The problem of wastewater treatment has long been one of the main issues of environmental safety.
Unfortunately, both on an industrial scale and in the context of the use of domestic sewer networks, insufficient attention is often paid to the preliminary treatment of wastewater. Therefore, all kinds of waste often enters the central sewerage system, which significantly exceeds the MPC of wastewater (maximum permissible values) according to various criteria.
What changed?
Experts call the amendments, additions and new control conditions large-scale and radical. The procedure for carrying out control measures and standards for the composition of wastewater have been supplemented with seven innovations:
- The frequency of scheduled control checks has been established - they should be carried out monthly, and not quarterly, as before.
- Visual control of wastewater has been introduced - inspection and verification of the presence of foreign materials, substances or waste in discharged waters. Their presence is checked without taking samples for analysis if they are visually noticed by a specialist. In order to determine the composition of wastewater, the water supply and utility organization must have special equipment.
- The use of automatic devices for conducting studies of collected water is regulated.
- The sampling conditions have been clarified.
- Specific methods and regulations for studying sampled wastewater are presented for specialists.
- The drains of transit organizations will be closely monitored. Control over wastewater systems not connected to the central sewerage main has also been tightened.
- The basis for wastewater control is explained in detail. Unscheduled inspections must be carried out in the following cases:
- emergency incidents;
- the threat of emergency situations in which permissible pollution standards are exceeded;
- lack of access for specialists from inspection bodies to wells.
A few words about domestic wastewater
The opinion that these requirements apply only to manufacturing enterprises is absolutely wrong. Quite often, employees of city water utilities discover illegal taps into storm water drainage systems and drainage systems.
And if there is no point in looking for heavy metals or radioactive substances in household wastewater, then they are not free from the presence of organic material. Therefore, MPCs also legally apply to household wastewater.
And if we are talking about large complexes of private buildings, the heating of which is carried out using boiler houses, the technological process of which involves the discharge of process fluids into the sewerage system, there is already a question about the content of both sulfates and chlorides in the wastewater. That is, it is quite possible that the question may arise that it will be necessary to purify wastewater from phosphates and other salts.
What do you need to know about wastewater composition standards?
The procedure for establishing standards for the composition of wastewater is regulated by Chapter XIII of the Rules. It specifies wastewater standards, an algorithm for monitoring compliance with standards, and a list of persons responsible for carrying out control activities.
- Standards for the composition of wastewater are established for pollutants for which the facilities of the corresponding water treatment plant have established standards for permissible discharges, as well as technological standards.
- The calculation of standards is entrusted to water supply and utility companies operating in the territory. For the accuracy of calculations, a special formula has been proposed, which is included in the contents of the document.
- Standards for the composition of wastewater are approved by municipalities or regional governments.
- Technologically regulated substances and elements have been installed for domestic and storm sewers.
Wastewater requirements
According to current regulations, in addition, wastewater that contains:
- Substances whose decomposition can cause the formation of explosive gases in the sewerage system (carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, various cyanides and others). Maximum permissible concentration standards in wastewater do not allow the presence of such substances in wastewater.
- Combustible substances, including various types of fuels and lubricants, resins, and insoluble fats.
- Substances with radioactive properties.
- Various biological inclusions that can cause bacterial contamination.
- Chemical elements that will have a destructive effect on the materials used in the construction of the sewer system.
- Various types of contaminants that contribute to the disruption of the sewer system and lead to the formation of blockages and deposits on the walls of pipes and collectors.
- Substances that are difficult to oxidize biologically.
- Chemical compounds for which the maximum permissible concentrations for wastewater have not been determined are also unacceptable to be discharged into the sewer system. The exception is for substances for which maximum permissible concentrations in water bodies that are intended for domestic use have been determined.
Indicators that wastewater must meet
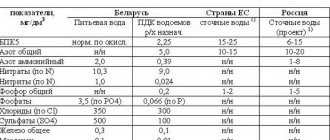
Maximum permissible concentrations of wastewater are measured in mg/liter and are:
- Substances in suspension - 500.
- BOD (full) - 500.
- COD - 800.
- Dense residue - 2000, including: Sulfates -500.
