Groundwater flowing in close proximity to the surface of the earth can often cause a lot of damage to buildings located on the site. The drainage system drains groundwater from the foundation, as well as the moisture that seeps from the surface of the site.
Drainage around the house allows you to increase the service life of the building. As a rule, the system consists of pipes, receiving and inspection wells, as well as sand and gravel backfill. Let's take a closer look at the functions and design of drainage around the house, how to make it correctly and which option to choose.
Foundation contour drainage
To drain water from an already built foundation, wall and ring drains are used.
Their operating principle is the same. The difference is that the wall system is made close to the foundation, and the ring system is made at a distance, usually 1.5-2 meters. Wall drainage is installed in non-filtering soil (clay, loam). Collects surface melt water, which seeps mainly along the wall, and not through impermeable soil.
The ring system is suitable for sandy filter soils. Lowers groundwater levels.
Types of foundation drainage based on pipe laying depth:
- Perfect
. Drainage pipes are laid on a waterproof layer of soil. Used if this layer is shallow. - Imperfect
. Pipes are laid above the waterproof layer if it lies deep.
Elements of wall and ring foundation drainage:
- Drainage trenches.
- Outlet pipes.
- Filter bedding, crushed stone or gravel.
- Filter fabric (geotextile).
- Basement waterproofing.
- Inspection wells.
We'll tell you how these elements are structured and why they are needed.
Drainage trenches
The RMD states that “in soft soils with insufficient load-bearing capacity, the drainage pipe must be laid on an artificial foundation.” This base is a sand cushion. For this we use river sand of 1.5-2 mm size. The thickness of the sand bedding is 50 cm.
Drainage pipes
Typically, corrugated pipes made of low-density polyethylene (HDPE) are used. The standard pipe diameter is 110 mm. The pipes have holes through which water flows. “The dimensions of water intake holes should be selected taking into account the granulometric composition of the soil to be drained” (RMD, 10.9)
Standard polyethylene pipe
Pipes are also used in geotextile filters. They are designed for sandy and loamy soils. These soils are easily washed away by water and can wash into pipes and clog them. The filter traps dirt.
Pipes in geotextiles
Crushed stone for drainage
Crushed stone is needed to filter groundwater so that the pipe holes do not become clogged. The filtering capacity of crushed stone depends on its fraction - the size of one grain. A fraction of 20-40 mm is considered optimal. We use exactly this crushed stone.
Geotextiles
Geotextiles protect crushed stone from erosion and also keep the soil from subsidence. As stated in the RMD, “a geotextile filter must pass water and screen out soil, not be unduly deformed and not limit the access of moisture to the drainage structure, and have bio- and chemical resistance” (RMD, 10.2).
Main characteristics of geotextiles:
- Manufacturing technology
. From one endless thread (monofilament) or from a staple (individual threads 5-10 cm). - Material
. Geotextiles can be needle-punched, thermally bonded or hydro-bonded. - Density
_ Geotextiles with a density of 200 g/m³ are used for drainage systems - Filtration coefficient
. Measured in meters per day.
RMD recommends the use of needle-punched monofilament geotextiles. This geofabric is also used by our company.
Basement waterproofing
To protect the base from moisture, waterproofing membranes are used. They are laid with a 10 cm overlap and connected using self-adhesive bitumen-polymer tape. Fastening is carried out using plastic dowel-nails in increments of 20-25 cm.
Manholes
Needed to monitor the operation of the system and for cleaning. The well consists of a bottom part, a vertical part and a cover. The pipes are either made at the factory or are cut in during installation. Wells are installed along the drainage route every 40-50 m. It is imperative to install wells at turns in the route, as well as when there are level differences.
Storage well
Serves to collect water and drain it into a ditch. Installed at the lowest point of the system. A float pump is placed in the well, which releases water into the ditch.
Foundation drainage device:
- Drainage trenches are dug around the perimeter of the house.
- The trenches are filled with sand. The sand is leveled.
- Geotextiles are laid at the bottom of drainage ditches.
- Granite crushed stone is poured into the geotextile in a layer of 10 cm.
- Pipes are laid on crushed stone. The minimum pipe slope is 2 mm per meter in clay soil, 3 mm per meter in sandy soil.
- Inspection wells are placed at the corners of the route, and a drainage well is installed at the lowest point of the site. Pipes are connected to wells.
- Cover the pipes on top with crushed stone.
- Wrap the edges of the geofabric so that they overlap and completely cover the pipes and crushed stone
- The trenches are filled with sand.
The drainage system cannot be combined with storm sewer. This will lead to storm and melt water washing away sand and crushed stone. It is recommended to do drainage and stormwater in parallel, in one trench.
Features of the closed version
Having figured out how to properly make drainage around the house and drawn up a project, you should prepare for further work.
You should stock up on materials, as well as the necessary tools. During the work you may need:
- twine for marking and marking the position of communications;
- building level and plumb line to control the slope of the pipes;
- bayonet and shovel;
- soil compaction tool;
- a bucket and/or wheelbarrow for transporting unnecessary soil;
- tape measure for taking measurements;
- hacksaw for metal, etc.
A certain number of drainage pipes will also be required. These are special designs with perforations, usually made of plastic. Instead, you can use plastic pipes for external sewage, after making holes on their surface with a regular drill.
Additionally, you need to prepare: geotextiles, sand, crushed stone or other similar material, inspection wells according to the number of turns, etc.
In the process of installing a drainage system around the house, geotextiles are used - a non-woven filter material, as well as crushed stone of large fractions
Geotextiles are necessary to protect the filler surrounding the drainage pipe from the penetration of fine clay particles and siltation. There is no need to skimp on this material. It should be enough to completely cover the walls and bottom of the excavated trench, and also cover the backfilled pipe with a substantial overlap.
It is recommended to first mark the ground and then begin excavation work. They usually start digging from the highest point of the system, gradually deepening the trench.
When calculating the slope of a drainage pipe, you can focus on the standard of 1%. If the length of the trench is 20 m, then the height difference between its starting and ending points should be 20 cm. The necessary measurements are made using a regular tape measure.
After the trench is ready, its bottom must be thoroughly compacted. Then a 10 cm layer of sand is poured onto the bottom, which is also thoroughly compacted. After this, it is recommended to cover the entire trench with a layer of geotextile so that both the bottom and walls of the structure are covered, and the edges of the material come to the surface and lie freely on the ground.
The construction of a closed drainage system uses perforated drainage pipes, geotextiles and backfill materials: sand, gravel, crushed stone (+)
Now, at the bottom, hidden by geotextile, you need to pour a layer of gravel about 20 cm. Any filter material will be acceptable: crushed stone, expanded clay, brick fragments, etc. The main thing is that its fraction is larger than the size of the holes in the drainage pipes, otherwise blockages cannot be avoided.
After laying, the gravel must be leveled and the slope of the communications must be checked; it must correspond to the previously carried out calculations and measurements.
If everything is in order, drainage pipes are placed on the gravel and connected to inspection and drainage wells. Then the system is covered with another layer of gravel (crushed stone, expanded clay, etc.). The height of this layer should also be 20 cm. The edges of the geotextile that remain free are wrapped over the backfill layer.
