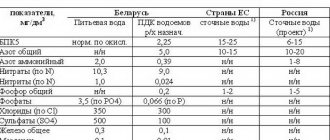
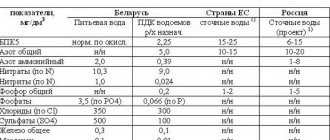
In the context of the topic of caring for the environment, the issue of keeping rivers and other bodies of water clean is often discussed. Now this is extremely difficult to do, because the wastewater that is discharged into water bodies is highly polluted.
After active participation in one or another industrial process, wastewater accumulates a huge amount of harmful elements, which, when released into an open body of water, lead to the death of aquatic inhabitants and plants, as well as other unpleasant consequences.
To measure the degree of pollution of wastewater, several indicators are taken as a basis, one of which is COD. what COD is and how to reduce this indicator in this material.
What are COD and BOD
The wastewater is oxidized by oxygen from the atmosphere. The calculations take into account other substances involved. They are converted into oxygen volume. O2 is required in an amount sufficient to convert hazardous substances contained in liquid sewage into harmless ones. Thus, the water is purified.
To characterize the state of wastewater, indicators of chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biological oxygen demand (BOD) are used. COD determines the amount of organic matter in 1 mg of oxygen per 1 liter. The BOD indicates how much oxygen the bacteria consumed while decomposing organic particles over a given time.
The wastewater contains a lot of organic matter, the processing of which requires oxygen, regardless of the treatment processes taking place. Its consumption increases with increasing percentage of organic impurities.
What factors influence COD
The composition of liquid waste depends on a number of circumstances:
- ongoing biological processes;
- atmospheric water content;
- nature of wastewater (domestic or industrial);
- climate change.
Effluents contain substances capable of oxidation to varying degrees. Some do not react with oxygen. To select reagents for analysis, the composition of the liquid is examined.
What is the difference between COD and BOD?
COD and BOD of wastewater indicate contamination, but they are different indicators. Purification is possible by oxidation of organic matter. BOD is a biochemical reaction, COD is a chemical reaction.
Microorganisms are used in biological research. They create a special environment for them, complete darkness, and keep them in such conditions for 5 to 20 days. In chemical analysis, purity is determined using oxidizing agents. The analysis is carried out for 2 weeks, no more.
COD shows the total organic content of liquid waste, and BOD assesses the contamination of a limited volume.
Methods for determining COD
For research, two methods are used: permanganate and bichrome. The first requires potassium permanganate and sulfuric acid. The result is called permanganate oxidation.
Wastewater COD diagram.
Bichrome analysis is carried out at the required temperature:
- Sulfuric acid and potassium dichromate are introduced into the liquid.
- There is a catalyst - silver sulfate. This substance does not enter the liquid resulting from the reaction.
- Chlorides are neutralized by adding mercuric sulfate.
The test results can be calculated theoretically. Under some conditions, the data obtained in practice differ from the theoretical ones. This occurs if there are many inorganic elements present that affect oxidation.
Separate oxygen consumption calculations are required. The result is subtracted from the total indicator. Research takes 2-3 days.
What is BOD complete and BOD 5
The amount of oxidizing agent that reacted is calculated over standard time units: 2, 5 and 20 days. Sometimes a different period is used, depending on the presence of suspected contaminants and how long complete oxidation takes.
Laboratory monitoring is carried out under strictly maintained conditions: in the dark, at a temperature not lower than +20° C. In case of violations, oxidation occurs differently, which affects the data. BOD is calculated as the difference in oxygen content before and after oxidation.
The index after the letters indicates the time period in days during which the analysis was carried out. BOD5 indicates that the study lasted 5 days. This is enough for oxygen to react with 70% of organic impurities in wastewater with average pollution.
Total BOD is the result when 100% of the oxygen is oxidized. The process lasts mainly 20 days under normal conditions. The nature of the organic matter affects the duration of complete oxidation.
Methods for determining BOD
The same amount of waste liquid is poured into 3 flasks. The temperature is brought to +20° C by heating or cooling the water. Shake for 1 minute to saturate the test material with oxygen.
The oxygen concentration is checked in one container. The other 2 flasks are temporarily placed in a thermostat for testing. When the time is up, the oxidizing agent content is measured and converted to liters. The result is determined as the difference between the data obtained from the first container and the average value in the other 2.
Determination of organic contaminants.
Standard COD indicator
The content of pollutants after cleaning is regulated by legally approved standards.
What factors influence COD
There are a lot of factors that can affect the composition of harmful substances and the acidity of a liquid. One of the key factors is the set of biochemical processes occurring in the reservoir itself . As a result of these processes, substances react with each other and form new ones, which may differ in structure from the previous ones and have a different chemical composition.
These substances can enter the reservoir as follows:
- along with precipitation;
- together with domestic or industrial wastewater;
- with underground and surface wastewater.
Their structure and composition can be very different, in particular which of them can be resistant to oxidizing agents . Depending on this factor, you need to choose the most effective oxidizing agent for certain substances.
In surface waters, organic matter can be suspended, dissolved, or colloidal. Oxidability differs for filtered and unfiltered samples . Natural waters are less susceptible to pollution by organic matter of natural origin.
Surface waters have a higher degree of oxidation compared to such types of water as:
- underground;
- ground and others.
For example, mountain rivers and lakes have oxidation in the region of 2–3 mg per cubic decimeter, rivers fed by swamps - 20 mg/cubic meter. dm and flat reservoirs - from 5 to 12, respectively.
