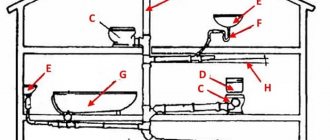
When living in individual country houses without a centralized sewer system, the owners have to solve the problem of recycling wastewater and storm water within the boundaries of their site. To do this, homeowners, independently or with the help of employees of specialized companies, construct utility lines to drain precipitation and liquid runoff into the ground, one of the main elements of which is a drainage pipe.
When installing any drainage system on a site, it is important to choose the right design and material of drainage pipes (drains), and to know the technology for their installation. When choosing components, products from different manufacturers are considered from the point of view of the optimal combination of quality, operating efficiency and product prices.
Rice. 1 Storm drainage diagram for a private house
Drainage pipes: what they are and how they work
They are also called drains. They perform the functions of receiving and discharging water, which are so necessary and important for draining the area. A system of interconnected drains is called drainage.
The principle of their operation is simple and clear, so land owners most often make the drainage system on their own. Drains are laid along or around the site (building) with a slope of 1% (1 cm per meter) towards any drainage basin (ditch, collector well, pit, canal, reservoir) or the lowest point of the area. Gravel, sand and soil are poured on top.
Drains can be drainage (suction) and collecting. On the walls of the drainage pipes there are holes located in a certain order. It is through the walls and connection points that water enters the drains and is transferred to collectors (drainage wells), and from there through collecting cavities it is discharged beyond the boundaries of the drained area. In this way, a sufficiently thick, dry, stable piece of land is formed.
Left: perforated drainage pipe. Right: collection drainage pipe (discharging water outside the site) without perforation
How does soil type affect?
The type of soil is the main criterion for choosing drainage pipes. It determines the degree of moisture saturation, the rate of water distribution, and the possibility of silting of the drain surface.
Selection rules:
- for sandy soil, fabric-wrapped pipes with gravel backing are required (minimum 30 cm around the pipe);
- on clay soils, drains without wrapping are used, but with crushed stone backing (fraction up to 30 mm);
- Wrapped pipes are laid on loams; bedding can be dispensed with;
- on chernozem a layer of bedding is required around drains without a filter;
- for rocky soils, the use of perforated pipes without additional elements is allowed.
Before purchasing and laying drainage, it is necessary to conduct reconnaissance and find out the composition of the soil layers in this area.
Types of drainage pipes
In the modern world, with the advent of new technologies, the requirements for drainage systems are constantly growing. The use of outdated schemes and materials is impractical and difficult.
Asbestos-cement pipes, as well as ceramic ones, are already a thing of the past. They have been replaced by plastic drainage materials - lightweight, comfortable, flexible, non-corrosive, reliable, safe and durable. They can withstand high temperature fluctuations (-70 to +50°C) and are easy to install, so you can easily install them yourself. For their manufacture use:
- Viniplast or UPVC (unplasticized polyvinyl chloride);
- polyethylene HDPE and PVC (low and high density).
Corrugated HDPE drainage pipe has higher strength. It can be buried to a greater depth than smooth-walled
Where are drainage pipes used?
Drainage pipes have found application not only in everyday life for draining excess groundwater from foundations and plinths and constructing drainage wells, but also in civil and industrial construction (land reclamation, laying highways). For each case, it is necessary to correctly select the dimensions and manufacturing technology of the elements.
Dimensions
When choosing drainage pipes, it is important to correctly determine their size. The performance of the entire system depends on the diameter of the drains. For domestic needs, materials Ø 200 mm will be sufficient, and to drain a large volume of water, pipes Ø 300–400 mm will be needed. The most common are elements with a diameter of 110 mm.
To accurately determine the size, you need to consider:
- soil texture;
- level of soil freezing and moisture;
- planned volumes of drainage;
- pipe laying depth (for each diameter there is a maximum permissible depth);
- trench width. It should be 40 cm larger than the diameter of the pipe.
