Behind the designation “plastic pipes” lies a huge range of pipe products made from various types of plastics and with different characteristics and sizes. Choosing the appropriate option for a plumbing system in a cottage or apartment is often incredibly difficult. Some of them are intended only for cold water, while others can also be used for hot water supply and heating. To make the right choice, you should carefully study all the parameters of PVC, PEX, PP and HDPE pipes for water supply. Otherwise, you will inevitably have to spend money on repairs due to the resulting flood.
The popularity of plastic pipes for water supply
The popularity of plastic water pipes is due to their low cost, resistance to corrosion and long service life. This is an ideal material for organizing your own water supply in your home. Steel analogues are more durable, but over time they rust and are difficult to install independently.
Application of plastic pipes
To understand which pipes for water supply are better, it is necessary to analyze all their parameters. The service life of all manufacturers of such plastic products is stated to be 50 years. However, the temperature and pressure of the water that will then flow through the assembled pipeline are extremely important here. If you take a pipe with properties that do not correspond to reality, then it will last much less than the half-century indicated in the technical data sheet.
Advantages of PVC pipes
Another important point is cost. In the store, you should look not only at the price of a plastic pipe, but also immediately estimate the costs of installing a water supply system from it. In some cases, you can get by with press fittings and wrenches, while in others you will have to get a soldering iron for plastic somewhere.
PVC
Pipes made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC, PVC), among other plastic analogues, are characterized by high tensile strength and a low coefficient of linear expansion. These products have a relatively low operating temperature (only up to +450C), so they are recommended for use only for cold water. However, due to additives, PVC is less flammable than polyethylene and polypropylene.
Among the advantages of plastic pipes for PVC water supply are:
- high impact strength;
- good frost resistance (can easily tolerate freezing down to -100C);
- resistance to acids and chlorine compounds;
- no tendency to crack after several years of use.
PVC is non-toxic, the water in pipes made from it is not colored and does not receive an extraneous chemical taste. The permissible pressure in a polyvinyl chloride water supply system, depending on the internal diameter and wall thickness, ranges from 6 to 16 atm.
Composition of polypropylene pipes
The main disadvantage of this type of pipe is poor tolerance to ultraviolet radiation and complete intolerance to high operating temperatures. If water heated to +700C is run through a water supply pipeline assembled from them, the PVC will begin to lose its plasticity and gradually deteriorate. For cold water supply and sewerage this is the best option, but for heating and hot water supply it is worth choosing something else.
Main technical characteristics
Polypropylene is an artificial material with high physical and chemical characteristics, obtained by the polymerization of synthetic substances. Pipes made from such a composite have the following properties:
- density - 0.92 kg/cm³;
- resistance to chemically active liquids;
- bending and tensile-compressive strength;
- high levels of electrical and thermal insulation;
- wear resistance;
- permissible temperature range - -15...+120°С;
- plastic deformation to the conditional yield strength - 50%;
- low linear elongation when heated;
- heat capacity 2.0 kJ/(kg.°C);
- low thermal conductivity.
Polypropylene
Polypropylene pipes for water supply have the highest operating temperature among plastic analogues (up to +700C). However, this plastic does not tolerate frost well and can crack when cooled below zero. In a house or apartment, a pipeline made from it will last for many years, but this option is not suitable for installation on the street.
Application of polypropylene pipes
When comparing pipes made of HDPE, PVC and polypropylene by price with the same internal diameter and equal length, the latter turns out to be the most expensive among them. But it has better almost all characteristics. Plus, fittings for polypropylene products are several times cheaper than those designed for polyvinyl chloride or polyethylene pipes. As a result, the final cost of plumbing in most cases is cheaper.
Areas of use
Now let's get back to a more practical area. What sizes should you use when building water supply, heating or sewage systems with your own hands?
Water supply, heating
- A 16 mm plastic pipe is used to connect one to three plumbing fixtures (faucets, shower cabins, toilet cisterns, etc.). It can also be used for installation in underfloor heating (cross-linked polyethylene is usually used for this purpose) or for manifold heating distribution.
