GOST Cast iron pipes contains the necessary requirements, subject to which it is possible to manufacture high-quality elements for the construction of pipelines. To ensure their protection against corrosion, they are coated with petroleum bitumen on the outside and inside. As a result of processing, the inner surface of the cast iron pipe becomes smooth. The requirements for such products depend on the casting method and are described in our article.
GOST 6942-98 is a document regulating the requirements for most cast iron pipes
Specifications
Official publication
INTERSTATE SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNICAL COMMISSION FOR STANDARDIZATION, TECHNICAL REGULATION AND CERTIFICATION IN CONSTRUCTION (INTKS)
Moscow
Preface
1 DEVELOPED by the Scientific Research Institute of Sanitary Engineering (NIIsantekhniki) of the Russian Federation
INTRODUCED by the State Construction Committee of Russia
2 ADOPTED by the Interstate Scientific and Technical Commission for Standardization, Technical Regulation and Certification in Construction (MNTKS) on November 12, 1998.
Voted for acceptance
| State name | Name of the state construction management body |
| Republic of Armenia | Ministry of Urban Development of the Republic of Armenia |
| The Republic of Kazakhstan | Committee on Housing and Construction Policy under the Ministry of Energy, Industry and Trade of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
| Republic of Kyrgyzstan | State Inspectorate for Architecture and Construction under the Government of the Kyrgyz Republic |
| The Republic of Moldova | Ministry of Territorial Development, Construction and Communal Services of the Republic of Moldova |
| Russian Federation | Gosstroy of Russia |
| The Republic of Tajikistan | State Construction Committee of the Republic of Tajikistan |
3 INSTEAD OF GOST 6942.0-80 — GOST 6942.24-80, GOST 4.227-83.
4 ENTERED INTO EFFECT on January 1, 1999 as a state standard of the Russian Federation by Decree of the State Construction Committee of Russia dated December 31, 1998 No. 31.
This standard cannot be fully or partially reproduced, replicated and distributed as an official publication on the territory of the Russian Federation without permission from the Gosstroy of Russia
ISBN 5-88111-166-4 © Gosstroy of Russia, State Unitary Enterprise TsPP, 1999
Content
1 Scope………………………………………………………………………..1
2 Normative references……………………………………………………………………………….1
3 Assortment……………………………………………………………………………………….2
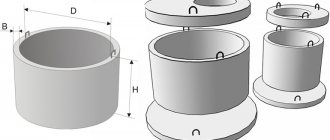
4 Types, designs and sizes……………………………………………………….6
5 Technical requirements…………………………………………………………………………………36
6 Acceptance rules…………………………………………………………………………………..38
7 Control methods………………………………………………………………………………………39
8 Transportation and storage……………………………………………………….41
9 Installation and operating instructions………………………………………………………..42
10 Manufacturer's guarantees……………………………………………………………….42
INTERSTATE STANDARD
CAST IRON SEWER PIPES AND FITTINGS FOR THEM
Specifications
CAST IRON WASTE PIPES AND FITTINGS Specifications
Date of introduction 1999-01-01
Quality of cast iron pipes
Certificate for pipes
When supplying pipes made of cast iron, as well as fittings for connecting them, a certificate must be included, which specifies:
- manufacturer (official name),
- customer (official name),
- batch number and standard number,
- name of the product, its dimensions (in the case of pipes - footage, weight, quantity),
- test pressure and data obtained during mechanical testing.
An example of a certificate of conformity of cast iron pipes to GOST requirements
Scope of application
Application of pipes made of cast iron
Areas of application of cast iron pipes:
- construction of sewer systems;
- construction of pressure pipelines;
- construction of heat supply systems;
- during installation of oil pipelines;
- in fire-fighting water supply systems;
- when creating pipelines for the chemical and mining industries.
The wide range of applications is due to the long list of product advantages. Let's consider the advantages of cast iron pipes compared to plastic counterparts:
- higher strength;
- increased wear resistance;
- lower noise level;
- increased fire safety;
- increased stability when temperature changes;
- lower susceptibility to stretching.
Couplings and other elements of standard 6942 and their parameters
If damage occurs to a small section of the pipeline (no more than three meters), it is not advisable to completely replace the pipe or cut it off. In this case, it is better to continue the train with a new section. When performing repair work on an existing pipeline, a slip-on coupling is used.