In the places where the drainage pipe turns, inspection wells are installed, which are necessary to monitor the condition of the system. They are covered with lids on top
The overlap of the layers of non-woven material should be about 30 cm. Sometimes it is recommended to secure the position of the geotextile material using twine or plastic fasteners.
Now you can fill the rest of the trench with sand (a 10 cm layer is needed) and soil. The sand again needs to be compacted, especially in the space on the sides of the drainage pipe. Previously cut turf is laid on top or paths are installed.
You can come up with your own version of decorating the place where drainage pipes are laid. There must be access to the covers of the inspection wells, as well as to the point of discharge of the diverted moisture.
Inspection wells are plastic vertical containers closed with lids. They are used to periodically check the status of the system.
A drainage well is a wider container; it can be round or square in configuration. Most often, an old plastic barrel is used to arrange it.
You can also use concrete rings of a suitable diameter or make walls from monolithic concrete. In the latter case, it is imperative to reinforce the structure. The top of the drainage well should be covered with a strong lid.
Useful tips
It is quite justified to lay out pipes simultaneously with the preparation of inspection wells. This technique will help to avoid mismatch and system inoperability. In all wells they place a container to collect sludge or simply leave space for it. Between the pipe entry point and the base of the well shaft, 0.2-0.25 m is reserved. Backfilling of crushed stone on the sides of the drains is mandatory; Closer to the foundation it is worth raising it to the height of the soil itself.
It is recommended to lift the layer of crushed stone above the drains from 30 cm. Geological textiles are placed above, preventing the mixing of materials and the accumulation of silt. Next, sand is placed, raising it to ground level. It is strictly unacceptable to compact the sand backfill; this will weaken the permeability of the soil to water. Experts and experts advise choosing drainage pipes with a high level of rigidity.
To learn how to install a drainage foundation, see the following video.
Water infusion of dandelion flowers
This is an excellent cosmetic product. It gets rid of freckles and age spots. I use the infusion as a regular face lotion. I wipe cleansed skin with it morning and evening. It refreshes and tones the skin, relieves puffiness.
I pour a glass of boiling water over a large handful of fresh or dried dandelion inflorescences. I insist for 1-2 hours (preferably in a thermos). I cool and strain.
Laying technology
For the system to work properly, you need to know how to properly lay the drainage pipe, depending on the type. For each drainage pipe, the installation technology will vary slightly depending on the design. But the initial stage is the same for everyone:
- Develop a drainage scheme: location of pipes, places for wells and revisions.
- Depending on the type of soil, the geological characteristics of the site, the location of groundwater and the required throughput, the size and type of drainage pipe are selected.
- Based on the planned route for wiring drainage pipes on the site, site planning and markings are carried out for excavation work.
The ideal option is when the drainage scheme is developed together with the house design
- They dig trenches. On dense soils with straight walls, on loose soils - with sloped walls, or strengthen them during work. The bottom is made 30 cm wider on both sides of the pipe.
- Level the bottom surface, compact the soil, form a slope towards the drainage well within 0.5-3.0% (minimum 0.5 cm and maximum 3 cm for each meter of length).
- Pour a layer of coarse sand about 15 cm thick and compact it, observing the slope laid down during the formation of the ditch bottom.
Further technology for laying the drainage pipe depends on its design.
Laying a drainage pipe with geotextile, if it does not have a factory winding:
- Geotextiles are laid on top of the sand. The width of the canvas should be sufficient so that the edges can then be brought together.
- Pour a layer of crushed stone (15 cm).
- Lay a perforated pipe and cover it with a layer of crushed stone on top.
- The edges of the geotextile fabric are wrapped and fastened together. As a result, the pipe should be uniformly filled with crushed stone on all sides of about 15 cm, the textiles should run along the sand-crushed stone boundary, and there should be free space left to the walls of the trench.
The principle of drainage is that water seeps through geotextiles, crushed stone and perforation, then flows by gravity through the pipe to the well
- Pour a layer of sand on the sides and top (about 15 cm).
- The removed or imported fertile soil is put back.
If the pipe has a factory winding made of geotextile, then the drainage installation procedure is reduced by two “steps”.
Note! You can buy geotextiles separately, choose perforated pipes without wrapping and wrap them before carrying out work.
When using pipes with a filter layer of polystyrene foam granules and windings, crushed stone is not covered. And if you believe the manufacturer’s advertising video, you don’t even have to fill in the sand.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=DloSGrkFtYA
What is drainage?
Drainage is a system that removes excess moisture from a building using a pipe structure. There is an opinion that to effectively collect water, only a blind area is enough, but experts in this field recommend installing a full-fledged drainage system, which allows for much better protection of the building from the harmful effects of moisture.
No matter how beautiful the blind area is, it will not completely protect the house from moisture. Source pinterest.at
A drainage system for a home can be of three types:
- Open. It is a structure where open type trenches are used as drainage drains, the depth and width of which is 0.5 meters. This is the easiest drainage option for self-installation. The disadvantages of such a system include the unaesthetic appearance, as well as the unreliability of the structure, which will require additional reinforcement of the walls with special trays;
- Backfill. This is a structure where prepared trenches are filled with coarse crushed stone or rubble, and turf is laid on top. The advantage of such drainage is its long service life and ease of installation. In addition to the advantages, there are also disadvantages: low throughput, inability to carry out maintenance;
- Closed. This is done by laying drainage pipes with holes in the ground. This system is efficient and does not have the disadvantages of other systems. Its disadvantage is that the installation is quite complicated.
A closed drainage system is difficult to do correctly without certain skills and knowledge. Source handmaster.ru
In what cases is wall drainage necessary?
Wall drainage must be installed in the following cases:
- If the level of hepatitis B is high.
- The amount of precipitation in the region is high.
- The basement and basement rooms of the house are used for household purposes. needs.
- If the ground floor is located below the hot water level on the site.
- Floors in the basement are no higher than 0.5 m above the level of hot water.
- If the soil on the site is loam or clay, the level of hot water is not taken into account.
- The house is located in a place of capillary penetration of moisture with unacceptable humidity in the premises.
But in some cases, wall drainage of the foundation is not enough. Then they make a layer on top of the system along the perimeter of the house with an angle of inclination of 20, and a width of at least 1 m. The soil with which the drainage system is filled is compacted, and a waterproofing layer of bitumen-based materials is applied to the foundation from the outside.
You should not install a drainage system near the foundation if the house is built on sandy soil, when hot water easily penetrates into the lower layers, and in winter freezing occurs at least 80 cm. In this case, it is enough to coat the foundation with protective compounds, and the moisture will not harm the structure.
Causes of excess humidity
If the building is located in a lowland on unstable soils, its foundation constantly interacts with water. The paths of moisture penetration can be different:
- in the absence or improper installation of a stormwater system, water collects during precipitation;
- melt water runoff in the spring increases the risk of flooding in low-lying areas;
- high level of underground water horizon, especially during periods of oversaturation of the soil with moisture.
These factors seriously affect the integrity of structures and reduce living comfort.