A significant factor that affects oxidation is seasonal changes occurring in hydrobiological and hydrological regimes.
Also, the oxidation of a reservoir can change under the influence of human activity; depending on the sphere of human activity, pollution of one type or another enters the reservoir.
BOD to COD ratio
COD and BOD are measured simultaneously to provide information about the effluent. Data is compared and correlated. If the COD is higher than the BOD, this means that the water contains a lot of organic matter that does not oxidize.
The differing results are explained by the reactions that occur. Oxygen consumption varies depending on the type of process: chemical or biological. The ratio is influenced by the nature of the liquid and its contents. An increase in the difference occurs with insufficient biochemical oxidation. This means that liquid sewage is of little use for biological treatment.
Based on assessments of monitoring results, effective cleaning methods are selected.
What is the threat of increasing BOD 5 PKD?
Even natural springs and reservoirs contain a certain percentage of organic compounds - animal remains, dead plants, etc. Their destruction (natural purification of the substance) is carried out by bacteria. The process is called anaerobic biochemical oxidation. The result is the release of carbon dioxide. In this case, oxidation occurs with the participation of O2 dissolved in the liquid. The more organic inclusions, the more oxygen is needed to process them. Therefore, exceeding the BOD 5 indicator by 40 times, for example, will indicate high contamination of the substance - the oxygen level decreases sharply, which makes the water unsuitable. Standards for O2 content in drinking water are 9-11 mg/l at a temperature of +220C.
Why are high levels of COD and BOD dangerous?
Poorly purified water.
Poorly treated water causes damage to nature:
- If harmful substances get into open sources, this threatens the death of animals drinking water from them.
- Accumulating in the soil, harmful substances are absorbed by plants. Infected vegetables and fruits end up on people's tables.
- In reservoirs with a high content of organic pollutants, the need for oxygen increases. It is spent on oxidation, and flora and fauna are deficient.
COD and BOD: pollution criterion
Chemical and biological oxygen consumption are the main indicators of the presence of organic matter. Chemical analysis evaluates the total amount of sewage that is found in the entire volume of wastewater. Biochemical studies take into account particles processed by aerobic bacteria per liter of liquid. Organic matter is contained in all wastewater, but its amount should not exceed the level that is oxidized naturally.
Stages of reduction of COD and BOD during the cleaning process
Enterprises, if the pollution standards of discharged water are exceeded, are obliged to treat it. Treatment facilities are being built that differ in performance, types and principles of operation.
The decrease in COD and BOD takes place in 4 successive stages, as a result of each oxygen consumption decreases. The change in indicators is influenced by the characteristics and origin of the wastewater. After each stage, samples are taken for control.
Pollution indicators decrease to a greater extent at the first stage after settling. Substances that are decomposed only by strong oxidizing agents are removed. After this, more impurities remain, which are oxidized biologically. Therefore, before biological treatment, their concentration is reduced. More often, enterprises build stations where only mechanical and chemical cleaning is used.
Effluents are not always subjected to all stages of treatment. The required standards are sometimes achieved after the first stage.
General information
The definition of COD is the chemical consumption of oxygen by water. That is, COD in water reflects the amount of oxygen spent on the oxidation of organic matter and mineral components containing carbon. This indicator is otherwise called the unit of chemical-oxidative process in a liquid, since organic matter is oxidized under the influence of oxygen. The latter is considered a very powerful oxidizing agent.
Oxidability taking into account the difference in oxidizing agents:
- iodate;
- bichromate;
- cerium;
- permanganate.
Based on COD, you can resort to water purification. For example, to reduce the concentration of harmful components to acceptable levels. Cleaning is carried out at wastewater treatment plants.
Many organic substances have pronounced characteristics in terms of organoleptic properties (smell, taste, color, foaming ability). This allows the presence of an unacceptable stage of contamination to be determined. But a lot of organic matter in natural waters is not visible at all and cannot be smelled or tasted.
And wastewater, in principle, initially has all these negative parameters. Therefore, unacceptable indicators can only be identified after sampling and analysis. Therefore, it is so important to periodically analyze the state of water.
Otherwise, you can significantly damage human health and the environment. For wastewater, the requirements are not as severe (compared to cleaner water), but even here periodic checks of the condition of the water are carried out.
Differences between domestic and industrial wastewater
The contents of wastewater depend on its origin. Household liquid sewage contains a lot of organic matter, garbage, and household chemicals. They oxidize quickly and require little oxygen.
The composition of industrial waste is determined by the industry sector. They contain pollutants such as petroleum products, salts of various metals, phosphates, etc. Such substances are difficult to oxidize. More oxygen is required, which is sometimes forcibly saturated with wastewater.
When wastewater from different origins is combined, it benefits biological treatment. Domestic wastewater contains a lot of organic matter, which supports the activity of processes.
Stages of wastewater treatment and reduction of pollution levels
To achieve standards, wastewater is cleaned. The process does not depend on the type of purifiers installed and goes through 4 stages:
- Primary cleaning. Drains get rid of fatty films, heavy particles, as well as numerous impurities that can be easily removed.
- At the second stage, suspended particles and impurities are separated from the liquid, incl. those whose share has already dissolved. Purification occurs by biological oxidation, because most substances are organic.
- The third stage is based on the use of various physical and chemical methods. The smallest particles and impurities are removed, incl. metal salts.
- The final stage is to remove water from the sludge to reduce its volume and weight as much as possible. The stage does not affect the quality of COD and BOD indicators.
If cleaning does not bring the required results, it is necessary to change the cleaning technology or update the equipment.