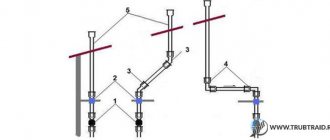
To operate efficiently, each piping system consists not only of pipes, but also of many components. After all, straight horizontal and vertical sections of water supply are constructed from pipes, and they are connected, branched, made turns and connected to different devices using fittings, they are also called fittings.
The pipe fittings are special parts that connect the pipes to each other. They ensure the tightness, flexibility and integrity of the pipeline, making it convenient to use. Even if the pipeline itself is absolutely straight, fittings are still needed at the entry and exit points, installing special sensors and equipment.
The fittings are designed for the installation of complex engineering communications: water pipelines, gas pipelines, drainage and sewer networks.
Types of plumbing fittings
Let's start with the typology of shaped parts with the material used for their manufacture. The material of the fittings does not have to match the material of the water supply pipes. For example, to branch cross-linked polyethylene pipes, plastic tees are used.
According to the material, shaped products can be:
- Steel;
- Cast iron;
- Plastic (plastic);
- Bronze (bronze alloys);
- Brass (brass alloys);
- Combined.
According to the type of fastening, fittings can be:
- Welded: attached to water pipes by hot or cold welding;
- Threaded: attached to water pipes with threads;
- Flanged: installation of water supply from pipes of medium and large diameters on bots with nuts.
Methods of connecting to the pipeline
Welded and threaded fittings are used to join traditional metal pipelines. Welded ones have smooth ends for ease of welding with the pipeline. The most common welded pipe fittings are bends, tees and reducers.
To connect water and gas pipes, threaded fittings with inch pipe threads are used. For a tight connection, use a strand of flax with paint applied to it, sealing tape or thread. The seal is screwed onto the thread along the pitch and reliably protects against leakage.
The surface of the parts must be free of holes and traces of welding. Cracks and damage to it are unacceptable. The end surface must be
perpendicular to the axis of free passage of the fitting. For strength, cast iron threaded fittings are equipped with a collar at the edges - a thickening.
There is another way to connect pipe fittings without threading or welding. It is used in so-called compression fittings. In this case, O-rings are used for tightness. Such joints are easy to install and dismantle, they reliably seal the gas environment and are resistant to vibration.
Plastic connections
The parts of polypropylene pipes are connected by soldering the ends using a special soldering iron. It heats the surfaces of the parts being connected simultaneously with the surface of the pipe end to a temperature of 260 °C. The molten surfaces are connected and, upon cooling, form a homogeneous sealed structure at the point of connection. This is a very simple and popular way of piping home heating appliances and plumbing.
Combination fittings are available. Their design is an adapter with a metal thread. Using combined parts, you can connect a plastic pipe with a metal analogue.
The simplest connection method is used in the installation of non-pressure PVC sewerage. In this case, the pipe simply fits inside the socket with a seal. The main thing is to maintain the dimensions and avoid distortion at the junction.
Metal-plastic connections
A press connection is the most reliable way to join metal-plastic pipes. It is carried out by crimping the pipe around a specially designed fitting. Crimping is performed with a tool that fits the configuration of the part profile. Press jaws must have an internal structure that matches the fitting being connected.
Compression or split ring fittings are an equally popular way of joining such pipes. They are used for heating and water supply pipelines with open installation. This joining system is not used for hidden pipe laying.
Basic plumbing fittings
The main (basic) shaped parts are:
- 90º angles: products for turning the water supply route at right angles;
- Tees: Provide a branch of the water supply line from the main route.
- Crosses: Provide division of the water supply system into two mutually perpendicular directions;
- Elbow: Provides a smooth turn of the water supply route.
- Transitions: Provide narrowing or expansion of the water supply system. Allows you to join pipes of different diameters.
Read: For a novice plumber - basic rules and some tips
Classification according to various parameters
In addition to functional differences and design features, the criteria for dividing devices into groups are their purpose and scope of application.
By area of application
Based on their application, devices are divided into four types:
- General purpose parts that can be used in various industries.
- Special-purpose fittings (these devices must have certain characteristics that are specifically specified).
- Sanitary, which is used in pipes intended to equip household equipment.
- Shaped parts for special operating conditions, for example, for highways transporting aggressive substances.
- For pipelines in the shipbuilding or transport industries.