Construction of base and grooves
Option 2. Scheme of a wall drainage system.
The first stage is the construction of a sand base. Here you will need sand, a laser level, gravel, a large geotextile fabric and a shovel for digging ditches. First, we level the area around the foundation slab, after which we fill it with sand about 20 cm. The sand needs to be wetted and lightly compacted, then, if necessary, topped up and leveled again.
After this, take a laser level and use it to measure the height fluctuations along the entire length of the future drainage system. Then mark the points where the system slopes using the same level. Place pegs in the designated places.
Now you need to lay geotextiles on top of the sand. Cut out pieces of the canvas of the required size in advance and lay them on the sand, pressing it there.
Option 3. Wall drainage scheme.
Geotextiles must be overlapped. Place gravel on top of it. The height of the gravel layer should be such that small grooves can be made in it, where pipes will be deepened to remove moisture (if the drainage is linear). In the case of reservoir drainage, the gravel layer should be slightly larger.
Now, in the places where the pipeline for pumping water will be laid, make a groove. The pipe should fit easily into it, but not be completely buried.
This is an important condition for the entire drainage system. The length of the groove should be equal to the length of the system from the top to the bottom drainage point.
Necessity and purpose
Drainage is an event that helps:
- maintain landscape design intact;
- extend the life of the house and ancillary buildings;
- effectively combat the forces of frost heaving;
- avoid the occurrence of pockets of moss, mold and musty smell;
- grow any crops you like, not just those accustomed to extreme humidity.
Drainage is necessary for any gardeners, vegetable gardeners and just real estate developers. Even if there are no subjective signs of excessive moisture, they may appear suddenly after construction or removal of part of the soil, when digging a well, and so on. You can even do the necessary work yourself. Moreover, as practice shows, self-drainage is no worse than professional solutions. It actively uses modern materials and methods to eliminate excess dampness.
In addition, this measure allows you to avoid the floating of septic tanks, stabilize the operation of the sewer system, and make the use of the site more comfortable. Walking on constantly wet ground is difficult and unpleasant; you have to spend time cleaning your shoes.
Drainage structures are required:
- on flat areas with no natural drainage;
- in the lowlands;
- in the presence of a pronounced slope;
- when normal plants are replaced by moisture-loving crops;
- on clay soils and loams, which almost do not allow rain and melt water to go deeper.
Installation of wall foundation drainage around the house
Before you begin installing a near-house drainage system, you need to decide on its type, which depends on several parameters:
- types of soil;
- whether the building has a ground floor or basement;
- the origin of the water that needs to be drained.
The wall-mounted underground option is used in the presence of a base, high groundwater level and loamy and clayey soils. If it is necessary to protect the foundation of the house only from precipitation, then a surface system will be sufficient.
To protect a house located on sandy or sandy loamy soils with water and without a basement, ring (trench) drainage is used.
Having decided on the type of drainage, you can begin drawing up a diagram, designing the system and planning all the work. This stage allows you to eliminate all possible shortcomings, which are then expensive to correct.
For the plan, you need to decide on the lowest point on the site for installing a drainage well, which will be connected to the general ring of the system by a pipe.
We assemble an air dehumidifier with our own hands: diagram and principle of operation.
It is better to draw the diagram on graph paper or in a special program. The drawing should show:
- house, as well as adjacent buildings;
- trees and shrubs;
- places where drains pass, depending on the type of drainage chosen;
- inspection and drainage wells.
Inspection tanks are installed at the point where the pipe turns, for example, in the corners of the house, or every 30 m for a straight section of the pipe.
The plan should also record the depth of the pipes. This indicator depends not only on the bottom slab of the foundation and the height of the floor, but also on the level of soil freezing. Pipes must go deeper than the point of zero winter ground temperatures
It is important to write down the diameter of the drains, which affects the width of the trench, and the required slope
It is better to entrust design to specialists. But you can purchase the necessary material and install the drainage system based on a competent plan yourself.
Valuable tips and tricks
If you follow the rules listed below, there will be much fewer problems with the functioning of the drainage system.
- Drainage pipes are installed along the lower border of the foundation base. The permissible step up/down is from 0.3 m to 0.5 m. If you lower the drains lower, groundwater and rainwater will systematically wash away the soil from under the foundation, which can lead to subsidence of the building.
- If it is not possible to protect the foundation with a geomembrane, you will have to build a clay castle.
- The level of accumulation of drainage water (drain zone) must be below the level of the finished floor in the basement or cellar.
- Backfilling with river sand is more effective than backfilling with “native” soil.
Considering the dynamic movement of groundwater, be sure to secure geotextiles when installing the pipeline. It should cover the filter “roll” tightly, without gaps.
A properly equipped drainage system lasts 20-30 years, so after installation is complete, you can begin choosing a method for landscaping the local area. One of the popular options is a flower garden
To more effectively remove excess moisture, along with wall drainage, a drainage system and a storm drain are installed - underground or external.
The process of constructing a ring drainage
Sand is poured into the bottom of the trench
To make it easier to create drainage for the foundation, you can make markings. For this purpose, various pegs are used, which can be easily removed.
You can arrange ring drainage as follows:
- At a distance of 5 m from the house, you need to dig a deep ditch larger than the height and width of the house foundation in order to fit a pipe with a diameter of 11 cm. There should still be 10 cm indentations from the pipe on each side.
- Sand in a layer of up to 100 mm is placed at the bottom with a slope towards the reservoir. This way the water can drain on its own.
- The drainage pipe is placed in the trench, on geotextiles, its ends are fixed to the walls of the ditch. The pipe is laid in a trench, covered with gravel to a depth of 50 cm, then wrapped in material twice. The seams of the structure are fastened and covered with sand or gravel.
- The pipes are connected, but not at a right angle, so that silt does not accumulate.
- To construct an inspection well, a hole is dug and a container with a hole for water drainage is placed. Here you also need to place geotextiles on the bottom to prevent pebbles from getting in.
- If the soil is heavy and does not allow water to pass through well, a solid pipe can be used for drainage.
- If there is a large accumulation of water in the reservoir, it can be pumped out and watered for garden plants.
Preparatory work
Before laying drainage, dig around the foundation of the house.
Proper drainage of the foundation of the house will help protect the structure from dampness. This work can be done comprehensively in several stages:
- At the very beginning, the base needs to be dug up, and the excess soil carefully placed nearby for reuse.
- If the house is not new, the soil is carefully cleaned from the tiled structures and the old waterproofing is removed.
- The base is thoroughly dried in open air; during wet weather, gas burners can be used for this purpose.
- Waterproofing the foundation.
Main types of drainage for foundations
Drainage systems can be divided into vertical, horizontal and combined. Vertical drainage is mainly used in mines or swimming pools. Such a system is equipped with pumps and special drainage wells for pumping out water. When the water drops, meter-long wells are made in the basement of the building and pumps with alarm floats are installed.
A horizontal drainage system is a horizontal pipe system. It can be open or closed. The system is divided into three parts: collecting, drainage and water receiving. Open horizontal drainage is often used to drain large areas, for example on farms. For private homes and industry, closed drainage is used. You can often find a combined type of drainage.