Couplings are used as connecting elements during installation and repair of highways
Since it does not have internal partitions, it can be moved around the product. This reduces the repair period and also speeds up the commissioning of communications. The sliding coupling is applicable when mounting shaped elements into a pipeline structure.
The coupling parameters according to GOST 6942 are given in the table.
Table 15
Symbolic passage in cm
| Weight without anti-corrosion coating, kg | |
| 5 | 1,3 |
| 10 | 2,7 |
| 15 | 5,0 |
Slip-on couplings have the parameters provided in the table. Linear dimensions are given in centimeters.
Table 16
Conditional pass
| Distance between sockets | Weight, kg | |
| 5 | 8 | 1,8 |
| 10 | 10 | 3,8 |
| 15 | 12 | 6,2 |
A cast iron plug is used to cut off part of the pipeline in the event of a malfunction or termination of further use. With its help, you can block the flow of water or other working medium. The plug is a circle with several holes to provide fastening. The selection of the required product is made taking into account the pipe diameter, material and operating pressure. Rubber plugs can also be used for cast iron pipes.
If a sewer branch is planned in the future, then it makes sense to immediately install a tee and close the temporarily unused hole with a plug
Audits provide access to the sewerage pipeline for cleaning. The design of the cast iron revision is bell-shaped. The main difference is the diameter and dimensions.
Thus, according to the document GOST 6942-98, a cast iron sewer pipe is the most reliable and durable for wastewater disposal systems. The advantages and relevance of their use are determined by their resistance to various hydraulic pressures, temperature changes, loads and environmental safety.
11 months ago
Posted in Do it yourselfTagged 6942-98, anti-corrosion coating, GOST, sewer, pipe, cast iron
Cast iron making
Fluxes, ores, and fuel are used to make cast iron .
Iron ores
They are the main type of raw material and contain chemical compounds of oxygen and iron. In addition, they contain empty alumina, oxides of magnesium and calcium. But the latter compounds have little effect on the value of the ore; the sample that has a higher iron content is suitable for processing. A nugget of ore may also contain harmful impurities that reduce the value of the nugget, such as phosphorus and sulfur. Red and brown iron ore are mined in Russia.
Fuel
As a heat source, coke is used, obtained from coking coal by heating in furnaces at a temperature of 1000–1150ºС without the supply of fresh air. Coke is an important component in the smelting of cast iron.
Fluxes
They are used as raw materials in the smelting of cast iron. The role of these mineral substances is to lower the melting temperature of waste rocks and release harmful substances from the alloy in the form of slag.
Fuel, ore and fluxes, combined together in certain quantities, make up the so-called charge. The size of the pieces is required 0t 2 to 4 cm, so large pieces are crushed, and small pieces are pressed to the desired size. Ore nuggets with low iron content are subjected to preliminary preparation for smelting by enrichment. This allows you to lower the melting point, improve the quality of cast iron and reduce fuel consumption.
Blast furnaces
They are a round shaft-type furnace. It is placed in a solid metal case, 2–3 cm thick at the bottom and 3.5–5 cm at the top . The inside of the furnace is lined with clay refractory bricks. The furnace design includes a shaft, a flue, a hearth, shoulders and steam.
The process of processing ore in a blast furnace involves the reduction of iron oxides, which occurs when gases are released from the combustion of coke and the lowering of the charge. The formation of iron occurs from oxides during the removal of moisture and the process of decomposition of carbonates. Under blast furnace conditions, iron is completely reduced and enriched with oxygen.
With the constant combustion of coke in a shaft furnace, manganese, silicon, sulfur and phosphorus are reduced. The carbon increase occurs to a level of 4.5% . This enriched iron alloy is called cast iron. Then it is poured into a receiving ladle and goes to the ingots for filling, or goes to the production workshop to fill molds.
Types of cast iron
According to the intended purpose, the resulting cast iron is divided into foundry, conversion and special. More than 85% of the melted material is white cast iron, which is characterized by increased hardness and brittleness. It is used to produce steel.
Gray (casting) cast iron has a high silicon content and is used for the manufacture of numerous parts. Its variety is alloyed natural cast iron, smelted from ores containing chromium, vanadium, nickel and other components. This type of cast iron is used for structural purposes . Cast iron pipes for sewer pipelines are made from this type of alloy.
