Have you ever wondered what storm sewer networks are like? What minimum requirements and SNiP must be taken into account and observed during installation. About everything in order in this article.
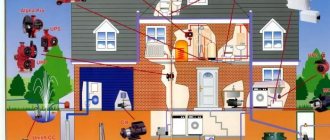
Rain or melt water requires organized disposal to pre-planned discharge points. Otherwise, areas of private households will turn into a kind of swamp, and runoff from industrial sites will begin to poison the soil around enterprises. To solve these problems, storm sewer networks are created that operate according to their own rules and regulations. A well-equipped system preserves the foundations of buildings from premature destruction and prevents erosion of the local area.
What is storm drainage
Storm sewerage is an extensive engineering system that ensures the removal of rain or snowmelt runoff. The purpose of the network differs from household systems in the absence of large organic inclusions. However, wastewater contains large amounts of silt, sand and other solid particles. This specificity requires the creation of revision devices that allow the removal of accumulated layers. Otherwise, blockages will occur that will prevent the network from working normally.
Storm drainage in most cases is a gravity-flow system. This means that in order to independently move wastewater, it is necessary to provide a certain angle of inclination of the trays or pipelines. The slope of the storm drain depends on the size of the conductive channels and is determined by the requirements of SNiP.
The drainage network includes:
- external channels (trays, gutters);
- sand filters;
- inspection and rain wells;
- collectors;
- sewer pipes.
Each of these elements can only function as part of a common system. Grids are used to cut off large objects (branches, debris and other debris). You cannot leave the receiving elements without them - they will quickly become the basis for a dense blockage of silt and sand, which is extremely difficult to clean.
Rainwater drainage via other networks
Private real estate projects traditionally include other communication networks along with storm drainage. Domestic sewerage and drainage systems are also part of household communications. The principle of their operation differs little from the functioning of storm drains, in which owners of private houses often see the possibility of using these networks.
Meanwhile, the combination of storm sewerage with a domestic or drainage drainage scheme is prohibited by SNiP. The ban on combining different types of sewage systems is due to obvious factors. Thus, provided that rainwater is discharged into the domestic sewer system and taking into account the high intensity of precipitation, the normal level of sewerage is increased several times.
Flooding of working wells leads to blockage of household and fecal wastewater. Mud deposits and natural debris flow into the domestic sewage system. As a result, after the next rainstorm, the organizers of the structure will have to clean the system.
Combining a stormwater system with a drainage main threatens to result in even more disastrous results. Overflow of drainage due to violation of design loads leads to flooding of the building foundation. Frequent flooding disrupts the structure of the soil, which causes displacement of foundation blocks, and in the future can lead to the destruction of the building.
Pipe immersion depth
A specific feature of storm networks is the depth of the storm sewer. The system operates unevenly, only during heavy precipitation or active snow melting. The rest of the time, the internal volume of the pipelines is empty. Therefore, the depth of the pipes may be small. In the cold season there is no water in them, there is nothing to freeze. This feature facilitates the construction of stormwater networks and reduces the volume of excavation work. The only task that arises when creating a storm drain is to ensure at least a minimum slope of the storm drain. As a rule, it is its value that becomes the main condition for immersing pipelines in the ground. To determine it, the SP has a corresponding table. In addition to the slope, it is also necessary to pay attention to the routes for laying networks. It is recommended to place them away from roads and other busy areas. Mechanical loads can destroy pipes, so you will have to bury them to great depths. The regulatory document that regulates the depth of installation of storm sewers, SNIP, allows for fairly wide limits for systems to be immersed in the ground. They are determined by various factors, mainly of a technical nature.
Experts' comments
“Not everyone can accurately calculate all the necessary parameters of a future sewer system. But this must be done. The more accurate the calculations are according to SNiP standards, the better the sewerage system itself will work. And there can be no trifles in this matter. Therefore, in case of difficulty, it is always better to seek help from specialists.”