So, drainage for the foundations of a house involves the creation of a special drainage system of channels for underground or surface water. The construction of a drainage system largely depends on the groundwater level, the topography of the site and the magnitude of the surface slope relative to the horizontal plane.
Consequences of the absence of a foundation drainage system
What entails constant or periodic flooding.
- In basements, underground garages and basement rooms, mold forms and fungus develops, an unpleasant smell of mustiness and dampness is concentrated, which cannot be overcome by the installed ventilation.
- The supporting base is washed away and the sand and gravel cushion is silted.
- Moisture penetrates into the thickness of the concrete and when it freezes, it breaks the structure.
- If water penetrates the metal reinforcement elements, it will cause their corrosion, and, therefore, an increase in volume. This process will lead to the formation of cracks and breaks in concrete monoliths.
The result of moisture penetration is the gradual destruction of the foundation, subsidence of the house, and the formation of cracks in wall and ceiling structures. Gradually, housing becomes completely unsuitable for use.
House foundation drainage
If the groundwater level is high, the foundation must be protected not only by careful waterproofing, but also by a well-designed drainage system. Only the combination of these measures will allow the structure to be maintained in its design condition without destruction.
Which system to choose
The foundation drainage of a house can have a different structure depending on the type of soil, the amount of groundwater and the depth of the structure.
Wall foundation drainage
Such a system is necessary when laying a deep foundation with a high groundwater level. It is often installed to prevent flooding even at normal groundwater levels to protect against intense precipitation.
The wall drainage system can consist of 2 parts:
- Foundation wall protection;
- Interlayer drainage, arranged under the foundation cushion, is necessary for voluminous and saturated groundwater layers.
The device for protecting the outer wall of a load-bearing structure is carried out on all soils except sandy ones - they themselves conduct liquid well into the lower layers of soil.
The wall system includes a complex of waterproofing walls and laying drainage pipes with inspection wells. Excess liquid is collected in the pipeline and removed at the disposal site into a sewer, reservoir, site for reuse, etc.
Ring drainage
The method of installation is similar to the wall one, but differs in location: the ring system drains the entire perimeter, incl. areas adjacent to the house. It is placed at a distance of 1.5...3.0 meters from the foundation, which is convenient when laying it after the construction of the building.
Ring drainage is optimally chosen for shallow foundations without a basement.
Interlayer drainage
It is often arranged as an independent protection of the foundation from saturated aquifers that the structure reaches. Interlayer drainage additionally prevents the walls from getting wet by capillary moisture. Its arrangement is possible only at the stage of preparing the foundation for the foundation.
The system is used mainly for slab foundations. It involves compacting the soil with large sand and gravel using drainage pipes located under the foundation.
To clearly determine which type of drainage is suitable for a particular home, use the table:
Any system is necessarily accompanied by waterproofing of the external surfaces of the foundation and the arrangement of a blind area with a slope along the entire perimeter of the building - it partially drains the water coming from above.
Calculation of system and materials
Proper foundation drainage begins with calculations of the drainage system and materials.
- The depth of the pipe in the trench should be 0.3...0.5 meters greater (deeper) than the foundation cushion. This reserve is sufficient to remove excess soil fluid from the supporting structure.
- The slope of the pipeline must be at least 2 cm per 1 pm of drainage for the natural removal of water from structures to their destinations.
To organize drainage on the perimeter, you need to find the highest and lowest points.
- A water collection well is located high;
- A receiving well is installed in the low one, from which it is discharged into a collector well for further transportation.
To calculate the amount of materials, follow several rules:
- Draw a diagram of the house indicating the sides. Draw on the plan the proposed drainage water line, taking into account the distance from the wall (up to 0.5 m for a wall outlet, 1.5...3.0 m for a ring outlet).
- For every meter, add 2 cm to the slope. If the length of the plot is 10 meters, we get 20 cm of slope from the top to the bottom point.
- Mark the position of the inspection wells. They should be located in the corners of the house or at every second turn, but at a distance in a straight line no more than 40 m from each other.
- Based on the data obtained, calculate the required number of pipes and wells.
- Provide couplings for turns, and separate special components for pipe connections.
Pipe selection
The efficiency of the entire system depends on the quality of the selected materials. Pipes made of ceramics and asbestos cement are currently practically not used due to their low efficiency; preference is given to PVC and HDPE pipes. For drainage, use products with perforations and filters:
It is optimal to use pipes with stiffeners to maintain the shape of water pipelines even under intense soil loads.
The variety of pipes and filters in stores will confuse any uninformed buyer. How not to make a mistake when choosing? – rely on the type of soil.
Calculation of a special drainage structure
When we have stocked up with all the necessary materials, we begin to calculate the special drainage structure
our site. We will need to calculate the depth of laying pipes and wells and the ideal pipeline slopes.
In most cases, foundation drainage
placed 0.3-0.5 m below the support structure. Pipes should be installed at such a slope so that water from them quickly reaches the collector - in most cases this is 20 mm, for any linear meter.
You should find the highest and lowest points of the site. In the top (basically the highest corner of the building) we will place a place where water is concentrated, and in the other we will place a well for reception. Likewise, we will create a natural slope, which will free us from the need to purchase additional pumps.
What tools do we need?
2 shovels - a scoop and a bayonet, a pick, a hammer drill and a wheelbarrow for removing earth and bringing in crushed stone.
Is wall drainage needed around the foundation of a house?
Many developers decide to build a house with a basement. The cost of building a basement is comparable to the cost of building a regular floor.
Only non-residential, auxiliary premises can be located in the basement - laundry, gym, sauna, boiler room, workshop, storage room, etc. All these rooms could be located on a regular floor or attic with better comfort and convenience.
In the recent past, it was customary to build houses on deep strip foundations. The construction of a basement in such a house was indeed beneficial - the foundation served as the outer walls of the basement premises.
The use of lightweight structures and shallow foundations in modern low-rise construction makes it unprofitable to install a basement in a house.
However, lovers of tradition and solidity often choose a house with a basement on a deep strip foundation. To comfortably use the premises in the basement, the basement must be protected from ground moisture.
Types of foundations. What does the choice depend on?
There are different types of foundations:
- slab, in the form of a solid reinforced concrete slab with a thickness of 40 cm or more;
- columnar, in the form of separate supports that are located under the walls or columns of the building;
- pile;
- tape, in the form of a monolithic or prefabricated “wall”.
The choice of a specific type of foundation depends on various factors, namely:
- soil composition and characteristics;
- groundwater level;
- dimensions and weight of the building;
- availability of certain materials and technologies;
- cost of materials.
For example, it is preferable to build heavy buildings on soft soils on slab, strip or pile foundations, while small light houses can be built on columnar foundations.
Since up to a quarter of the cost of a private low-rise building can be the cost of the foundation, it is quite understandable to want to save on its construction, but without compromising quality and strength.
Therefore, in private construction, when a low-rise building (house, summer house, bathhouse) is being erected, preference is often given to a strip foundation. It is more economical to manufacture than slab, but it is quite reliable, durable, and also allows you to create a basement in the house. This is a very practical option, because the basement or basement can be used not only as a storage room, but also as a technical floor, where a home theater or gym, laundry room, or workshop can be located.
