With the advent of plastic products on the building materials market, their scope of application is gradually increasing. And most often people give preference to PVC pipes, using plastic structures in everyday life to furnish their apartments and houses. Namely, for the construction of energy and water supply systems, as well as heating, sewerage, and ventilation. Therefore, most potential consumers have a painfully pressing question: “What is the real shelf life of plastic pipes and what does it depend on?”
Technological process of welding PP
Welding polypropylene pipes is based on the ability of this type of plastic to soften when heated to a certain temperature, acquiring a state similar to soft plasticine.
When two molten parts come into close contact, a process of mutual penetration (diffusion) of materials occurs, resulting in a strong connection that is not inferior in durability to the entire structure. There are two main methods of connecting polypropylene pipes: butt and coupling. In the first option, the ends of the parts are heated simultaneously with a special disk soldering iron, after which they are joined together; this technology is widely used when joining large-diameter pipes in industrial construction.
When using polypropylene pipes of small diameters (up to 63 mm) in the construction industry for laying water supply and heating networks, the butt method is absolutely unsuitable for the following reasons:
- welding of polypropylene pipes of only one diameter can be realized;
- after joining, a convex seam is formed inside the pipeline, reducing the cross-section of the passage channel - this significantly increases the hydraulic resistance of a small-diameter pipeline and reduces the efficiency of its use, increasing the likelihood of blockages.
- the connection has less strength than a coupling connection.
Soldering technology using couplings consists of using a transition piece (a section of a conventional single-layer PP pipe) with an internal diameter corresponding to the outer diameter of the pipe sections being connected to join pipes. To carry out the work, a special soldering iron is used to simultaneously heat the outer surface of the pipe and the internal adapter coupling, after which the parts are quickly connected manually. A similar procedure with heating of the coupling and the outer pipe shell is carried out with the second section to be joined. It is clear that after insertion into the coupling, the ends of both pipe sections are almost connected end-to-end without a convex seam, and if you use an adapter with different diameters, you can join pipelines of any size.
Rice. 5 Soldering plastic pipes - technological process
Range of PVC products used in the installation of internal sewer networks
GOST 32412-2013 provides that the diameter of the sewer pipe can be in the range of internal dimensions from 32 to 315 mm. The corresponding range of wall thicknesses is respectively from 3.0 to 7.1 mm.
The range of horizontal dimensions of plastic pipes for sewerage is not regulated in terms of their values, and depends on their design - with straight ends, with a lead-in mounting chamfer of no less than 150 and no more than 450, or with a conical extension for a fitting. Maximum linear deviations along the length of sewer pipes cannot be more than ±10 mm.
Flared ends (can be parallel or conical) are available in the following options:
- With a cylindrical groove for installing a rubber sealing element;
- With a conical groove of the same purpose;
- With a lock for subsequent installation of the retaining cover;
- With dovetail profile groove;
- For subsequent connection using specialized glue.
The tables, which are located in GOST 32412-2013, help to choose the standard value of the sizes of the sockets. In particular, it is possible to reduce the wall thickness by 5%. The choice of design is determined by the limiting pressure that may arise during pipeline operation.
The following are used as shaped parts that are used in conjunction with sewer plumbing PVC pipes:
- Bends with straight, conical, combined or curved ends;
- Transition couplings;
- Pipes;
- Tees.
Expansion of the above range of fittings is allowed.
The assortment symbol consists of the name, indications of the material from which the product is made, the value of the external outer diameter of the pipeline and the smallest thickness of the pipe in its cross section. Marking can be done by thermal embossing or black printing. The distance between adjacent markings cannot be more than 1000 mm.
What is the service life of polypropylene pipes, what temperature can they withstand?
Polypropylene pipes have proven themselves well in heating systems. They have become a worthy replacement for metal heating pipelines.
The service life of polypropylene pipes is no less than the service life of metal ones.
PP pipes are not afraid of corrosion, are resistant to chemicals used in everyday life, and they are not destroyed when water freezes.
Therefore, polypropylene pipes can be used in heating systems for 25 years, and in cold water supply pipelines - about 50 years.
The strength and reliability of polypropylene water pipes is also ensured by the method of their connection. It is carried out by welding. This ensures solidity and strength. During operation, there is no need to constantly tighten connections, as is the case with metal pipelines.
