Microorganisms come in many forms and are adapted to different living conditions. Therefore, there is practically no corner on the planet that is not inhabited by microflora. There are microorganisms inside the human body - on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, urinary system, and on the skin.
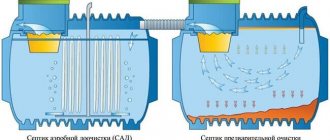
Depending on the need for oxygen and resistance to its negative effects, microorganisms are divided into aerobic, anaerobic and intermediate forms. These microorganisms are also used as components that accelerate the breakdown of organic waste for septic tanks (local treatment facilities).
Aerobic organisms, significance for humans
They can live and develop only in the presence of oxygen. It is necessary for oxidation processes, which produce energy in the form of ATP molecules. It is spent on vital processes - movement, growth, digestion of food, reproduction. In the absence of oxygen, such microorganisms die.
Aerobes include bacteria that live in soil, air, water, and on living organisms. They are divided into gram-positive and gram-negative. Shaped like cocci (in the form of a ball), sticks.
Some of them can provoke the development of diseases in humans:
- Vibrio cholerae;
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- tularemia bacillus;
- staphylococcus;
- streptococcus;
- Proteus.
Aerobic microorganisms are specially grown in the pharmaceutical industry, oil refining and mining industries.
What bacteria are used in our sewers?
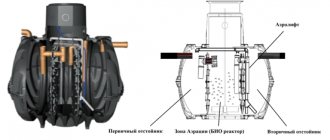
All our stations use only aerobic (live and naturally occurring bacteria). It would be more accurate to say that they themselves appear and multiply in autonomous sewer systems, since oxygen is constantly supplied to them.
Autonomous sewage system Unilos Astra
Autonomous sewage systems Sani
Biological treatment station Kolo Vesi
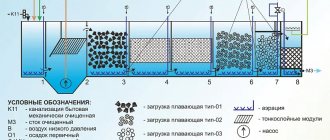
Septic tank Volgar
Septic tank Zorde
Septic tank Novo Eko
Anaerobic microorganisms and their role in nature
Anaerobic organisms are those that do not require oxygen. They are also heterogeneous. Highlight:
- facultative anaerobes. Feature - they can exist equally effectively both in the presence of free oxygen and without it. Without air access, they switch to simple reactions (for example, glycolysis);
- obligate anaerobes - exist only in the absence of O2 or at its lowest concentrations.
Among anaerobes, there are bacteria capable of forming spores (clostridium) and those without such ability (bacteroides, actinomycetes, velionella). Interestingly, in the spore form, microorganisms become insensitive to oxygen and can remain viable for a long time, whereas without this they would quickly die.
Anaerobes also include bacteria that use photosynthesis to produce energy. Humanity has found application for such microorganisms in everyday life. For example, they can be used to purify contaminated water.
Anaerobic bacteria that form spores are used in the textile industry to produce flax fiber. And microorganisms that retain nitrogen improve soil fertility and participate in the decomposition of cellulose and pectins.
To avoid problems with sewerage
Aerobic or anaerobic bacteria can provide irreplaceable help in summer cottages and country houses without a central sewer system. Bacteria added to the cesspool completely eliminate the unpleasant odor within a few days. Insects, constant companions of outdoor toilets, will also disappear. In addition, the contents of the pit themselves will significantly decrease in volume and turn from a problem into a benefit - it will become fertilizer.
In the past, some people used bleach (bleach) to eliminate odor. However, the effect of its use was rather dubious. Instead of one smell, another, no less unpleasant, appeared in the area - the sharp, corrosive smell of bleach.
In addition, after using this drug for a long time, nothing grows in the place of the toilet or next to it, not even weeds. And the natural process of decomposition of waste products slowed down significantly or even stopped altogether.
Intermediate forms
These include:
- capneic anaerobes - they feel better at low concentrations of oxygen and high carbon dioxide;
- microaerophiles grow well at an oxygen concentration of about 2%. They need it for oxidative processes, but in high concentrations it inhibits the activity of important enzymes;
- aerotolerant ones can live in the presence of O2, although they do not use it for energy metabolism;
- Moderately strict anaerobes can lead active life in an oxygen-containing environment, but at the same time lose the ability to reproduce.
Video about how an autonomous sewage system with bacteria works
When adding biological drugs, all these unpleasant consequences simply do not exist. In addition, thanks to the work of bacteria, there is less need to pump out waste, waste is disinfected faster, without destroying concrete or plastic coatings and walls, and without irritating human mucous membranes and skin. Aerobic and anaerobic flora are also effectively used for blockages in the sewer system, when it is necessary to quickly start the cleaning process after a long break, when actively using the sewer system, to clean the settling tank (septic tank) of an individual sewer system, etc.
Features of metabolism
Aerobic organisms use glucose as an energy source. It breaks down to pyruvic acid during glycolysis, and then, in the presence of oxygen, turns into water and carbon dioxide. In this case, the breakdown of one glucose molecule is accompanied by the formation of 38 ATP molecules.
The process of oxidative phosphorylation occurs in aerobes in mitochondria on membranes. A chain of cytochromes is concentrated here, which transfer electrons to each other up to the final acceptor - oxygen.
Aerobes are capable of extracting energy from the oxidation of methane, hydrogen sulfide, iron- and nitrogen-containing substances, and hydrogen.