- Chlorides - 350.
- Substances from which ether can be extracted - 20.
In addition, wastewater must have a temperature of no more than 40 degrees, neutral acidity (6.5-8.5 pH).
Exceeding the maximum permissible concentration of wastewater leads to the imposition of penalties on an enterprise or individual.
How are fees for discharges in excess of standards calculated?
The issue of payment for the discharge of pollutants in wastewater is regulated by Chapter XV of the document.
- The amount of payments for discharges in excess of wastewater composition standards is based on the tariffs for payment for negative environmental impact, to which clarifying coefficients may be applied.
- Payment by all users of compensation for damage caused to the centralized sewerage system, if a specific culprit has not been identified.
The rules establish the amounts of fines for various types of violations. But there is no final version yet. The document continues to be updated with new information.
Criteria for assessing the state of wastewater
The main task of monitoring the condition of wastewater is to prevent pollution of surface waters. SanPiN wastewater requirements in this matter set quite stringent conditions for the content of harmful impurities in wastewater discharged into water bodies.
The main characteristics are:
- The amount of suspended and floating impurities.
- BOD of wastewater, a characteristic that determines the amount of oxygen required for the biochemical oxidation of substances of organic origin present in the wastewater. That is, the more polluted the wastewater, the greater this value will be.
- Wastewater COD determines the amount of oxygen required for the chemical decomposition of organic impurities.
- Contains various chemicals that can harm both humans and the environment.
- Effluent acidity.
Acceptable values of indicators according to SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00
Based on these indicators, it is determined whether it is possible to discharge wastewater into water bodies.
Purpose of innovation
The purpose of amending the Water Supply and Sanitation Rules 2021 is to improve the environmental situation.
Thus, according to Federal legislation, users who exceeded the discharge standard for the same pollutant more than twice during the year, or exceeded this standard once by 3 times, must develop a program, the implementation of which will reduce harmful discharges. The cost of doing so will be deducted from their payment for excess discharges.
What is storm drainage
Storm drainage (technical designation K2, in everyday life simply storm drainage) is a system for receiving and transporting rainwater to the discharge point. Precipitation flows from the roof of buildings or from the surface of the earth into special receivers. Through them, water moves to the collector, enters the treatment plant (WTP), and then is discharged into the reservoir. To the question - is it necessary to have a storm sewer - there is always an affirmative answer. The presence of a properly equipped storm drain is a mandatory requirement for the improvement of a populated area. Rainwater collection must be properly organized, as required by current legislation. Tasks of K2 systems:
- removal of excess rain and melt water;
- protection of foundations and other supporting structures of buildings and structures;
- exclusion of flooding of basements, tunnels, subways and other objects.
Discharge of storm sewerage into a water body (drinking reservoir) without treatment is prohibited. However, extreme discharges are allowed when the volume of wastewater is greatly exceeded during prolonged rainfall. As a rule, the volume of water does not increase immediately, so the first surface flush is treated. The following volumes of wastewater are considered conditionally clean, so they are allowed to be discharged into a water body without treatment. This justifies the discharge of stormwater into the sewer system if the stormwater does not come from industrial sites, parking lots and other polluting sites. However, each case of such a discharge must have a technical justification and appropriate permits.
Legislative norms
The mandatory presence of storm drainage is determined by law. Discharge of untreated wastewater into water bodies entails administrative and criminal liability for managers or perpetrators. The massive flow of waste into a body of water is equivalent to an environmental disaster. The main danger comes from industrial enterprises, but stormwater systems can also carry large volumes of harmful substances. Surface washouts carry petroleum products, lubricants, and various types of fuel. If these components are not removed, central treatment facilities will be overloaded and untreated wastewater will flow into water bodies.
Storm sewerage is mandatory due to SNiP 2-07-01-89. Discharge of wastewater into water bodies must be agreed upon with the Federal Fisheries Agency and other environmental organizations. Within the boundaries of the serviced area there must be local treatment plants (LTPs) that ensure the preparation of storm water for supply to the central wastewater treatment plants.