What temperature can polypropylene pipes withstand?
Many people are still distrustful of polypropylene pipes in heating systems. Let's figure out what temperature they can withstand, what the service life of polypropylene pipes is and whether it is possible to use them for heating a house.
The material used to make pipes is obtained by polymerizing polypropylene with the participation of metal catalysts. Polypropylene softens at +140C, this material melts at a temperature of +175C.
It becomes obvious that prolonged exposure to high temperatures and excess pressure will lead to deformation of the pipeline.
Manufacturers guarantee the normal operation of polypropylene pipes in the heating system at temperatures up to +95C. But there is still a safety margin that allows a short-term increase in the temperature of the coolant to a temperature of +140C. But frequent temperature jumps to this value will lead to a reduction in the service life of the pipeline, although the pipeline itself will not melt.
When buying polypropylene pipes, you need to pay attention to their markings. For the cold water supply system, polypropylene pipes PN10 to PN25 are used
PN20 pipes can be used up to +60C, and PN25 can be used if the coolant temperature is up to +95C.
What pressure can different types of polypropylene pipes withstand?
Many buyers who decide to install a polypropylene pipeline for cold water supply or heating are interested in what pressure they can withstand. The service life of polypropylene pipes will depend on this. This question is very important. Since the pressure in the plumbing system or in the heating system, which polypropylene experiences throughout the entire period of its use, affects the service life of the product. If the pipeline has a constantly high temperature but low pressure (or vice versa), then the pipe will last quite a long time. But if the system has both high pressure and high temperature at the same time, the service life will be sharply reduced.
In order for the pipeline to serve the 50 years promised by the manufacturer, the pressure in the system must be 4-6 atmospheres, and the coolant temperature must not exceed 75 degrees.
Polypropylene pipes in the heating system
Polypropylene pipes are now a fairly popular material for installing heating systems. They are resistant to deformation, abrasion, and are characterized by low oxygen permeability. In addition, they can withstand sub-zero temperatures well and are not afraid of water freezing.
But, when choosing them, you need to consider the following points:
Polypropylene pipes are rigid and do not bend. To create contours or turns, you need to use corners, which is not always convenient. For polypropylene pipes, fittings are produced with a large cross-section when compared with fittings for other elements of the system, for example, radiators. This circumstance negatively affects the appearance of the system. Polypropylene stretches strongly when heated
If the system is made in an open way, then it looks unsightly due to sagging pipes. It is important not to overheat the pipes during installation, as the passage may be reduced when inserting pipes into the fittings. Such an installation error will lead to poor performance of the heating system.
It is not recommended to use polypropylene pipes when piping boilers. In boiler rooms, the temperature of the pipes often changes, and polypropylene is not a suitable material for such conditions.
If we take into account all the negative aspects described above, then polypropylene pipes for heating systems are a good option.
Effective operation time depending on category
The period of effective operation of PPR pipes is influenced by 3 indicators:
- working temperature;
- Nominal pressure category (PN);
- maximum permissible pressure (P).
Comparison table showing actual service life in relation to pressure and temperature:
| Service life, years | Temperature, degrees | P for PN10, MPa | P for PN16, MPa | P for PN20, MPa | P for PN25, MPa |
| 10 | 20 | 1,32 | 2,13 | 2,13 | 3,31 |
| 25 | 20 | 1,29 | 2,05 | 2,59 | 3,23 |
| 50 | 20 | 1,25 | 2,03 | 2,53 | 3,17 |
| 10 | 50 | 1,37 | 1,7 | 2,3 | 2,13 |
| 25 | 50 | 0,79 | 1,25 | 1,58 | 1,96 |
| 50 | 50 | 0,71 | 1,15 | 1,44 | 1,8 |
| 10 | 70 | 0,52 | 0,83 | 1,05 | 1,3 |
| 25 | 70 | 0,44 | 0,71 | 0,89 | 1,16 |
| 30 | 70 | 0,43 | 0,68 | 0,86 | 1,08 |
| 50 | 70 | 0,42 | 0,66 | 0,83 | 1,06 |
| 5 | 80 | 0,42 | 0,68 | 0,85 | 1,06 |
| 10 | 80 | 0,38 | 0,62 | 0,77 | 0,96 |
| 25 | 80 | 0,36 | 0,57 | 0,72 | 0,9 |
The period of effective use is also affected by the quality of installation and raw materials used for manufacturing. This must be taken into account when paying attention to the labeling.