The strip foundation can be made of concrete or reinforced concrete, blocks, bricks. The strongest and most durable is a reinforced concrete monolithic foundation, the service life of which is up to 200 years.
It can be done independently.
Any foundation is always buried in the ground to one depth or another.
Depending on the type of soil, groundwater level, and depth of soil freezing, the following types of foundations are distinguished according to their depth:
- Non-buried strip foundation . Such a foundation is practically not deepened; a trench is dug to the height of the sand cushion.
- A shallow foundation is buried to a depth less than the depth of soil freezing. In the case where the groundwater level is below the depth of soil freezing in the region, and the soils are predominantly clay or loam, you can deepen the foundation at the level of half the depth of soil freezing (data on the depth of soil freezing, as well as the depth of the foundation, depending on the type of soil, can be viewed in tables).
- When the groundwater level is higher than the freezing depth of the soil, a buried foundation is required. It is laid to a depth of 10–20 cm lower than the freezing depth of the soil. On peat bogs, as well as on swampy soils, the foundation can be deepened even further (the depth of the trench is selected to the hard layers of the soil).
Important!
The depth of the foundation is the distance from the base of the foundation to the surface of the soil. The depth of the trench is the sum of the depth of the foundation and the height of the sand cushion.
The depth of the foundation is regulated by the Code of Rules SP 22.13330.211 “Foundations of buildings and structures” (SNiP 2.02.01-83).
Reservoir method of water drainage
Drainage under the foundation slab is necessary to ensure that the properties of the structure are maintained when in contact with water. This means removing water and preventing its effects on the foundation of the house. For more information about drainage work on the site, watch this video:
Drainage under the foundation slab can be done in various ways. One of the popular ones is the layer type. Its essence is as follows:
- A ditch is dug 1 m deep than the size of the building.
- A slight slope is established from the center to the sides.
- Geotextiles are laid, then a 10 cm layer of sand and a 30 cm layer of crushed stone are alternated to level the bottom of the pit.
What is a blind area and why is it needed?
The blind area is part of the waterproofing of the foundation; a waterproof path built around the perimeter of the house and having a slight slope to the side of the building to drain water. Its function is to prevent water dripping from the roof from entering the ground. Thus, the blind area protects the soil around the house from getting wet.
That is why it is important to perform the blind area immediately after the construction of the building.
In addition to the main one (water drainage from the building), the blind area also has additional functions:
- gives the building a finished, neat look;
- protects the foundation from splashes of water and dirt;
- insulates the basement part of the foundation;
- acts as a walking path around the house.
The most common material for blind areas is concrete.
Stages of constructing a concrete blind area:
- The boundaries of the future blind area are marked. Usually its width is at least 90–100 cm. Moreover, it should be at least 20 cm wider than the overhang of the roof eaves. The thickness ranges from 7 to 12 cm.
- The top layer of soil and all plant debris are removed.
- The formwork is installed from boards so that its top is 80–100 mm above the soil level.
- Leveling layers of sand and crushed stone (gravel) with separating layers of geotextile are poured onto the bottom. This cushion is necessary not only to remove water from the top layer of soil, but also to evenly distribute the load from the concrete, as well as the weight of people who will move along the blind area.
- For insulation, extruded polystyrene foam 100 mm thick is laid.
- A film for cut-off waterproofing is laid on top (for example, CEMMIX PowerBarrier 500 microns). The film is placed on the facade wall 10 cm above the level of the future blind area. This is necessary to ensure that water does not leave the concrete mixture during the entire concrete hardening stage.
- To prevent the formation of cracks and increase strength, the blind area is reinforced with a frame made of metal or composite reinforcement. The reinforcement should be positioned so that the protective layer of concrete is at least 20 mm on each side of the blind area.
- Concrete is laid, maintaining a slope to the sides from the walls of 3–5 cm per linear meter.
- On the blind area, transverse expansion joints are installed in increments of 2–2.5 m. For this, boards of 15 or 20 are used. After the concrete has hardened, the boards are removed. Expansion joints, as well as the joints where the blind area adjoins the rear walls, are subsequently filled with high-strength polyurethane sealant (ClearFixa).
- In order for concrete to harden under optimal conditions, a canopy must be installed over the blind area to protect it from direct sunlight.
- 2–3 hours after laying, cover the concrete with rags, pour water from a watering can and cover with film. Concrete is moistened within 1–2 days after laying.
What kind of concrete is used to make a blind area
Concrete for blind areas must have increased characteristics in terms of density, water resistance, and frost resistance. These characteristics are interrelated, because the denser the concrete, the fewer pores it contains, the less it absorbs water and freezes.
For the blind area, it is recommended to use concrete with a strength class of at least B15. To prepare a cube of such a concrete mixture you need:
- cement CEM I/II 42.5 (M500 according to the old marking) - 280 kg;
- clean sand of medium fractions - 730 kg;
- crushed stone - 1250 kg.
Wall foundation drainage
Wall foundation drainage is designed to remove water from the foundation of the house, which will protect the foundation from destruction. The drainage system is installed around the perimeter of the house. There are two ways to drain groundwater from a house:
- Open,
- Closed.
The open method allows you to collect and drain rainwater. But it is of little use for draining groundwater. Especially if trays or sawn halves of large pipes are laid at the bottom of such a ditch surrounding the house. For foundation drainage, deep ditches are required, below the level to which the foundation is buried. And leaving such ditches open is not entirely safe.
Therefore, the drainage for the foundation is closed.
Foundation drainage diagram: simple and clear
The foundation drainage scheme should take into account:
- Distance of the pipe from the foundation. It should be no more than the thickness of the foundation.
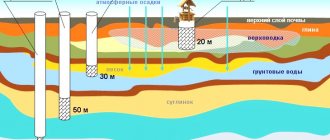
- The depth of the pipe. Consequently, the depth of the trench. The drainage system should be located below the foundation level. In addition, the depth of the pipes should take into account the depth of soil freezing. The pipes are laid 50 cm below this mark.
- Presence (absence) of a drain pipeline;
- Location of inspection wells.
And since the process of digging a ditch for drainage is labor-intensive, it is advisable to install the foundation drainage simultaneously with the construction of the foundation itself, or immediately after it. The drainage pipe is laid with a slight slope (2-5 cm of slope per meter of pipe is enough) so that the water accumulated in it flows out in a given direction. The wall drainage system of the foundation should be located below the foundation itself, regardless of the type chosen: strip, slab or pile. Geotextiles are laid in the trench. This porous material acts as a filter. It is needed to prevent sand and small fractions contained in the soil from getting into the pipe. Gravel 15-20mm in size is poured on top of the textile. A smaller one will block the holes in the pipe. The pipe is laid on the crushed stone. And the top is covered with crushed stone, which is covered with the edges of geotextile.
The degree of its perforation depends on humidity. The construction market offers pipes
- with full perforation, when the holes are located along the entire perimeter of the pipe at an angle of 60 degrees and in a checkerboard pattern, along the length of the holes are located at a distance of 10-20 cm.