A wide trench is dug under the drainage pipes. Then it is covered with crushed stone, which prevents silting
Drains with a diameter of over 300–400 mm are considered industrial; in everyday life they are used to build wells. The drainage system does not always consist of elements of the same diameter; in this case, a reducer (adapter) will be needed for the connection.
Design Features
The main difference between a drain and a regular pipe is the presence of perforation (partial or complete). With full perforation, holes measuring 1.3 mm are located every 60° around the circumference of the cross-section. Partial perforation provides three slotted holes in the upper part of the shell. Holes are made between the corrugations (stiffeners) which ensure the rigidity and durability of the system.
To create shallow drainage, where materials are laid to a shallow depth, single-layer corrugated drains with a stiffness class of 2–4 kN/m² are perfect.
Double-layer drains, which have high strength and stiffness class, are usually used to solve more global problems that require deep installation. In places with a high probability of clogging (sand, small grains of soil), drains with a filter layer or special filter material are used.
Video description
For more information about drainage systems and the rules for their installation, watch the video:
In ring systems, the distance of the upper parts of the trenches from the foundation or walls of the house should be at least 3 m. The concrete blind area around the walls of the building should be no less than 1 m.
When carrying out calculations, the lowest point of the system is first planned where water will be discharged. Based on the obtained value, the depth of laying the upper part of the channel is determined. Measure the distance of the highest point from the bottom and set the slope to 1%.
The upper point, as a rule, is located at the level of the corner of the building, and the lower one at the installation site of the collector well.
For systems where it is impossible to install a well at the required depth, it is recommended to use drainage pumps that will forcibly pump out the incoming water.
Diagram of a drainage system with a pump Source kanalizaciya-expert.ru
Types of drainage pipes
To create a drainage system, you can use the following types:
- ceramic;
- asbestos-cement;
- polymer.
The first two types are used less and less over the years. This is due to their high cost and short service life.
Asbestos cement pipes were very popular in the past, but are now rarely used
Polymer pipes have a number of advantages, the main ones being the low cost of layout and operation, long service life and the ability to make a drainage system yourself.
Perforated pipes
Almost all polymer pipes have a corrugated surface and thin walls. Therefore, drainage products even of large diameter have little weight, which facilitates the organization of drainage in general.
Can I make the perforation myself? It is possible, but not advisable, unless you are an expert in strength of materials and higher mathematics. Factory perforation is thought out to the smallest detail and has ideal geometry. If made in a makeshift manner, it will be unreliable - the slightest mistake can affect the operation of the entire system and lead to the formation of a swamp instead of reclamation.
Manufacturers perform perforations in precisely calculated places so that the drainage effect is maximum.
The holes are made in the form of narrow and long slits to minimize the entry of debris into the pipes. The number of such slots per circle is almost the same for all manufacturers:
- 360° - the holes are located generally around the entire circumference. Such perforation is used in heavily flooded areas with approximately equal amounts of groundwater and precipitation;
- 240° - the lower segment in 1/3 of the perimeter of the section circle remains unperforated. These pipes have proven to work well as drainage bases in areas with heterogeneous soil or natural slope;
- 180° - commonly called half, it is used in areas where one type of water exceeds another (for example, there is much more melt water than ground water or vice versa) or as an application to storm drains;
- 120° - an infrequently used configuration, used for low-volume surface drainage.
Common system installation mistakes
Carrying out incorrect calculations and choosing poor materials can completely disrupt the functioning of the system. The most common mistakes made are:
- The type of soil is not taken into account when choosing the type of pipeline.
- Absence or incorrect calculation of the angle of inclination of the channels.
- The system does not provide for the drainage of collected water from the well into a natural reservoir or sewer.
- Absence or insufficient layer of filter filling, geotextile.
- There are no holes in the pipes.
- Poor installation.
Drainage pipe manufacturers
The construction market offers a huge range of imported and domestic drainage products. Among our manufacturers, the most famous companies are Ruvinil, Nashorn, Politek, KamaPolymer LLC and others. Polieco, Uponor, Wavin and Rehau products are popular among foreign suppliers.