What temperature can polypropylene pipes withstand?
To determine the purpose of a polypropylene pipe by appearance, there is a special marking. In addition to the manufacturer and brand name, the generally accepted classification is applied to the pipe.
- name of modification of polypropylene;
- standard proportional ratio;
- nominal outer diameter and wall thickness;
- nominal pressure;
- manufacturer's standards.
The maximum temperature of PP pipes is 95° C. This is perhaps the only drawback of polypropylene; it cannot withstand high temperatures. At 140° the material becomes soft and easily deforms, and at 175° it melts.
The temperature in heating systems is also not designed for such indicators, so PP pipes are quite suitable for use for heat pipes.
Short-term increases in temperature rarely lead to failure, but it is important to take into account that operating pipes at temperatures of 100° significantly reduces their service life. 50 years declared by the manufacturer can actually turn into a year and a half, because durability depends not only on its technical characteristics, but also on operating conditions
The 50 years declared by the manufacturer can actually turn into a year and a half, because durability depends not only on its technical characteristics, but also on operating conditions.
Duration and storage conditions of PPR products before use
The shelf life of polypropylene pipes before use is not standardized by GOST and is determined in accordance with the technical conditions developed in production.
In practice, it is at least 3 years from the date of manufacture. If storage and transportation conditions are violated, the period is reduced or terminated.
Recommendations for storage conditions:
- It is necessary to place it on a flat surface, without sharp protrusions and irregularities;
- Dumping from vehicles and loading points during unloading is prohibited;
- placement under a ventilated canopy in the open air (tents, storage rooms without thermal insulation) is allowed;
- pipe packages can be stored in stacks no more than 2 m high;
- products must be protected from exposure to ultraviolet and solar radiation;
- open and closed storage is allowed at air temperatures in the range from -50 to +50;
- relative air humidity according to the annual average - 75% at 15 degrees, upper - 100% at 25 degrees, absolute - 11 g-m-3;
- It is prohibited to store pipes at a distance of less than 1 m to heating devices;
- products must be protected from the accumulation of dust and dirt, the formation of mold fungi and the influence of microorganisms;
- long-term storage is allowed only in closed, dry and isolated premises;
- Long-term open storage without a canopy or insulation for more than 1 day is not allowed.
For products for which, in accordance with technical conditions, during storage and transportation through regions with cold climates, storage at temperatures below 50 degrees is allowed, a value of -60 degrees is accepted.
Loading and unloading of products at a temperature of -21 degrees is prohibited. When transporting in temperatures ranging from -11 to -20, it is necessary to take measures to prevent mechanical stress and freezing of products.
It is allowed to transport pipe packages during rail and road transportation only in rolling covered trains. Transportation in an open body or wagons is not allowed.
Nuances when soldering polypropylene pipes
Soldering propylene pipes requires certain skills and experience; when carrying out work, inexperienced installers should take into account some nuances:
- Polypropylene pipes reinforced with an internal aluminum shell require a slightly longer heating time, which can be determined experimentally by conducting experiments on joining short pieces.
- PP pipes reinforced with aluminum located under a thin outer polypropylene shell require preparation for soldering; it is necessary to remove this aluminum layer to the depth of connection with the fitting so that the foil does not interfere with soldering. To do this, use a special device for stripping - a shaver, produced in several versions: manual and for a drill. If you have to install aluminum-reinforced PP pipes in large volumes, it is better to purchase an attachment for a drill (screwdriver) - removing the aluminum layer when using it occurs faster and with higher quality than with a hammer drill model.
- If the aluminum reinforcement is located in the middle between the inner and outer pipe walls, experienced welders usually do not strip the pipe. But, if experience is not enough, then it is recommended to use trimmers for internal reinforcement - trimmers. Their design differs from the shaver mentioned above in the presence of a knife that cuts the foil from the inside from the end of the pipe.
Rice. 13 Sequence of soldering PP pipes reinforced with foil on top
- They do not clean the pipe shell of the joining parts from dirt - this mistake leads to poor diffusion of polypropylene and further depressurization of the joint.