Master installer of sewer systems,
Konstantin
“In order to be able to calculate all system parameters as accurately as possible in accordance with SNiP, the customer must provide the maximum possible amount of initial data. This can include indicators such as:
- information about geological work and surveys on the site;
- detailed site plan and site development plan;
- information about nearby bodies of water;
- climatic conditions of the area with information on the depth of soil freezing;
- average annual precipitation and maximum possible precipitation;
- as well as the customer’s wishes regarding spillway or water accumulation.
Of course, for a private owner of a small plot of land such detailed reporting will not be required, however, I repeat: the more initial data the contractor receives, the more accurate the calculations themselves will be.”
Designer of storm sewer systems,
Alexander.
In some cases, all design work and coordination of the project itself with the authorities are undertaken by the performing companies. Thus, the customer is freed from the need to calculate anything on his own, is insured against mistakes, and does not have to “knock out” offices in order to “knock out” this or that permit.
Sergey.
Types of storm drains
Storm networks are created in different design options:
- point;
- linear.
Point systems are individual wells that collect natural wastewater. The water from them is gradually absorbed into the soil, for which the base is made without a bottom, and an embankment of large crushed stone is formed in the lower part. The volume of the rain well should correspond to the amount of water falling to the ground during the heaviest and longest rainfall. Such systems are used in small private households where wastewater volumes are relatively small. In this case, the depth of the storm drain does not matter, since the wells are located close to the house. It is important to ensure that the trays or pipes are only tilted.
Linear networks are created in regions with high rainfall. They are designed to collect and drain moisture to discharge points - reservoirs, ravines, ditches along roads. The methodology for constructing such networks directly depends on the terrain. Sometimes, in addition to gravity lines, it is necessary to install pressure systems that use pumps to supply water from lower levels.
There are two main types of linear systems:
- open (external, superficial);
- closed (underground).
Open networks are considered economical and cheap. Their advantages:
- minimum amount of excavation work;
- cleaning trash trays is not difficult;
- repair work does not require time and effort.
The disadvantage of open systems is the need to allocate a certain area for them. According to the regulations, the security zone should be 5 meters on both sides of the axis of the tray. This interferes with landscaping and reduces the usable area of the site. It is more difficult to ensure a minimum slope of an external rainwater drainage system, since the starting point, due to terrain conditions, may be lower than the final point. Typically, open gutters are installed around the house to collect rain runoff from the roof. Then the water enters the collector, and from there it goes into the underground part of the system.
You may also like:
Storm sewer calculation: example and basic rules!
The sewer is frozen, what to do and how to warm the pipe!
Materials and internal structure
Important features of laying sewer pipes
- When installing a pipeline system in deep basements or in places with low relief, versions with an extremely low sewer installation depth are provided, in which the installation of a pumping station is provided. The depth of the pressure line must be calculated according to the requirements of regulatory documents.
- Practice has shown that in problem soils (water-saturated, compacted to strong and silty) communications should be laid to a depth of four meters, in dry soils the depth is determined from four to seven meters.
- Communications built with a depth of less than 0.7 meters must necessarily have a sewerage protection zone on the surface of the earth. The security zone is equipped with a system to protect against possible mechanical damage to the pipeline.
- When carrying out projects for laying sewer communications, it is mandatory to take into account the difference in terrain relief lines.
Basic Design Rules
When creating a project and calculating storm sewerage, we are guided by the following regulatory documents:
- SP 32.13330.2012 (adopted to replace SNiP 2.04.03-85);
- GOST 3634-99;
- SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00.
The project is created for the entire system at once. It is impossible to calculate it in parts, since the volumes of wastewater are different everywhere. Various influencing factors must be taken into account:
- analysis of wastewater volumes;
- the maximum possible amount of drainage during rain;
- land area;
- duration of flow of wastewater through the system (calculated value);
- relief features.
Based on the results of the analysis, the diameter of the pipelines or the size of the trays is calculated. It is necessary to take into account that the minimum diameter of storm sewer pipes must be 200 mm (SNiP). If concrete channels are used, the smallest size will be 300 mm. This option is expensive, inconvenient to install and is rare.