Special cast irons are used for alloying steels. They contain large amounts of two minor components.
Pipe manufacturing
The production of cast iron products involves the use of one of the proposed methods: casting using the method of pouring into a sand mold; method of centrifugal continuous casting in molds and casting intermittently; de Lavaux centrifugal casting method.
Modern cast iron pipes for laying communications have a gradation of diameters, ranging from 50 mm to 1200 mm . The smallest wall thickness is 1 cm. The length of pipes ready for sale starts from 2 m and ends at 7 m, depending on the diameter of the product.
The dimensions of cast iron pipes are determined using the value of the nominal (internal) diameter of the product. The inner diameter is called Dy, and the outer diameter is called Dout. A very large number of pipes with internal diameters from 5 to 40 cm are characterized by a high strength index. They are produced with smooth edges and a length of 3m. Detachable shaped elements are produced in lengths from 150 cm to 3 m .
Despite the emergence of modern new materials for sewer lines, cast iron pipes are still in demand due to their strength and long service life. A cast iron pipeline can serve for many years; an indispensable condition for this is compliance with installation technology and choosing the right products.
Pros and cons of products
The disadvantages of cast iron pipes and connectors for them include their impressive weight, which requires the use of great effort when laying sewer pipes.
One of the bad qualities of cast iron pipes is their impressive weight, which is why transportation and installation often require the involvement of equipment.
The process of connecting such communications is also highly labor-intensive. Installation requires more time than a similar process with products made from other materials.
You need to pay attention! The installation of urban sewerage networks often requires the use of specialized equipment so that assembly work is carried out in full compliance with the rules and regulations.
However, cast iron products have many good qualities. They have quite significant strength due to the properties of casting and alloy. Reliable operation is guaranteed for more than one year. The shortest service life of such communications is 40 years, the highest is 80-100 years.
Neither sudden temperature changes nor very high temperatures deteriorate the parameters of cast iron pipes. The anti-corrosion coating protects products well from the aggressive effects of drains, rust formation and plaque. They have high fire safety and a relatively low price.
Characteristics of crosses
When installing communication systems, it is important to consider the pipe branching factor. Using a cross for these purposes allows you to save space and use the material most efficiently. Branching occurs in two planes. Document 6942 contains the characteristics of the crosspieces. The angle between the primary and secondary axis is 87° 30′ with a tolerance of 1° 30′.
Note! The mass of straight crosses with an offset axis of removal is 7.6 kg. The axis shifts by 25 mm.
The characteristics of oblique crosses at 60° with a permissible deviation of 1° 30′ are given in the table. Linear dimensions are given in centimeters.
Table 13
| Conditional passage: main/branches | 5/5 | 10/5,0 | 10/10 | 15/5 | 15/10 |
| Distance from branch point to socket | 6,2 | 8 | 11,0 | 9,2 | 12,2 |
| Distance from branch point to shank | 10,8 | 9,5 | 12,5 | 8 | 10,8 |
| Distance from branch point to outlet socket | 6,2 | 9 | 11,0 | 12,0 | 13,5 |
| Weight without anti-corrosion coating, kg | 3,0 | 5,8 | 5,8 | 7,0 | 10,0 |
The characteristics of oblique crosses at 45° with a permissible deviation of 1° 30′ are given in the table. Linear dimensions are given in centimeters.
Table 14
| Conditional passage: main/branches | 5/5 | 10/5,0 | 10/10 | 15/5 | 15/10 |
| Distance from branch point to socket | 9,0 | 11,5 | 15 | 14,0 | 18,0 |
| Distance from branch point to shank | 10 | 7,5 | 11 | 8,5 | 8,5 |
| Distance from branch point to outlet socket | 9,0 | 12,5 | 15 | 16,0 | 18,8 |
| Weight without anti-corrosion coating, kg | 4,0 | 6,9 | 10,5 | 7,3 | 10,5 |
Two-plane crosses according to GOST 6942 are available in left and right versions.
Pipeline requirements
Pipes for sewer lines and fittings for them are manufactured strictly in accordance with the requirements of GOST; special requirements for quality and installation method are prescribed in the work project and technological maps for the operation of the facility. Design documentation is approved in accordance with the established procedure.
