
These LIOS are designed to remove suspended substances and petroleum products from storm water to certain requirements that apply to the process of their discharge into reservoirs of various categories, or onto the terrain.
Depending on the requirements of the customer enterprise, special treatment facilities have been developed where wastewater is further treated.
These facilities use specifically a variety of methods for treating stormwater:
- sorption,
- mechanical
- and physico-chemical.
These methods provide the most effective purification and neutralization of wastewater from all harmful impurities and petroleum products. For more thorough purification of wastewater from oil industry products and suspended particles, it is recommended to install LIOS.
With their help, storm drains are purified to the required discharge standards into bodies of fishery importance, where wastewater is disposed of.
In turn, the treatment of industrial storm water occurs through the use of specially developed technological schemes, which include several methods of water purification, depending on the degree and type of pollution.
The general scheme for treating all storm drains must in a certain way ensure a minimum discharge of pollutants not exceeding the maximum permissible standards into the reservoir.
The use of LIOS allows the use of completely purified storm water in industrial production, significantly reducing the overall costs of the enterprise for water supply and wastewater disposal, releasing purified water through the cycle.
Operation of storm drainage systems in urban environments
The drainage capacity must remain maximum under all conditions. Otherwise, after rains and during snow melting, flooding may occur in the area, and water will not drain from it. In order to ensure the functionality of the linear drainage system, do the following:
- its periodic cleaning from sediments, silt, and other contaminants;
- regular inspection of ground elements, monitoring their condition, cleaning of leaves, branches, debris, etc.;
- condition monitoring using inspection wells;
- in winter - removal of ice and snow. Can be done using mechanical tools or by installing heating cables;
- maintenance of elements of drainage systems installed on roof overhangs and building facades.
At individual facilities, additional control is exercised over the composition of the discharged water. To do this, samples are periodically taken and examined to determine the presence and concentrations of pollutants. The implementation of such control may be mandatory according to the requirements of the organization servicing the centralized network.
carries out installation of storm drainage systems at urban development sites. You can order both design and installation work from us. We offer competitive prices and guarantee high-quality and prompt order fulfillment.
Cleaning options
- Until recently, the most common method was wastewater disposal by holding the volume of sewage in specialized storage tanks with their subsequent emptying using sewage disposal equipment.
- A chemical method was also used, involving the use of chemicals that accelerate the decomposition process.
- In modern conditions, conventional structures cannot cope with constant loads, which is why we have to look for more effective and safe cleaning methods.
These include such a method as biological wastewater treatment. It not only gives good results, but is also recognized as environmentally friendly and safe in all respects.
Who should pay for drainage if a drainage pit is used?
Separate drainage pits are used not only in the private sector, but also for apartment buildings where there is no possibility of connecting to a centralized sewerage system.
In these cases, the fee is paid to the account of the company with which the contract is concluded. If the sewerage fee has not disappeared from the receipt, you must submit an application to the Criminal Code. If you suspect that the meters are not working correctly, you can order a meter verification. Line in the receipt: charge for sewerage.