Purpose
Sewage fittings are among the main parts of drainage systems. They are no less important than pipes or other components, since they are involved in the transportation of wastewater. In addition, fittings perform dispatch functions. They form a network and make its work possible. During reconstruction or repair, using fittings, new sections are connected and connected to other lines.
Shaped products, or fittings (sometimes also called additional elements) are used to change the configuration of the drainage network. They are installed at different points in the system:
- rotation of pipelines in a horizontal plane;
- change in channel cross-section;
- branching or connecting an additional line;
- installation of service elements;
- connecting dissimilar parts of the system;
- connecting plumbing fixtures;
- connection to containers or collectors.
Using certain types of fittings, you can assemble a sewer network of any size, length and configuration. In addition, you can change an existing line, add additional bends or devices to it. Shaped sewer parts can be installed at any point in the system if required by the assembly drawing or if the need arises during operation of the network. The possibilities of fittings are very large. It can be said with good reason that the configuration of the system is determined by the fittings, and the pipelines only connect them to each other.
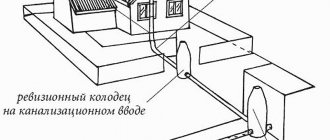
Schematic diagram of internal sewage system made of polypropylene:
Internal sewerage installation diagram
Related article:
Sewer cleaning - methods, options, tools and means. A separate article describes in detail how to independently deal with sewerage blockages in a city apartment and private house. Read it, it might be interesting.
Materials and components
The materials used for the manufacture of shut-off valves and components must comply with the general technical specifications in accordance with the standards of the Central Design Bureau of Valve Engineering (TsKBA) “Pipeline Valves. General technical conditions”, put into effect in January 2006, as well as current national standards and industry specifications. The main criterion in choosing a material for the body of any fitting is its strength. The housing is the basis for installing all other parts into it. It is like a foundation in construction - a supporting structure for the whole building.
The bodies of most pipeline shut-off devices are made of cast iron or steel. Sometimes other metal materials are used for this: bronze, copper, aluminum and brass taps and valves for household appliances are commercially available. Fittings made of non-ferrous metals and their alloys have a good feature - they are not subject to corrosion and have a good appearance.
The most economical material for fittings is plastic, which under its general name combines products made from PVC (polyvinyl chloride), polypropylene, polyethylene and other artificial alloys of plastic material. But such fittings cannot withstand high pressure and temperatures, as they are not durable. But for pipes of small diameter and low pressures, this is a completely suitable alternative to metal products. In addition to being cheap, plastic pipelines and fittings are valuable for their resistance to corrosion - the main scourge of similar steel devices.
For casting valve bodies, malleable, gray or high-strength cast iron is used, depending on the area and conditions of use of a particular product. Due to their fragility, fittings with a cast iron body are not used at high pressures in pipelines, as well as where water hammer and sudden temperature changes may occur. In such situations, the cast iron body may simply burst.
Steel cases are made from various grades of steel: alloy, heat-resistant and carbon. For the manufacture of valve bodies installed on pipelines with aggressive substances or having a particularly clean working environment, stainless steel with high corrosion resistance is used. Housings made of heat-resistant steel are used for valves operating at elevated operating temperatures. The use of a particular material, as well as the design and type of flange, are determined by a number of factors, the main of which are the following:
- nominal diameter of pipelines;
- working environment pressure;
- flow direction;
- temperature conditions.
The sealing materials are:
- metal products in the form of rings that have corrosion resistance, anti-friction properties, and are well processed (steel, brass, bronze, monel);
- deposition of various hard alloys: stellite (cobalt alloy), sormite (iron-based alloys);
- non-metallic products (rubber and rubber-metal rings, polymer seals);
- sealing packings made of material of plant origin (cotton and flax fiber), talc, fiberglass;
- fluoroplastic and graphite for stuffing box seals in aggressive and high-temperature working environments;
- sheet rubber, paranit and fluoroplastic for gaskets.
Cast iron and steel fittings equipped with flanges have undeniable advantages in terms of tightness, maintainability and strength of the pipeline network compared to flangeless ones. But the mass and dimensions of such reinforcement sometimes reach large values (in tons and several meters, respectively). To this we also need to add control devices (hand wheel, electric drive or pneumatic drive, mounted on the valve). Flanges lead to increased metal consumption and labor intensity in their manufacture.