- With partial perforation, providing for the presence of 3 holes only on the upper half of the pipe, also at an angle of 60° and at a distance of 10-20 cm.
Important note. Under no circumstances should the drainage pipe serve as a storm drain; rain gutters from the roof of the house cannot be connected to it.
The reason lies in the perforation of the drainage pipe.
Geotextiles. This porous material acts as a filter for drainage
When the drainage system overflows, drainage water flows from the pipe into the ground, which leads to an increased moisture content in it.
But blind drainage pipes can be laid next to the perforated ones, or above them, in the second tier. This will prevent you from digging unnecessary ditches.
In the corners of the house, inspection wells should be provided into which pipes enter. Nowadays, drainage inspection wells made of plastic are purchased on the construction market along with pipes and geotextile.
Selection of materials for creating drainage
The selection of the necessary equipment and materials depends on the selected type of drainage for the site. For wall or ring applications, gratings and trays are widely used; for surface or deep applications, geotextiles are used.
Regardless of the drainage system used, the main elements for it are pipes and wells. The first perform the tasks of removing and concentrating water flows. The second ones are based on accumulation.
The general list of equipment and materials consists of the following elements:
- trays;
- sand traps;
- pipes;
- geotextiles;
- wells;
- consumable and connecting components: couplings, rings, plugs, cuffs.
Trays
They serve to direct water flows and remove moisture from the soil. When creating drainage, trays are selected based on their throughput, which depends on the material used and dimensions. Calculations are made during the preparation of the project based on data on the condition of the site and the level of water inflow.
Trays with a galvanized steel grid can withstand a water flow of up to one and a half tons. Trays with cast iron grates have increased stability - up to 25 tons. The main materials used in the manufacture of drainage trays:
- Cink Steel;
- cast iron;
- plastic;
- concrete;
- polymer concrete;
- reinforced concrete.
An addition to the trays is a filter system: sand traps, grates for collecting debris, siphon partitions.
Sand traps
When creating several types of drainage systems at the same time, it is necessary to install sand traps.
Connecting drainage systems is possible when each of them performs different tasks: wall drainage - draining water from the roof of the house, deep drainage - removing excess moisture from the ground.
Sand traps prevent blockages from occurring during the final stages of water removal. Sediments of heavy mineral particles remain in the pipes if the system is not equipped with sand traps. The accumulation of sediment leads to a decrease in pipe capacity and a subsequent decrease in water output volumes, which leads to flooding.
Pipes
Like gutters, drainage pipes direct water flow to outlet points. The throughput capacity depends on the diameter of the pipes; choose in the range of 75-200 mm. The service life of the pipes depends on the material used. The following materials and combinations are used:
- asbestos-cement;
- ceramic;
- polymer (high and low pressure);
- porous.
Water enters the pipes through drainage holes or pores on the surface. It would be correct to use pipes in conjunction with the geotextile covering of the area. Pipes are great for making your own site drainage on clay soils.
The pipes are laid with a slight slope - at least 2-3 mm per meter. Numerous additional elements are used to connect and install pipes: couplings, fittings. There are ways to install drainage without pipes.
Geotextiles
When installing deep drainage, the surface above the pipes is covered with geotextile. This layer helps strengthen the soil and also prevents the penetration of unwanted particles: grains of sand, silt, small pieces of soil.
The geotextile shell protects the drainage system from the formation of mold, fungi, and a favorable environment for insects and rodents. The material is made of polyester or polypropylene, and for drainage a fabric with a density of 150-300 g/m is used. Lower density means lower wear resistance, which will lead to partial disruption of the properties of the drainage system.
Wells
The place where excess water is sent is a drainage well. Two types of wells are used depending on the type of material:
- concrete;
- plastic or fiberglass.
Wells for drainage usually have a diameter of up to 1 meter and a depth of up to 6 meters, where the system pipes are discharged. 3 types of design are used:
- rotary - at the place where the pipe turns;
- absorption – underground without an external part;
- water intakes - for storing large volumes of water.
The choice of well depends on the remoteness of the water discharge site and the volume of drainage. Previously, concrete rings were common in the construction of wells, but they were replaced by lighter and easier-to-install plastic and fiberglass structures. The joint with the pipes is made at least 20 cm from the bottom - this protects against blockages due to settling at the specified height.
Next, we will consider in detail how to make drainage on the site with your own hands, step by step. Using examples of several types of systems: wall, ring and surface.
Wall foundation drainage according to SNiP
According to building codes, when installing wall drainage, the following rules must be followed:
- pipes are laid with a slope of 2 cm per meter in the direction of the collector or well;
- inspection wells are placed in increments of no more than 40 meters in a straight line and no more than 20 when turning a corner;
- drainage pipes must be immersed deeper than the freezing of the soil;
- ditch width from 25 cm to half a meter;
- with ring drainage, the system is removed from the walls of the house at a distance of one and a half to three meters;
- the distance from the pipe to underground electrical communications must be at least 15 cm (for a pipe with a cross-section of 5 cm).
The project also provides details:
- pipe section;
- filter material and type;
- soil type and characteristics;
- design capacity of the drainage system.
To install drainage near the foundation, you can use PVC, polypropylene, or low-density polyethylene pipes. There should be two perforated zones in the opposite walls of the pipe. The total perforation area is about a percent of the entire surface of the water pipeline. The solid walls of the pipe should look up and down, the perforated walls should look to the sides.
Filters are made from coconut fiber or geotextile. Their purpose is to protect perforated areas from the ingress of soil particles. Water pipes may already be equipped with filters or sold without them. If filters are not provided, the pipes are wrapped in several layers of geotextile before laying in the ditch. Fix the canvas with a nylon cord, plastic tape or other polymer material. Pipe sections are connected with polymer couplings and fittings.
Sometimes in wall drainage, polymer profiled membranes are used - this is the name of a polyethylene film, on which protrusions 8-20 mm high are made using hot molding technology. A two-layer membrane includes a geotextile layer, while a three-layer membrane also includes a smooth polyethylene film. The membrane is installed on the surface of the base after waterproofing, with the geotextile side facing the ground. This enhances waterproofing and improves drainage efficiency.
In places where pipes are laid, it is recommended to pre-lay thermal insulation material - this will make the thermal insulation of the base more effective and protect the pipes themselves from freezing and, accordingly, from ruptures. Pipes should be laid on top of a bed of sand, crushed stone, or gravel. There should also be 3-5 cm of this mixture on top: it will act as a filter layer and direct moisture from the surface to the drainage pipes.
At the last stage, a concrete blind area about half a meter wide is made. The edge of the blind area should be located further from the wall than the projection of the cornice.
In addition to SNiP, the installation of a drainage system is regulated by GOST 1839-80.
Rules and nuances of design
The choice of drainage type for a country house or the location of channels is influenced by many factors. For example, the terrain is of great importance. If the house is located on a hill, and the rest of the territory is located at a slight slope, then wall drainage is most likely not required, and groundwater can be drained from the site by creating a canal system.