Pipe compliance with technical specifications
In the manufacture of cast iron products and fittings, defects should not be allowed that would reduce the operational and installation qualities of the pipeline. These include slag layers on the internal and external surfaces, metal drops and build-ups, and bays. When laying in the installation position, minor defects, which are regulated by a special GOST, can be corrected on site.
Chill on the outer surface of cast iron pipes and shaped accessories should not exceed a depth of 1 mm , and from the smooth ends on the outside and at the end, the distance to the first defect should not be less than 6 cm. Chill on casting connectors is allowed to be no more than 2 mm deep.
The difference in the dimensions of the design value and the actual value is allowed no more than 2 mm on the larger and smaller sides, with regard to the diameter of the pipes. The length of manufactured products may differ from the nominal size by no more than 0.9% in both directions.
Changes in the thickness of smooth pipe ends are only permitted up to 2 mm over a distance of 15 mm. The same thickening is allowed on the shanks of the bells with a section of no more than 7 cm in length. In this case, it is allowed to reduce the internal diameter of the pipe in the defective area by 2 mm.
Permissible deviations from nominal values are strictly regulated and are indicated in the materials and paragraphs of GOST 2645, which corresponds to an accuracy class of 11 t .
Deviations in terms of the mass of finished products are included in the tables presented in the provisions of GOST 26645, and dimensional differences are also stated here. All calculations are made using the accepted density of cast iron of 7.1 g per cubic centimeter. Finished cast products having a mass greater than the nominal value are allowed for installation in the pipeline if all other control characteristics are within acceptable values.
The straightness of pipes with a diameter of 100 mm is considered acceptable if the deviation does not exceed 2 mm in a section 1 m long. For pipes with a diameter of 50 mm, this control indicator is increased to 5 mm.
After installation in the installation position, securing the pipes, sealing the sockets and applying an anti-corrosion layer to them, the pipelines must withstand a hydraulic pressure of at least 0.1 atmosphere or 1 KGS per square centimeter. Due to their high quality characteristics, sewer pipes made of cast iron alloy are used in various facilities with heavy loads:
- in large production workshops;
- at enterprises of the food and processing industry;
- in hospital and health centers;
- in educational institutions;
- in industrial and non-industrial laboratory complexes.
Compliance with the quality of components, materials and raw materials
All components of the sewer main are made of gray cast iron in accordance with the requirements of GOST 1422; individual parameters for the manufacture of cast products are specified in the provisions of GOST 26338.
Surfaces inside and outside the pipe must be treated with a bitumen-based anti-corrosion coating in accordance with the provisions of GOST 9542 and technical specifications. It is allowed to use insulating materials that soften at a temperature not lower than 60ºC and have high resistance to heating. The operating conditions of the anti-corrosion coating are specified in paragraphs of GOST 15250. The anti-corrosion coating layer should not have interruptions, cracks or bubbles; continuous, durable waterproofing, smooth, without defective areas, is allowed for use.
Imprints from supporting structures during the manufacture and rolling of pipes are allowed on external walls. Imprints and marks from hanging hooks of container chains are allowed on the surface of fittings and sockets. Drips of waterproofing are allowed when excess drains from sockets and fittings.
Each cast iron product bears a marking cast or written with indelible paint , which contains the information:
- name and trademark of the product manufacturer;
- designation of the brand and parameters of the product according to GOST;
- indication of this standard provision.
For transportation and transportation, pipes are packaged in containers. Sometimes it is allowed to form products into bags, bundles and cassettes, followed by tying them with wire. When laying, the direction of the sockets is provided in opposite directions alternately. To complete cast iron products, the rules of GOST 25598 are provided. Shipment of empty or half-filled containers is not allowed.
Transport for transporting pipes is used of any lifting type. Transportation rules are selected in accordance with the standards that are defined for this type of machine.
They are stored in special warehouses, divided in accordance with the nominal diameter indicators. Shaped parts are stored in groups according to types and sizes, under conditions under which mechanical damage is impossible. The batch is assembled for shipment to the buyer in accordance with the wishes of the customer and in accordance with the technical characteristics of the highway facility under construction.
Requirements for inspection acceptance
To facilitate acceptance, a batch of pipes and other cast iron products is checked and documented in one document. This name usually defines the number of fashion products produced during one work shift at the enterprise.