The depth of the storm drainage system is determined, the standards of which are regulated based on the operating conditions of stormwater systems in a given region. There are no direct requirements; all parameters are selected based on the characteristics of the soil, the amount of precipitation and the shape of the relief. It is not necessary to calculate the slope of storm sewer pipes yourself; the SP table contains ready-made values for the minimum and maximum values.
Individual slope calculation
Laying sewer pipes with your own hands in a private house is carried out according to the standards that appear in SNiP. But you can calculate the parameters for the arrangement of sewerage and water supply networks yourself. To do this, use the following formula:
- K is a special coefficient that takes into account the properties of the material that was used in the manufacture of the pipe;
- V – speed of passage of wastewater;
- H – pipe filling capacity (flow height);
- D – section (diameter) of the pipe.
The slope of sewer pipes can be calculated independently
- coefficient K, for pipes made of smooth materials (polymer or glass), should be equal to 0.5, for a metal pipeline - 0.6;
- indicator V (flow velocity) - for any pipeline is 0.7-1.0 m/s;
- H/D ratio - indicates the filling of the pipe, and should have a value from 0.3 to 0.6.
Internal and external sewer systems
When laying sewer and water supply networks in a private house, you should take into account some features that are determined by the location of their individual sections.
Internal systems
When installing sewer pipes in a private house, two diameters are mainly used - 50 mm and 110 mm. The first is for drainage, the second is for the toilet. The laying of the sewer pipe should be carried out in accordance with the following recommendations:
- turning the pipeline (if it is horizontal) should not be done at an angle of 90 degrees. To change the direction, it is better to install the bends at an angle of 45 degrees, this greatly facilitates the passage of the main flow and reduces the likelihood of accumulation of solid particles;
- in places where the system turns, fittings should be installed for inspection and ease of cleaning or dismantling in case of clogging;
- in short individual sections, it is permissible to increase the slope, exceeding the recommended norm. Such a short sewer branch can be a pipe connecting the toilet to the riser;
- in each individual section, the slope of the pipeline must be uniform, without sudden changes, because their presence can create conditions for the occurrence of a water hammer, the consequences of which will be the repair or dismantling of an already operating system.
External (external) systems
Proper laying and installation of sewer pipes is necessary not only inside, but also outside a private home, from the point of exit of the internal sewerage system to the septic tank.
Therefore, you should pay attention to the following points:
- laying of sewer networks is carried out in trenches with a depth of 0.5 to 0.7 meters. The depth of penetration depends on the characteristics of the soil and is adjusted to specific conditions;
- when preparing trenches, sand should be used at the bottom to be able to establish the correct slope by adding it;
- highlight the pre-calculated slope (per linear meter) as a guide from the cord stretched between the driven pegs. This will avoid unnecessary subsidence or elevation of the sewer system in certain areas;
- After laying the pipes at the bottom of the trench, check again for the correct slope and, if necessary, correct it using a sand cushion.
Installation procedure
Installation of storm drainage consists of several stages:
- drawing up a diagram;
- site marking;
- excavation;
- installation of wells and receiving tanks;
- laying pipes and connecting them to each other or to wells;
- backfilling trenches or cavities (for the open part of the system).
It is necessary to observe the calculated or tabulated values of all system parameters. For example, the minimum slope of a storm drain with a diameter of 200 mm should be 7 mm per 1 m of length. All the necessary indicators are included in the storm sewer project.
Design and production of storm water treatment facilities in Moscow
You can order modern treatment facilities for storm drains at industrial and private facilities. All materials used in the production process of equipment are of high quality and maximum reliability. Thanks to individual storm drain design, the system will be created specifically for your needs, but taking into account the requirements and existing sanitary and hygienic standards.
You can get answers to your questions by phone: +7 or send a request to us by email This email address is being protected from spambots. You must have JavaScript enabled to view..