Pipes for drainage "Perfokor"
Perforated polyethylene products. Designed for the assembly of high-quality drainage systems. They have increased resistance to aggressive atmospheric conditions due to the double wall, white inside (smooth) and black outside (corrugated). The rigidity of the rings ranges from SN4 (in 50-meter coils) to SN8 (in 6-meter sections).
They are produced in Russia according to the standards prescribed in technical specifications 2248–004–73011750–2007. For different diameters it is possible to use a wide range of Korsis shaped parts (bends, tees, couplings, adapters, plastic wells), and drains Ø 110–160 mm are perfectly connected without the use of O-rings using ECOPAL couplings.
Perfokor drainage pipes with perforation are simply and conveniently connected using shaped elements of the Korsis and ECOPAL brands
Korsis drainage pipes
Specialized for the installation of storm drains and non-pressure sewerage. Made from high quality polyethylene according to technical specification standards 2248–001–73011750–2005, they have a double wall - black corrugated on the outside and white smooth on the inside (or yellow for PR-2 and PR-3 contours).
Corsys shaped components are used to connect the system. Moreover, elements of large diameter (from 250 mm to 1200 mm) are produced with an already welded socket, so only one sealing ring is used during assembly. Pipes of smaller diameter are connected with a Korsis coupling and two rubber O-ring seals.
The main one, which has its own facilities in many regions of Russia, Kazakhstan, Belarus and Ukraine.
Corrugated pipes Korsis SN4, SN8 are used for external sewerage
Pragma drainage pipes
This is a development by PipiLife for the needs of storm, municipal and industrial drainage, for drainage during road construction. The material is a special type of polypropylene (PP-b), which is slightly vulnerable to impacts and can withstand powerful drains and large temperature differences (-60°C to +100°C). This is where Pragma drains compare favorably with PVC pipes.
The high ring stiffness of 8 kN/m² makes them indispensable in particularly difficult laying conditions. The undoubted advantages of Pragma materials: they are easy to install, easy to cut and seamlessly connect with each other, with HDPE and PVC pipes, smooth-walled sewer lines, as well as with polymer and concrete wells. Assembly and installation do not require the use of heavy construction equipment, which allows saving on construction and installation work.
Pragma pipes compare favorably with PVC pipes: they are resistant to mechanical damage at any temperature
Softrock drainage pipes
Produced using technology from the foreign company SoftRock. Areas of application: closed drainage of septic tank, land plot, basement, foundation, roof drainage. They quickly gained popularity. The main advantage is that working with them is simple and fast. The SoftRock drainage system consists of a flexible perforated pipe with Russian-made polystyrene foam filler (“cube”) or imported (“hedgehog”). The SoftRock design eliminates the need for crushed stone and increases the efficiency of the drainage system by 20–50%.
PVC products
The use of PVC drainage pipes is typical for surface installation. The diameter of such products varies from 5 to 30 centimeters. There are corrugated single-layer (or double-layer) and perforated models of PVC drainage pipes.
Note! The products are well mounted on the pipes of concrete and plastic wells, and elements with snaps are used for connections.
These structures are easy to install, however, preliminary preparation of the site will be required - the presence of a crushed stone cushion and protection with geotextiles. PVC pipes have different classes of ring stiffness: SN16, 8, 6, 4 and SN2. The nature of the execution divides the products into rigid sections of 6 and 12 meters and flexible options of 40-50 meters in a coil.
Pipes for storm drainage
Storm drain pipes will help drain melt and rainwater away from the building. They, together with gutters, trays and storm inlets, form above-ground or underground storm drainage systems and ensure the safety and durability of the structure. Requirements for materials: strength, resistance to solar and mechanical influences, sedimentary reagents, temperature changes.
For the construction of drains, cast iron, polymer or reinforced concrete pipes are used (laying under roads). It is important to choose the correct diameter so that the storm drains do not overflow. For private houses, sewer pipes Ø 100 mm are used.