The location of groundwater is important. Difficulties with installing buried objects may arise if the level is high enough - from 1.5 m in depth
With this arrangement, installation of a drainage structure is necessary both to ensure the protection of buildings and for the safe development of the soil layer
Difficulties with installing buried objects may arise if the level is high enough - from 1.5 m in depth. With this arrangement, installation of a drainage structure is necessary both to ensure the protection of buildings and for the safe development of the soil layer
The nature of the surrounding area should also be taken into account. If the area around the site is swampy or a river flows nearby, and the plot seems dry, then for preventive purposes it is also necessary to design a drainage system.
Let us consider in more detail the nuances that should also be taken into account when laying pipelines and trenches.
#1: Line depth and dimensions
The location of the pipes of a closed drainage system is chosen based on the design development, taking into account the slope towards the drainage basin. The depth of installation of system elements depends on the groundwater level. For a wall-mounted device, trenches are dug at the level of the foundation base, since its goal is to enhance the waterproofing qualities of the underground structure and protect the basement.
Pipes arranged in a ring pattern are located at a distance of up to 3 m from the foundation. The depth of the pipes is greater than that of the wall structure, and most often below the location of the foundation (+)
Ring drainage is chosen if the construction of the house has already been completed, and accordingly, all waterproofing and protective measures have been completed.
If the soil of the garden plot constantly suffers from flooding by precipitation or seepage of groundwater, systemic drainage is required throughout the entire territory. There are many options - from arranging a system around the perimeter to an extensive network that includes all dacha objects (buildings, road surfaces, garden plots).
The direction of canals and pipelines is strict - towards drainage structures or ditches located outside the territory of the personal plot. In this direction, drainage pipes are laid with a slope necessary for the free movement of groundwater collected by drains to the unloading objects.
#2: Slope standards for drainage pipes
Water in horizontally located pipes will stagnate if installation is carried out without a slope, the parameters of which are specified in regulatory documents.
For clay and sandy soil, which has different degrees of water permeability, the standards are different:
- loams and clay – from 0.003 or more;
- sand and sandy loam - from 0.002 or more.
If you convert the values into millimeters, you get 3 mm/linear. meter and 2 mm/linear. meter respectively.
The minimum parameters are taken taking into account the fact that the lowest speed of water movement through channels and pipes is 1.0 m/s. This is possible if the drains are in working condition, that is, not silted or clogged with sand.
When calculating the maximum possible speed, the properties of the surrounding soil, as well as the quality of the sprinkling, are taken into account. You cannot make a slope at intervals - it must be observed throughout the entire length of the pipeline/channel
For hilly areas, options for installing drainage with differences are possible, with the installation of adapters in inspection wells.
Drainage system
Work in dry weather
Water is removed from the foundation by organizing drainage around the house. Before implementing it, you need to know some features of the work:
- installation work is carried out in summer in dry, warm weather;
- to build a foundation drainage with your own hands, it will take 2 to 3 months;
- After preparing the ditches, it is advisable to build a canopy over them to protect from rain;
- if the soil is in a loose state, then the walls of the ditch must be thoroughly strengthened;
- from the appropriate authority you need to obtain information about the condition of the soil, as well as conduct a small experiment to determine where moisture is most collected;
- Having learned comprehensive information, you can draw a drainage diagram for the building, calculate how much material will be needed and the cost of the structure.
CemAqua
Waterproofing additive for concrete.
More details
To ensure the concrete characteristics necessary for the manufacture of a blind area, it is recommended to use special additives:
- Plasticizer CemBase. Provides high mobility of the concrete mixture, due to which the labor intensity of concrete laying work is reduced, the need for vibration treatment is eliminated, the concrete is more dense (and therefore has increased frost resistance and water resistance). The CemBase additive can reduce the water requirement of the concrete mixture, increase the strength of concrete, and save about 10–15% of cement without loss of strength (in this case, the savings from each cube of concrete will be 30–40 kg of cement). For a cubic meter of concrete mixture of strength class B15, 2.8 liters of CemBase additive will be required.
- Polypropylene or basalt fiber CEMMIX (reinforcing fiber). It is used as an addition to reinforcement to increase the strength, impact strength, durability of concrete, reduce shrinkage and abrasion (which is especially important since the blind area is used as a walking path). A cube of concrete requires 900 g of fiber.
- Hydrophobizing additive CemAqua. It is used for volumetric hydrophobization of concrete, as a result of which it acquires water- and dirt-repellent characteristics. At the same time, the air permeability of concrete is maintained and its thermal conductivity is reduced.
Important!
CEMMIX additives are easily mixed with the components of the concrete mixture, without forming lumps, and are evenly distributed in it. All CEMMIX additives are compatible with each other and with any types of domestic cements. If it is necessary to add a water repellent and a plasticizer at the same time, the total amount of additives is divided, for example, in the ratio of 30% plasticizer and 70% water repellent.
Without modern additives for concrete mixtures, it is difficult to achieve professional results. CEMMIX additives not only improve the quality of concrete, but also save cement. They are available for purchase wholesale and retail, directly from the manufacturer or in retail chains and online stores. You can select supplements, find out availability and cost, and purchase them here.
You can buy CEMMIX products without leaving your home, with discounts from 5 to 33%!!!!
Buy on Ozon
Buy on Yandex.Market
Buy on Wildberries
Buy at Leroy Merlin
Organization of waterproofing for different types of foundation
Arrangements for protecting a constructed building from moisture vary depending on the type of foundation. The most common types are slab, pile, column, strip and monolithic foundations.
Plates
Here it is best to wrap the foundation with rolled roofing felt. When any irregularities are detected.
They must be removed using a leveling screed.
Then a water-repellent material and insulation are placed on the concrete slabs and the surface is leveled again.
Pile and column types
It is not easy to waterproof concrete piles and pillars. It is provided by adding water-repellent additives to concrete. Wooden structures are treated with special liquids that prevent rotting and moisture absorption.
Strip and monolithic foundations
Most often, monolithic structures are insulated with hot bitumen mastic
To properly waterproof these types of foundations, the following several methods are used. They are varied and quite effective.
- Treat the foundation with a special mastic, only the surface must be dry and smooth. This method is not entirely reliable, so to strengthen the composition it is necessary to cover it with insulation or build a brick wall.
- Just as in the first case, you need to carry out all the manipulations using hot bitumen mastic, and stick roofing material on top in 2 layers with an overlap of about 15 cm.
- Using a special sprayer, a water-repellent composition is applied to the dry foundation. It is advisable to use geotextiles on top, then the waterproofing will last a long time.
- Another reliable and high-quality method is penetrating waterproofing. It contains quartz sand, cement and special additives. This mass has penetrating properties.
Features of waterproofing device
Be sure to waterproof the basement and basement
Before draining groundwater, it is necessary to waterproof the walls and floor of the basement, basement and foundation base. Here are some important points to consider:
- the coating used for these purposes must be complete without gaps or cracks;
- on the side that experiences greater moisture pressure, additional protection is applied with insulating material;
- It is necessary to have a blind area around the house, choose the correct width and degree of inclination. It will allow water to be removed from the building not only by drainage, but also by installing a storage pit. If there is a blind area, puddles will not form. It protects the foundation and soil from water penetration.