- They cannot withstand a 90 degree cutting angle. The error leads to the fact that when inserting pipe sections into the heating nozzles, they are not completely immersed and during installation, too large a gap is formed between their ends - this weakens the connection and leads to the accumulation of dirt in the resulting groove.
- If the pipes in the coupling are joined too tightly or not deeply enough, in the first case an internal shaft is formed at the joint, reducing the diameter of the passage channel. If the pipes in the coupling are placed too far apart from each other, an internal groove is formed and the strength characteristics of the connection deteriorate.
- They do not maintain a right angle when joining parts. In the absence of a control tool, maintaining a right angle, or rather the alignment of the connection, is quite difficult for a novice installer; distortions have a detrimental effect on the quality of the joints and make it difficult to install long sections into pre-cut straight grooves.
- Parts are underheated or overheated. In the first case, diffusion will be insufficient, the connection will subsequently delaminate and a leak will appear, and when the pipe shells overheat, fusion will appear inside, narrowing the passage hole.
- Rotate or adjust the position of parts during the welding process. This violation of technology leads to further depressurization of the connection.
- They do not observe time intervals when soldering or joining. Deviations from the recommended table values lead to defects in the form of overheating or underheating of pipe shells, their delamination and, accordingly, poor-quality joining of parts.
Rice. 14 How not to weld polypropylene pipes
Dimensions and diameters
The diameter of plastic sewer pipes for a private house or apartment is chosen 110 or 50 mm. For household appliances, showers, bathtubs and sinks, 50 mm is suitable. For a toilet – 110 mm. Large diameter pipes are used for laying industrial sewerage: 200 – 300 mm.
Regardless of the type of pipes, their dimensions remain standard so that products from different materials can be used in one system.
Pressure pipes differ from non-pressure pipes in the thickness of their walls. In a free-flow system, where the liquid flows due to a slope, the thickness can be about 3 - 5 mm. If a pump is used that creates pressure, the wall thickness must be selected based on the expected pressure.
Size chart for PVC sewer pipes for a private home.
| External diameter | Wall thickness | Where is it used? |
| 50 mm | 1.3 mm | Shower, bath, bidet, washing machine |
| 90 mm | 2.2 mm | Dishwasher |
| 110 mm | 2.7 mm | Toilet |
| 200 mm | 4.9 mm | External sewerage if there is a sauna |
| 315 mm | 7.7 mm | Pool |
Dimensions are given for non-pressure sewer systems.
Why do you need pipe reinforcement?
To ensure a sufficient level of heat in apartments, it is necessary to turn on the return pipeline and increase the water temperature to 10 ° C. At close operating temperatures, simple polypropylene pipes begin to lose their properties and, in addition, a linear expansion of their dimensions is possible.
This is especially important when laying pipelines with high temperatures in a concrete screed. There is a possibility of cracking of concrete and breakdown of the entire heating system
To reduce this effect and completely eliminate it, polypropylene pipes are reinforced.
Reinforcement is the strengthening of the load-bearing capacity of the base material of a product with another material that has a higher level of strength. This increases the ability to withstand temperature changes. Reinforced pipes fully comply with the standards of the heating system, and do not deform when it increases significantly.
The following materials are used to reinforce polypropylene pipes:
- aluminum foil applied to the surface;
- the inner layer of aluminum located along the entire diameter of the pipe, closer to the outer surface;
- fiberglass inner layer;
- inner layer combining fiber and glass fibers.
Aluminum and fiberglass cost about the same. The price mainly depends on the parameters of the pipe itself and the manufacturer. Nevertheless, fiberglass reinforcement has a number of advantages over aluminum:
- no cleaning of the pipe edge is required during installation;
- short time for soldering joints (as with unreinforced pipes);
- there is no internal delamination due to the fusion of glass fiber into polypropylene;
- the strength of the product increases.
There is only one drawback of fiberglass - the linear thermal expansion of pipes reinforced with glass fiber is 6% higher than that of pipes reinforced with aluminum.
Purpose
PVC pipes are divided into the following types:
- for installation of internal sewerage;
- for external sewerage;
- for the construction of pressure systems;
- for gravity drainage.