Inspection of pipes and other cast iron products according to GOST requirements and technical specifications consists of conducting periodic tests and acceptance of castings at least once a quarter. Acceptance measures are allowed during inspection:
- the presence of chill on the surface is allowed in half of the inspected products of the batch;
- identification of build-ups, slag deposits and defects in the anti-corrosion coating is checked for all 100% of products in the batch;
- The compliance of the material of the waterproofing layer with the standard and its stickiness is checked for 2% of the products in the batch.
Pipes and fittings are subjected to periodic testing if the cast iron products have passed the tests of the acceptance commission. At this stage, the cast iron parts are checked for the softening limit of the anti-corrosion layer and the strength of its adhesion to the surface of the pipe. The buyer has the right to conduct a control check of the product for any of the quality indicators.
If acceptance reveals at least one discrepancy in any indicator, then double the number of iron castings from the proposed batch is checked. Repeated rejection leads to the fact that the entire batch is checked individually with a thorough check of the indicators for which a negative result was obtained.
Good to know
Humanity has been familiar with pipes since ancient times. They were once made from wood and clay. Later, about 3 thousand years BC, bronze pipelines appeared. The first mentions of cast iron pipes date back to the 15th century. They radically resolved the issues of water supply and wastewater disposal. The most famous cast-iron water supply was laid during the time of Louis XIV from a pumping station located on the Seine to the Castle of Versailles. It was 15 miles long and supplied water to the royal fountains for over 300 years. In the 17th century, cast iron pipes began to be used in Russia.
Trench for pipeline
The main advantage of cast iron is its sound insulation. The walls of the pipes perfectly absorb any sound vibrations, but due to their massiveness they increase the weight of the products. This affects the labor intensity and complexity of installation work and is their main disadvantage.
There is no specific data on the service life of cast iron pipes. Many claim that they can be used for at least 50 years. But only if the installation was carried out in compliance with all requirements and standards without the application of deforming forces. Otherwise, cast iron products will begin to crack and collapse too quickly. High-quality and competent installation, as well as proper operation, will lead to the fact that the internal sewer network or external pipeline will serve for decades, being in excellent condition.
Ordinary cast iron is not suitable for aggressive and high-temperature environments. In these cases, it can be replaced by ceramics and steel. But for domestic wastewater, laying sewers from steel pipes will be too expensive an option, so using them in this case does not make sense.
To seal the joints of bell-shaped pipes (chasing), it is recommended to use a heel - a rope made of plant fibers, impregnated with resin-bitumen mastics or oil and antiseptic solutions prepared using special technologies. And only then the joint is covered with cement mortar. Without a heel, the cement will quickly crack and inevitable leaks will appear.
When dismantling pipes, butt joints filled with sulfur are heated with a blowtorch, a gas torch, or a more modern tool - a hair dryer. In this case, work must be carried out in a gas mask or respirator. Otherwise, fumes can lead to poisoning and even respiratory paralysis.
Sequence of installation work
General rules for laying pipelines
It is carried out according to the general rules applied in all sewer lines. When transporting and laying using lifting mechanisms, gentle gripping devices that do not damage the anti-corrosion coating of the top layer. Individual pipes or sections of the main line assembled together are rearranged.
All stages of intermediate and permanent activities must be reflected daily in the work log, indicating the volume produced, compliance with design requirements, the depth of laying the next section and the option for strengthening the trench walls.
When installing the design slope of a free-flow sewer cast iron pipeline, pipes with sockets are laid along the trench with the wide part up. Carrying out a straight section between two wells, perform a visual inspection of the light using a mirror. This check is done before the soil is completely backfilled , and the gap should be round in shape. A horizontal deviation of no more than 50 mm in each direction is allowed. Vertical deviations are not permitted.
Deviation from the design axis of external pressure mains in plan is allowed, which cannot be more than 100 mm. Markings of free-flow trays do not have a height deviation of more than 50 mm. These requirements are standardized for all types of sewer routes, and if requirements other than those in GOST are provided, they are specified in the technical passport for the facility.
The pipeline is laid along a curved line, the joining of the sockets is carried out only with the installation of rubber gaskets. For mains made of pipes with a diameter of up to 600 mm, it is allowed to turn the pipe only by 2º. Pipes with a diameter of more than 600 mm are allowed to be rotated only 1º.