Design Features
The efficiency of the drainage and wastewater disposal system on the site is inextricably linked to the features of the project
When choosing or creating a project yourself, special attention should be paid to the following parameters:
- depth of installation of drainage pipes;
- minimum distance between trenches intended for laying pipes;
- slope of drainage channels;
- the topography of the area where the drainage system will be installed;
- depth of aquifers;
- physical and technical properties of the special materials used.
The method of installing the drainage system is selected taking into account the geological properties of the soil at the work site. The maximum distance between equipped drainage channels should not be more than 11 m for clay soils. If work is carried out on sandy and sandy loam soils, this distance can be increased to 22-25 m. In general, the distance between the channels is inextricably linked with the depth of the drainage trench.
Important! It is advisable to select a place for drainage of drainage water in advance. For these purposes, the nearest ravine or reservoir can be used, if there is one in the immediate vicinity of the site
The depth of the ditch intended for laying the pipe should be in the range from 0.5 to 1.2 m. This value is determined by a number of factors: the magnitude of the slope, the size of the area, its topography and other objective features. The slope for each linear meter of pipe should be in the range from 15 to 20 mm.
The throughput of a pipe is determined by its diameter. The smaller the pipe diameter, the greater the slope required to increase throughput characteristics. In addition, a small diameter drainage pipe is more susceptible to clogging.
To install any type of drainage system, you will need the following tools and building materials:
- gravel;
- crushed stone or pebbles (preferably of different fractions);
- sand;
- coconut fiber;
- set of perforated pipes;
- set of drainage wells;
- shovel.
Drainage pipes for drainage of groundwater
They are the basis of drainage systems. They collect water and remove it off site. They help cope with high soil moisture, dampness in cellars, the appearance of mold and frost, the formation of puddles and ice on paved surfaces, and prevent rotting of the root system of plants.
Waterproofing (foundation, walls) is not always effective. An effective drainage system is needed. When choosing its design, first determine the type of soil and only then start purchasing material. To ensure that the drainage network operates smoothly, drains are placed at a specially calculated depth. To do this, two conditions must be met:
- lay pipes below the ground freezing level;
- lay at least 50 cm deeper than the bottom mark of the base of buildings (near which drainage is carried out).
The drainage pipe must be laid 50 cm below the base of the foundation
For deep installation, use pipes with increased strength (double-sided pipe).
Table: drainage for different soils
| Soil type | Recommended drainage pipes |
| Sandy | With geotextile (or coconut) filter piping + crushed stone embankment |
| Loamy (combined) | With geotextile or coconut fiber filter |
| Shchebnevyy | With perforation without filter trim |
| Clayey | With or without filter + crushed stone embankment (0.2 m) |
Which drain to choose based on characteristics
Flexible single-layer products equipped with perforations can be used at a depth of no more than 3 meters. The category of products based on ring stiffness can also indicate the desired depth of installation. For example, SN-2 products can be buried no more than 2 meters, and SN-4 - 3 meters.
The two-layer drainage has smooth inner walls. Its outer layer is corrugated. In most cases, the strength of such products is SN-6. When laying the drainage network, two-layer elements no more than 4 meters long are used. They can be wrapped in geotextile or coconut fibers as a filter layer.
Flexible single-layer perforated and corrugated products belong to strength class SN-8. They can be equipped with a textile filter or supplied without it. They can be laid to a depth of up to 10 meters. Double-layer drains of this type are buried no more than 8 meters. They do not come with a filter.
Do-it-yourself drainage pipe installation
A large accumulation of groundwater can cause irreparable damage, for example, flooding the foundation, as a result of which a house built seemingly for centuries will shrink. There will be a distortion of the roof, walls, doors and windows. Excessive humidity will affect the health of those living in the house, because mold and mildew will constantly form in the dampest places. You can avoid all this by installing even the simplest, but high-quality drainage system.