Drainage
Storm sewers also include drainage networks. They remove excess moisture from the upper layers of the soil. Drainage pipelines are connected to storm sewers after passing through special treatment tanks. These are sand traps, grates and other filtering devices. Similar equipment is also available for stormwater systems. The main difference between drainage networks is the underground placement of pipelines. If the immersion depth is too great, you have to build a pumping station and lift the wastewater under pressure into a higher reservoir. From there they flow by gravity into the collector.
We recommend
Water supply and sanitation in 2021. New environmental standards and requirements. Wastewater control. Seminar in Moscow + Online broadcast
Practicing experts will give recommendations on reducing and preventing antimonopoly risks, preparing for obtaining a comprehensive environmental permit in 2021, rules for establishing temporarily permitted discharges, calculating payments for the negative impact on the central heating system, implementing measures to reduce discharges in order to reduce subscription fees, and other topical issues in the field of water supply and sanitation in 2021.
Features of the household drainage system
Domestic (K1, fecal) drainage systems are designed to remove human waste products. The composition of household wastewater is considered the most complex, since everything that gets into the residential sewer is poured into it. The collection of wastewater is not random; the pipelines are connected to plumbing drains, kitchen sinks, washing machines and dishwashers.
Household systems are divided into internal and external. The first ones are connected to plumbing and are located inside buildings. The latter receive wastewater from internal areas and supply it to the OS. Discharge of fecal water into storm sewers is impossible in principle. Most rainwater systems are open, running through gutters on the surface of the ground. In addition, in winter the rain nets are empty. Sewage cannot be transported through them, as the liquid will freeze. This is the main difference between the two systems.
Another difference between the stormwater and household networks is the unevenness of the load. Domestic wastewater flows more evenly, and storm flows occur only during precipitation or spring snowmelt.
Is it possible to combine stormwater and household systems?
The possibility of combining stormwater and household networks exists. When questions arise about whether it is possible to discharge storm water into a domestic sewer system, it is necessary to remember the existence of all-alloy systems. In addition, according to SNiP standards, it is allowed to combine storm and utility sewers before entering treatment facilities. An exception is storm drainage at an enterprise, the requirements for which differ from conventional rainwater systems. Drains from industrial sites are replete with petroleum products, chemical compounds and other components. They pass through an area covered with waste, containing a lot of parking lots, landfills and other infrastructure elements. Industrial storm sewers are required by law to have their own treatment facilities that remove harmful components. The plant is responsible for treating waste liquids to normal levels.
Aerobiological station and treatment plant: what are they and what should be supplemented with them
An ordinary person may not know what is hidden under the concept of “aerobiostation” or “small treatment plant”. These are the well-known asters, topas, eurobions and similar septic tanks, with the help of which wastewater is purified.
Do you want to know more about what a septic tank is? Then read this article !
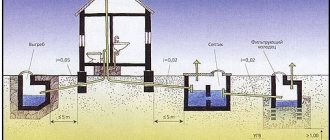
The underground filtration system, equipped on its own and complementing septic tanks, is also officially recognized as a treatment facility. The operating principle of this cleaning is extremely simple:
- Wastewater is sent to the ground. Usually a tunnel, perforated pipe, crushed stone and the like are used.
- The soil receives runoff, acting as a biological natural filter.
Natural disinfection of wastewater, thanks to the natural aerobic and anaerobic processes occurring during this process, is a treatment that fully complies with the requirements of the Chief Sanitary Doctor of Russia.
The great advantage of such a structure is that it can be easily erected on a summer cottage, even by a non-specialist.
Fines
Violation: Lack of registration of the right to use a water body.
Regulatory act: 9th article of the 2nd part of the 11th article of the Water Code of the Russian Federation dated June 3, 2006 No. 74-FZ. Art. Code of Administrative Offenses: Article 7.6 provides for the imposition of a fine. So, the amount of the fine will be:
- for citizens from 1 to 3 thousand rubles, for officials - 10-30 thousand rubles,
- for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from 10 to 30 thousand rubles,
- for legal entities - from 50 to 100 thousand rubles,
- Punishment for legal entities and persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity may be administrative suspension of their activities for up to 90 days.