- 20 mm is enough to distribute water supply throughout a cottage with 4-6 plumbing fixtures and to operate a heating system with forced circulation, serving a house with an area of up to 100 m2.
- 25 mm are used as heating and water supply risers in houses with no more than 5 storeys.
- A diameter of 32 mm is typical for risers in high-rise buildings and for bottling water supply and heating in a small number of apartments.
- 40 mm – bottling in an apartment building or in a cottage with a gravity (gravity) heating system.
READ ALSO: HDPE pipes for cables in the ground: underground laying of corrugated pipes, laying, in which pipes the cable is laid
Sewerage
Gravity waste systems are characterized by the following size distribution:
- A 50 mm plastic pipe is used to connect 2 – 3 washbasins, sinks, shower cabins, etc. In short, any plumbing fixtures, with the exception of toilets.
The sewerage installation for the bathtub, washbasin and washing machine is made with a 50 mm pipe.
Important: to connect a simultaneously used bathtub and shower cabin, a plastic pipe of 75 mm or higher is used. What is the instruction related to? With the fact that when draining a full bath, the 50 mm sewer will be filled; We will not talk about normal drainage from the shower stall.
- A 90 mm plastic pipe is used relatively rarely, mainly for connecting installations of wall-hung toilets. But the 110-mm one, on the contrary, is extremely in demand: this diameter is used for connecting a toilet, laying sewer risers and beds (horizontal branches connecting risers).
- 150 – 600 mm are used as an outlet to a well and for transporting wastewater between wells.
- A diameter of 600 mm or more is typical for collectors that combine wastewater from an entire city district.
The photo shows the laying of a polyethylene sewer collector.
Polyethylene pipes (HDPE)
Polyethylene pipes (HDPE) can easily withstand temperatures from -40 to +400C. This is the best choice when it is necessary to lay outdoor water pipes in the ground. However, under the rays of the sun, this plastic begins to age, becoming brittle. It cannot be left without UV protection. HDPE pipes can withstand pressure up to 10 atm. This is more than enough for cold water and hot water supply in the house.
Design and installation of polyethylene pipes
Among the main advantages of polyethylene pipes it is worth noting:
- a large assortment of adapters for steel and copper and other connecting parts for a variety of sizes;
- flexibility (these pipes are usually supplied in coils);
- availability of three connection options (welding, electric couplings and compression fittings).
The main disadvantage of HDPE pipes is the sagging of the pipeline when heated. This plastic has the highest linear expansion coefficient. It easily tolerates a short-term supply of water heated to +700C. But then the sagging HDPE water pipe does not look very aesthetically pleasing. This point must be foreseen in advance when designing the water supply, so that polyethylene pipes can expand without interference and are not visible behind the finish.
Errors in connecting polyethylene pipes
This type of pipe products also includes PEX pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene. They consist of several layers of plastic “cross-linked” at the molecular level. This option is superior to conventional HDPE polyethylene pipe in strength and operating temperature (up to +900C). But it also costs more. Moreover, in terms of the range of produced sizes and lengths, they are identical.
Cross-linked polyethylene
Polyethylene material is used for hot water supply. The connection can be either fitting or compression.
Advantages:
- flexible structures;
- the bay allows installation without joints;
- the structure does not deform or collapse when in contact with solvents, chemicals, gasoline;
- the maximum permissible temperature of the working fluid and coolant is up to +75°C.
If all requirements are met, the material will last about 40-50 years. Disadvantages include destruction of the structure when exposed to ultraviolet rays. The main difference is the small diameter. The material cannot maintain an even shape, so the products are practically not used for open laying. They are presented in the middle price category.
Metal-plastic
The metal-plastic version (PEX-Al-PEX) is a layer cake made of inner and outer layers of polyethylene, between which aluminum foil is sandwiched. These products are more intended for heating systems. But it is quite possible to make a water supply system from such a pipe. It will just be quite expensive.
The main disadvantage of metal-plastic lies in its multilayer structure. Due to the presence of an aluminum layer, such a pipe is more difficult to solder. Plus, over time, these layers can separate from each other.
Marking
There are several types of plastic used to make pipelines:
- PVC pipes;
- polypropylene products;
- polyethylene parts.