When connecting, cast iron pipes are centered so that the straight tail of the pipe entering the socket forms a gap equal around the perimeter, which must subsequently be sealed with cement mortar. Rubber seals must comply with the quality stated in GOST; in winter conditions, they are defrosted before being installed in the working position.
Joint sealants and sealants are those developed in technical documents and specified in the project. The flange connection must comply with several rules:
- flanges are installed perpendicular to the design center line;
- with a flange connection, the heads of all bolts are placed on one side of the connecting plates, they are gradually tightened according to the principle of a cross;
- installation of spacers to level verticality and grinding of edges is not allowed;
- connecting planes are checked before installation, but uniformity and curves are rejected and not installed;
- Connection of nearby sections of the pipeline is carried out only after tightening the flange connection.
If a trench wall is used for additional support, they try not to disturb its solidity with digging. If reinforced concrete supports are used for installation, then the gaps between them and the cast iron pipe are sealed with cement-sand mortar. Work completed and then hidden under the surface layer of soil must be documented with special documents. Drawing up an act for hidden work is carried out in the following cases:
- works on preparation and construction of the foundation;
- installation of supports made of reinforced concrete and other materials;
- if gaps in butt joints were eliminated, then the method of sealing and the use of seals are indicated;
- wells for any purpose were built or installed;
- implementation of anti-corrosion protection of individual areas;
- waterproofing was carried out at the intersections of the pipe with the walls of wells or other sewer connections.
Laying cast iron pipes with socket joints
The straight part of the pipe is inserted into the socket of the previous one. The gap formed at the junction is sealed with tow and cement-sand mortar in the standard case. The tow is driven tightly into the gap using non-metallic tools to preserve the intact surface of the cast iron pipe. Instead of cement mortar, it is allowed to use special modern sealants, which are regulated by special GOSTs.
To make fixed-degree turns, special shaped parts made of cast iron, crosses, bends at different angles and tees are used, made of a material of the same composition as the pipes themselves. In modern docking options, elastic seals are installed, which ensure reliable docking and tightness of the connection.
Installation of cast iron pipes without socket
In recent years, cast iron pipes have gained popularity, which are made without expanding the end part - the socket. They are joined using separate clamps made of stainless steel.
The connection of cast iron pipes is made end-to-end. The clamp is delivered to the site complete with a rubber ring, which has the ability to withstand aggressive chemical irritants and in this case retains its insulating properties.
The connection is covered with a cuff around the perimeter, and then a steel clamp is installed, tightened with a bolt and nut until it stops. If the design of the sewer system involves pumping wastewater under high pressure, additional requirements are imposed on the connection point. To increase strength, another crimp casing is installed on top of these materials. The convenience of connecting in this modern way is that it can be easily disconnected and returned to its working position during repair work.
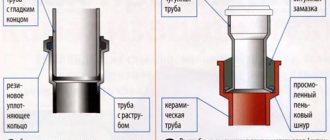
Device for connecting a cast iron pipe to a plastic one
Sometimes it is necessary to connect two different materials together in a sewer line. To make the connection, the socket of the cast iron pipe must be cleaned, then dried with a rag . A rubber cuff is placed in the socket and its edges are treated with insulating silicone. After installing the plastic pipe, the connection is additionally insulated with sealant.
If a cast iron pipe that does not have a socket at the end is to be connected, then an adapter is put on the end of it, and the end of the plastic pipe is placed through the gaskets. For a more reliable connection, silicone is used.
How to lay a pipe under a road using the puncture method
Often the sewer line encounters an artificial barrier in its path in the form of a highway or railway tracks. To make a pass from below the obstacle, use the horizontal puncture method . Modern methods use an efficient drilling unit that is equipped with advanced control methods.
The puncture is carried out with a drill head. A special device is installed on it, emitting rays and transmitting a correction signal to a locator installed at the opposite end of the planned pipeline. The coordinator sees the entire process of passing the route under an obstacle on the display, interfering with the operation of the drill if necessary.
Then the process of expanding the trench occurs with the cutting blades of a special tool. Typically its width is one quarter larger than the cross-section of the pipeline being laid. Then comes the automated process of laying pipes. Calculate the required length of the pipes and place them at the entrance to the trench. A hinged device is connected to them, which moves forward with a translational movement to the opposite end of the puncture and pulls the pipes along with it.