- Ditch preparation:
- First, all the ditches and the location for the collector well into which groundwater will be discharged are marked. There must be a slope towards the water intake, otherwise the water will stagnate in the pipes. If the surface of the site is uneven, then ditches are dug according to the relief. On a flat surface, the slope is created artificially;
the number of trenches depends on the type of soil and the degree of its moisture. On clay soils, drains are laid more often. The depth of the ditches depends on the type of drainage, but not less than 0.5 m, the width increases as they approach the catchment area (well);
- When the trenches are dug, the bottom is prepared for laying materials. They create a shock-absorbing cushion - a 10-centimeter layer of granular sand and on top the same layer of crushed stone, on which drains are placed in a geotextile winding (for other types of drains, geotextiles are laid in such a way that when backfilling they cover the pipes).
- Pipe laying and system assembly. The drainage is laid out in ditches and connected to each other using shaped products (crosses, tees, couplings), forming a single network. After laying the pipes and assembling the system, you need to make a control check of the slope using an ordinary household cord stretched along the line of passage of the elements. At turning points and where the slope angle changes, inspection wells with covers must be installed to clean the entire system.
Laying pipes in prepared trenches. Laying pipes without geotextile lining using geotextiles (left). Laying pipes in geotextiles (right)
- Connecting drainage elements to each other. The most important thing when connecting is good sealing:
- one of the simplest ways is to attach PVC pipes to glue: the grease-free surface of a smaller diameter joint is coated with glue, the elements are connected, and the joint is once again treated with moisture-resistant glue;
You can use heat welding (only for polypropylene types): the joints are heated, the pipes are joined and left to cool. Molten polypropylene, when solidified, provides good tightness;
- Small diameter elements can be connected with compressor fittings and turnbuckles. The quality of the connection is not inferior in strength to welding.
- Perform backfilling. After checking the operation of the system, it is backfilled (if the system is closed). For better water permeability, the pipes are sprinkled with gravel or crushed stone, covered with geotextiles, and then with a layer of sand (10–15 cm). The soil is poured on top above the soil level. Precipitation will pass, snow will fall, and over time the earth mounds will settle and become level with the surface of the site. The open drainage system is decorated with crushed stone of different sizes. If the last layer is decorated with marble chips, and plants are planted along the edges of the ditches, you will get a unique landscape design.
Properly dug ditches sloping and widening towards the catchment area (left). Bottom preparation diagram (right)
When connecting drainage pipes, it is important to check the strength of the fastening; the latches of the couplings must be locked
Video: do-it-yourself open drainage from pipes and scrap iron
Criterias of choice
When purchasing a pipe for driving through a ditch, you should take into account the following indicators:
- Ability to withstand heavy loads. Trucks and special equipment can enter the construction site, so such a product must have high mechanical strength to withstand the pressure of heavy vehicles and embankment material weighing several tens of tons.
- Trench dimensions. The volume of passing wastewater directly depends on them. To ensure that the drains do not erode the embankment, but completely leave the ditch, the pipe must be of a suitable diameter.
- Cost indicators. There are many types of pipes on the construction market that can be used for laying in ditch. The choice often depends on the financial capabilities of the owner.
Cleaning drainage pipes
A clogged drainage system is not able to fully perform its functions, so it is important to periodically clean it to get rid of limescale build-up inside.
Mechanical method
Different methods are used depending on the location of the system. If it lies on the surface, then you can clean it manually yourself. For deep drainage, you will need a pneumatic installation with a cleaning roller and a special attachment for crushing large build-ups. Cleaning should be done every 3-4 years.
The easiest way to unclog a drainage system is to lower a steel cable into it. When it reaches the blockage, you can break through the resulting obstruction using rotational and translational movements
Plastic pipes are predominantly used; they have a number of advantages:
- long service life, up to 60 years;
- have high strength, the double-sided pipe has stiffening ribs and the loads are distributed evenly;
- pipes are resistant to acidity of precipitation and do not rust;
- they are not heavy, which makes them easy to unload and stack;
- the inside of the pipe is smooth and blockages do not remain, but are easily removed with water;
- The entire system does not need to be cleaned if you put a special material on the pipes that will prevent debris from entering;
- plastic pipes are economical, as they have a low cost and are easy to install independently, without requiring additional expenses;
- You can take any size, which allows you to drain a large amount of water.