A separate group includes tubes, during the manufacture of which a reinforcing layer of aluminum foil or fiberglass is placed between layers of plastic.
The marking varies depending on the type of polymer. There is no point in describing the designations on PVC, since this material is not used for the manufacture of water supply and heating pipelines. This type of polymer releases harmful substances when heated and has low performance characteristics.
Polyethylene marking:
- PE 32 is a type of polyethylene with the lowest density. It is rarely used for making pipes.
- PE 63 - used for assembling non-pressure systems. This could be sewer drains, an outdoor shower. This type of polyethylene cannot withstand high pressure and is destroyed by water hammer.
- PE 80 is a type of polyethylene with a high strength index. Used for assembling cold water supply systems. If the pipeline is laid outside buildings, additional insulation must be used.
- PE 100 - pipes made from this type of polyethylene have the highest strength index. They are used for the manufacture of industrial pipelines, hot and cold water supply systems, heating circuits.
The marking of polyethylene tubes contains the abbreviation SDR, followed by numbers. The lower this indicator, the stronger the product.
Marking of polypropylene tubes:
- PN10. Products with this designation can withstand pressure up to 1 MPa. The permissible liquid temperature is 45 degrees Celsius. Due to their low strength and heat resistance, such tubes are used for assembling sewage drains and cold water supply pipelines.
- PN16. The maximum permissible pressure level is 1.5 MPa. The coolant temperature should not exceed 60 degrees. Popular for the manufacture of cold water supply systems. Rarely used for assembling hot water circuits.
- PN20. Tubes made of this type of polypropylene can withstand pressure up to 2 MPa. The maximum permissible coolant temperature is 80 degrees. Used for assembling hot and cold water supply systems, heating circuits.
- PN25 is the most durable type of polypropylene. This material can withstand pressure up to 2.5 MPa. The coolant temperature can rise to 95 degrees. Withstands temperature surges - up to 110 degrees.
Marking of multilayer products:
- PPR - the outer layer of the tubes is covered with polypropylene;
- AL - has a reinforcing layer of aluminum foil;
- PP-RCT is a designation for modified polypropylene, which has increased thermostatic properties.
If there is a layer of fiberglass inside the pipe, the marking will contain the letters FG, FR.
Heating pipes made of polypropylene
Features of installation and connection of plastic pipes
Plastic pipes for water supply are connected:
- PVC – gluing with special glue;
- PP – soldering with a soldering apparatus;
- HDPE and PEX – electrofusion welding and compression fittings;
- PEX-Al-PEX – press fittings and compression fittings.
Installation of plastic pipes
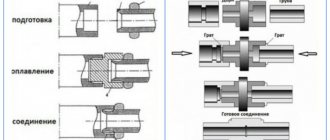
The most difficult thing to install is metal-plastic. Here you need to make sure that the aluminum layer does not wrap inside the pipe and is not over-tightened when cutting it. At first glance, gluing and soldering are easier. However, in this case, it is extremely important to correctly set the temperature of the soldering iron according to the corresponding tables from the manufacturers, depending on the thickness of the pipe walls. Plus, the device itself needs to be rented somewhere else; buying it for a one-time job will be expensive.
Welding time for plastic pipes during installation of water supply and sewerage systems
Soldered or glued plastic pipes form a non-separable pipeline. It is more difficult to repair, but it is more reliable. Fittings (especially wrench-type ones) are easier to work with. But they will then have to be regularly inspected for leaks and tightened.
Connecting plastic pipes using fittings
How to choose a diameter
When choosing pipes, in addition to quality characteristics, you need to take into account the outer and inner diameters of the product, the size of which affects the hydrodynamic properties of the system.
Pipeline capacity depends on many factors, including:
- number of sources;
- purpose of the water supply;
- pressure force;
- maximum load;
- number of branches (consumers);
- distance between the starting and ending connection points.
Connection to the central water supply for individual use is made using pipes Ø 32 mm. For internal networks, profiles with an outer diameter of 16-25 mm are used.
In everyday life, water pipes from 20 to 32 mm are considered the most used.