The use of this classification is applicable to such pipe models, the material for the production of which has been processed accordingly.
Now there are two types of PVC pipes:
- PVC polyvinyl chloride (PVC);
- unplasticized polyvinyl chloride PVCnp (PVC-U).
PVC-U pipes are most often used in construction, since they have the best technical characteristics and can be used in pressure sewer systems.
Soldering polypropylene pipes step by step instructions
One of the main advantages of connecting polypropylene pipes by soldering is the speed of installation work; the process of joining and readiness for further installation of pipes with the most common diameter of 25 mm takes no more than 15 seconds. In order to complete the work without unnecessary time expenditure, all preparatory operations are carried out responsibly and then the pipeline is installed, strictly adhering to the technological process of the operations.
Rice. 9 Tool used to weld PP pipes
Preparing tools and components
Before soldering polypropylene pipes, prepare the components: pipe sections, tees, corner bends, couplings, adapters from plastic to metal, valve shut-off valves.
To carry out the work, you will need a soldering iron and a set of nozzles, as well as auxiliary tools, some of which are included with the device:
- Pipe cutters, usually scissors with a maximum permissible cutting diameter of 40 mm are used for cutting pipes; for larger sizes, more powerful scissors or roller cutters are used.
- Tape measure for measuring dimensions, marker or pencil for marking the length on the pipe casing.
- Gloves to protect your hands from burns while working.
- Level for checking the horizon when installing water sockets.
- A screwdriver or hex wrench for securing attachments to the heating iron.
Rice. 10 Main stages of PP welding
Marking and cutting
For ease of work, free up space in the middle of the room and set the table at a convenient height, lay out all the elements around the perimeter of the room according to the diagram, after which they begin to cut them sequentially with soldering. If the pipeline runs along the perimeter of the room, installation begins from the end wall - this makes installation more convenient. The work is carried out in the following sequence:
- Measure the required section of pipe and place a mark on its surface with a marker or pencil, departing a distance from the end taking into account the heating depth.
- Cut the pipe with scissors for polypropylene pipes, trying to accurately maintain an angle of 90 degrees. If the tool is sharpened, there will be no burrs on the inner walls and the pipe will retain its geometry.
- If the pipe at the end has small irregularities or burrs, then, in principle, this is not a big problem, since when the pipe is heated they will melt anyway.
Rice. 11 Soldering PP pipes - main steps
Soldering
For soldering polypropylene, soldering irons with a flat iron are mainly used; work is carried out in the following order:
- Connect two parts of the screw attachment to the device using a hex wrench, connect it to the network and turn on the heating element or both heating elements by pressing the keys.
- The thermostat is used to set the required temperature; usually the standard temperature for soldering polypropylene pipes is set to 260 °C.
- After the indicator changes its color to green, indicating that the heating element has reached the set heating temperature, soldering begins. First, it is better to carry out test work on short pieces of pipe; after determining the optimal holding time (for this, a table for soldering polypropylene pipes is used), begin welding the main pipeline.
- The outer or inner surfaces of the parts to be joined are placed simultaneously on both sides in heating couplings, trying to maintain a strictly horizontal position of the parts; to hold the short coupling, use the gloves included in the kit. After a certain time, the parts are quickly removed from the soldering iron and connected to each other in a strictly fixed position, trying to keep them on the same axis for the allotted time.
- After the cooling time has passed, the unit is ready for further operation - soldering the second pipe section into the coupling.
Rice. 12 Shavers for removing external reinforcement of PP pipes and an example of their use
Product stacking
During installation, plastic pipes for sewer systems must be supplemented with various fittings to prevent blockages.
To install the products as correctly as possible, you need to proceed according to the following scheme:
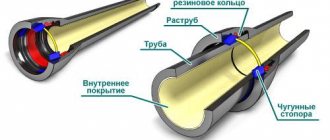
choose the right design according to wall thickness; remove all burrs from the surface of the product, while the outer part of the product must be chamfered; it is important to lay the structures at a slight angle to prevent liquid stagnation; if pipes of a suitable diameter are difficult to fit together, use a special lubricant to solve this problem; do not use steel clamps or hangers to secure the structure (to avoid physical damage); When using a socket connection, create a seal by using an O-ring.