Dismantling and disassembly of cast iron sewer line and connections
This work is classified as difficult, since it is sometimes not possible to disassemble the joint between two cast iron elements without breaking it. Over time, the joining planes and seams become overgrown with lime salts, and the weight of the products is quite large. For disassembly, it is recommended to use a large mallet-type hammer, a grinder saw and other tools that are at hand.
In accordance with safety requirements, work on dismantling cast iron sewers is carried out wearing safety glasses and a respirator to protect the respiratory system.
If there is no need to keep the remains of the sewer intact, then it is better to break them up in random order and throw them away. If you are replacing only a certain section, you should try to leave the sockets of the sewer pipes intact, since with their help it is much easier to connect other parts of cast iron pipes.
Replacing a cast iron sewer riser in an apartment
First of all, you need to remain careful in your work so that pieces of broken pipes do not fall into the working risers and blockages do not build up around them. Therefore, you should tap the joints with a mallet, trying to knock out the cement mortar and remove the tow. If the seams have been cleared of mortar and sealant, then try to pull the end of the pipe out of the joint using circular rotational movements.
The work will require a lot of patience, as this process cannot be rushed . They combine tapping with a mallet and, from time to time, performing rotation. Sometimes, in order to preserve the socket of the common riser in the house, they cut the apartment section of the pipe and take it out in parts along with the mortar and sealant. Most often, plastic is installed in place of a broken cast iron pipe.
If during the dismantling process a crack appears on a cast iron pipe that is still needed for operation, then the place is sealed with rubber gaskets and crimped with a casing. It is much less effective to use a bandage made of cement-sand mortar and gauze or other fabric on site.
Pipe sizes
A pipe is a shaped element of a cast iron pipeline, which is necessary to change the type of connection. This part is used to compare systems made of different materials.
To connect cast iron pipes, pipes are used, which are available in a variety of shapes and sizes.
GOST distinguishes between transition and compensation pipes. They are used in sewage systems for fecal and household wastewater in public, industrial and residential buildings.
Note! The compensation pipe is used when it is necessary to connect several sewage systems that differ in their structure.
The dimensions of the pipes according to document 6942-98 are given in the table. Linear dimensions are given in centimeters.
Table 7
| Conditional pass | Weight without anti-corrosion coating, kg | Construction length |
| 5,0 | 2,0 | 25 |
| 2,5 | 35 | |
| 2,8 | 40 | |
| 10,0 | 3,8 | 20 |
| 4,4 | 25 | |
| 5,7 | 35 | |
| 15,0 | 8,8 | 40 |
A special feature of the expansion pipe is the elongated socket. The parameters of such a pipe according to GOST 6942 must correspond to the table. Linear dimensions are given in centimeters.
Table 8
| Conditional pass | Weight without anti-corrosion coating, kg | Shank length | Bell length |
| 10 | 4,5 | 8 | 13 |
| 10 | 8,4 | 8 | 37 |
| 15 | 6,5 | 8 | 13 |
| 15 | 12,8 | 8 | 38 |
The linear dimensions (in centimeters) and weight of the cast iron adapter pipe are given in the table.
Table 9
| Conditional pass | Weight without anti-corrosion coating in kg | |
| Dy | dy | |
| 10,0 | 5 | 1,85 |
| 15,0 | 10 | 3,2 |
Expanders and indents: their parameters
Expanders are used to rotate the pipeline during its installation. No communication system can do without them. GOST distinguishes expanders for 110°, 120°, 135° and 150°. Their parameters are given in the table. Linear dimensions are given in centimeters.
Instrument tees are made in left and right versions. Their weight according to document 6942-98 is 7 kg.
Cast iron indentation is used in non-pressure sewer networks for the removal of waste and fecal waters. It connects to the pipes thanks to a socket connection.
You need to pay attention! The indentation has good technical and operational parameters, low price and long service life.
Such a connection element as a drain can be found in virtually every sewerage system
The characteristics of cast iron indents standard 6942-98 are shown in the table. Linear dimensions are given in centimeters.
Table 11
Conditional pass
| Weight without anti-corrosion coating, kg | Bend radius | Length to flare | |
| 5 | 2,1 | 6,0 | 21 |
| 10 | 5,0 | 8,5 | 25 |
| 15 | 8,0 | 9,0 | 25 |