The blind area is important in protecting the building from moisture.
WHY ARE WELLS NEEDED?
At every 90° turn, inspection wells are installed (sometimes, to save money, they are made at every second corner).
On straight sections they are installed every 50 meters.
They are made from large diameter pipes. You can also find ready-made prefabricated wells on the market.
It is recommended to create a sludge collector at the bottom so that small particles that fall into the pipe can settle in it without clogging the pipe.
To do this, the drainage pipe is fixed at a level of 20 cm above the bottom of the well.
When there is quite a lot of sludge, it is removed with a special pump. The pump is lowered into the well, then, after agitating the water at the bottom with a pressure jet, it is turned on.
What forces destroy the foundation?
Moisture in contact with a concrete strip causes a number of destructive processes:
- Erosion of the sand cushion, which results in subsidence and damage to the integrity of the foundation.
- Water soaks into concrete and destroys it from the inside in winter.
- When the temperature drops, the moisture in the soil layers surrounding the tape freezes, expands and begins to put pressure on the base or foundation walls (frost heaving of the soil).
Most often, these factors act simultaneously, which increases the danger to the foundation and the entire house. The waterproofing gradually fails, the insulation peels off, exacerbating the destruction process and changing the microclimate in the house for the worse.
The situation is dangerous, since all processes proceed slowly and secretly, the results become noticeable only when destruction, cracks and other signs of failure of the foundation appear.
Features of drainage arrangement in areas with a slope
Experts believe that in areas with a slope of no more than 8°, drainage is arranged in the same way as in areas with normal terrain. If the slope is more than 8°, the arrangement is carried out taking into account special requirements.
Sloping areas are characterized by a heterogeneous soil structure. If in one part of the territory groundwater lies deep, then in another it can come close to the surface. At the same time, geological surveys are carried out. They provide information about the structure of soils and the location of the aquifer. This data is necessary when designing drainage.
The purpose of the drainage system on a site with a slope is to effectively drain the area. To do this, it is necessary to solve the following problems:
lowering the groundwater level throughout the entire territory to the required value (below the depth of freezing, depth of the foundation and root systems of plants on the site); safe collection and removal of surface moisture during rains and snowmelt
It is important that water does not flow throughout the entire area, washing out the soil. Instead, it is sent to the storm drain, organizing the flow through gutters and drains; drainage of water from the lowest point of the site. To prevent moisture from accumulating in the lower part of the territory, it is collected in a collector well and diverted to the nearest water intake
Another option is to build an artificial reservoir to collect moisture or collect water for use for irrigation.
To prevent moisture from accumulating in the lower part of the territory, it is collected in a collector well and diverted to the nearest water intake. Another option is to build an artificial reservoir to collect moisture or collect water for use for irrigation.
To solve the above problems, complex work is carried out: using buried open or closed drainage, storm sewerage, and local water collection structures. Specific solutions are selected individually: according to the characteristics of the site, the level of soil moisture, requirements for drainage of the territory, and the expected cost of work on arranging the drainage system.
Step-by-step instructions for carrying out work
Whatever foundation does not require protection, installation is carried out according to a certain algorithm, taking into account the implementation of basic operations.
Preparatory work
To do this, you need to carry out work taking into account certain rules and in a certain sequence:
- The foundation is excavated along the perimeter of the building, which needs to be cleared of old waterproofing. The width of the trench must exceed the diameter of the pipes by at least 200 mm. The slope angle to the main well should not exceed 80. A slight expansion is made at the corners to install a rotary well;
- Now you need to dry the blocks using a hair dryer or heat gun. When working in summer, it can be left to dry for several hours;
- After the surfaces have dried, a layer of waterproofing is applied. The best solution would be to use bitumen mastic.
Different foundations require different preparation schemes. For a house on a shallow foundation, you will need to make a trench no deeper than the main blocks. Wells will be installed at the corners of the building to contain water containers.
If groundwater is close and the house is built on a pile foundation, you will need to dig a trench at a distance of at least 3 meters from the piles, sand and gravel filling is made at the bottom. Gravel can be replaced with waste bricks. After compacting the backfill, you can begin the main stage of work.
To protect the strip foundation, you will need to dig a trench deeper than the base of the building. Then the work is carried out in the same way. This protection will prevent water from seeping into the foundation. In any case, before filling the trench with sand and gravel, geotextiles are laid, and then a cushion is made for the perforated pipes.
Completion of the main stage of work
In order to protect the foundation, you need reliable and high-quality drainage. Therefore, work should be taken responsibly. When dehumidifying a house with your own hands, you should prepare tools and materials for work. For this you will need:
- a certain number of special drainage pipes with a diameter of no more than 300 mm.
Their number depends on the size of the private house. Such products are produced from various materials, with full and partial perforation. Advice! Finished pipes will require significant costs. This problem can be solved by purchasing simple PVC pipes and drilling holes in them according to the pattern. - If desired, you can use broken bricks left after construction or ready-made crushed stone.
- sand for pillows;
- To make an absorption well, you can use a simple barrel, preferably a plastic one. It is better to use a large barrel, but this will require digging a larger hole;
- you will need to purchase wells to make pipeline turns;
- clamps for pipeline installation;
- geotextile fabric.
Do-it-yourself foundation drainage takes place in several stages:
- Drainage pipes are mounted on the made layer of geotextile and sand and gravel cushion. They are fastened together with special copper clamps.
- Rotary wells are installed at the corners of turns. With their help, pipes will be cleared of blockages in the future;
- the pipeline must then be led to a large absorption well. Its height is at least 700 mm, but this value depends on the barrel purchased. Geotextiles are laid along the entire perimeter of the prepared pit, then backfilling is done and the barrel is mounted. First, holes should be drilled in the walls in increments of about 80 mm. In the barrel, according to the markings, a hole should be made for the drainage pipe;
- the pipeline is finally mounted to the rotary wells and led to the absorption device;
- Carefully fill the pipeline and the gaps between the walls of the wells with a mixture of sand and crushed stone. Filling should be done so that the geotextile panels are securely connected to each other with large overlaps.
- Then the following work scheme is used. Having wrapped the sheets of material, we lay plant branches on top of it. They will serve as protection against breakage when digging a trench and will increase the rigidity of the structure;
- We completely fill the trenches and voids between the walls of the wells with soil.
Now you need to install a water pump in the absorption well. It is used to pump out water. This completes the process of installing a drainage system for the house. For greater clarity on how to make a security system with your own hands, you can watch videos on the Internet.
Where to send excess water
In the autumn or spring period of the year, the earth is oversaturated with moisture and has considerable weight. As a result, the pressure on your foundation increases significantly. The foundation is also affected by the constant alternation of frost and thaw. Water, with its properties, penetrates into the smallest cracks, increasing and eroding them in size. This can be prevented by organizing proper drainage.
In this situation, it is better to turn to professionals who will design a drainage system for you, but the price for the services provided will be high. If you have the necessary materials, then you will be able to carry out the drainage yourself
It is important to know that the water you drain should not accumulate in one place on the site or paths. It is best if she leaves your area