In anaerobes, only glycolysis occurs, then pyruvic acid undergoes fermentation:
- lactic acid – bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, streptococci;
- alcohol - mushrooms of the genus Candida;
- butyric acid - clostridia;
- formic acid - enterobacteria.
The energy output in this case is 2 ATP molecules. The enzymes that participate in these reactions, dehydrogenases, are located on the cell membrane and inside the cytoplasm.
Normally, fermentation processes predominate in the intestines. In this case, the pH of the environment shifts to the acidic side - putrefactive flora cannot exist in such conditions. With insufficient activity of normal microflora, pathogenic intestinal bacteria (bacillus perfringens, sporogenus) are activated, protein breakdown predominates, and the pH shifts to the alkaline side. This process is accompanied by signs of intoxication, an unpleasant odor, and problems with bowel movements.
Rules for the use of bioactivators
To start or enhance the biological treatment process, sometimes additives are needed - bioactivators in the form of dry powders, tablets or solutions.
They replaced bleach, which did more harm to the environment than good. For the production of bioactivators, the most persistent and active strains of bacteria living in the soil were selected.
When choosing a bioactivator, you should take into account factors such as the type of treatment plant, the location of the backfill, the specificity of the bacteria and enzymes included in the preparation
Drugs that help speed up the process of decomposition of organic matter usually have a universal complex composition, sometimes a narrowly targeted one. For example, there are starter varieties that help to “revive” the cleaning process after winter storage or long-term downtime.
Narrowly targeted types are aimed at solving a specific problem, for example, removing large amounts of grease from sewer pipes or breaking down concentrated soap effluents.
The use of bioactivators in VOCs and cesspools has a number of advantages.
Regular users note the following positive aspects:
- reduction in the volume of solid waste by 65-70%;
- destruction of pathogenic microflora;
- disappearance of the pungent sewer smell;
- faster cleaning process;
- prevention of blockages and siltation of various parts of the sewer system.
For rapid adaptation of bacteria, special conditions are required, for example, a sufficient amount of liquid in the container, the presence of a nutrient medium in the form of organic waste, or a comfortable temperature (on average from +5ºС to + 45ºС).
And do not forget that living bacteria in a septic tank are threatened by chemicals, petroleum products, and antibiotics.
An example of a universal type is the French bioactivator “Atmosbio”. Recommended for use in septic tanks, cesspools, country toilets. The cost of packaging is 300 g. – 600 rub.
The market for biological products does not experience a shortage; in addition to domestic brands, foreign ones are also widely represented. The most well-known brands are “ Atmosbio” , “Doctor Robik” , “BioExpert” , “Vodograi” , “Saneks” , “Mikrozim Septi Treat” , “Biosept” .
The presence of systems that protect the cell from aggressive forms of oxygen
Only those microorganisms that have protective antioxidant systems can live in the air. During the transformation of oxygen, various toxic compounds are formed: superoxide anion, singlet oxygen, hydrogen peroxide.
They are neutralized by special enzymes - superoxide dismutase, catalase, cytochromes. The latter are found in aerobes (usually there are 3 of them). Facultative anaerobes have fewer of them (1–2), while obligate anaerobes have them completely absent.
Many anaerobic microorganisms in the presence of catalase are able to normally tolerate exposure to oxygen. They do not have their own enzyme.
When oxygen concentration increases to 40–50%, aerobic organisms stop growing. Pure O2 has a detrimental effect on all living things. It is not even the concentration of free oxygen molecules that plays a role, but the ratio of hydrogen and oxygen. It is called the redox index. The range of conditions for the optimal existence of bacteria is from 0 to 40. For anaerobes, an environment with an ORP of less than 14 is suitable.
Popular models
ASTRA 3
- Accommodation: 3 people
- Productivity: 0.6 m 3
- Weight: 120 kg
77000 rub.
65450 rub. More details ORDER
ASTRA 5
- Accommodation: 5 people
- Capacity: 1.0 m 3
- Weight: 250 kg
94000 rub.
RUB 79,900 More details ORDER
ASTRA 5 midi
- Accommodation: 5 people
- Capacity: 1.0 m 3
- Weight: 225 kg
96300 rub.
81855 rub. More details ORDER
Features of DNA in aerobes and anaerobes
It is believed that anaerobic forms of life preceded aerobic ones. As oxygen accumulated in the atmosphere, the richness and diversity of bacteria increased all the time. It was noticed that simpler microorganisms without cytochromes have a different DNA composition - the bases Adenine and Thymine predominate in the molecule. Later and more evolutionarily developed forms have cytochromes, and the genetic material contains more bases Guanine and Cytosine. Some anaerobic organisms do not have a clearly defined nucleus, and DNA is found in the form of a nucleoid in the cytoplasm.
How to keep bacteria from dying?
There are rules that, if followed, will extend the life of bacteria in the sewer:
- Use the septic tank regularly (remember, microbes need food too).
- In case of long-term absence, preservation of the autonomous sewage system is required (for example, for the winter).
- Avoid detergents that contain alkalis, formaldehydes, phenol, acids and chlorine.
- Treat the sewer with care: do not clog it with hard paper, garbage, cleaning materials, gaskets, etc. Read our article about what should not be disposed of in an autonomous sewer system.