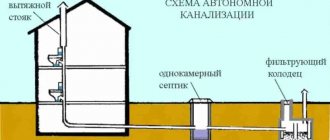
People are accustomed to laying any communications underground. The explanation for this is very simple. The fact is that soil is a safer environment than air. Which pipe should I use for underground water supply? Builders often ask this question. The use of underground water pipes depends on many different factors.
The entire volume of passing groundwater is much less than the volume of precipitation, the impact of different temperatures is much weaker, and another plus is that underground pipes are much more difficult to damage than those laid on the surface.
Initial stage of work
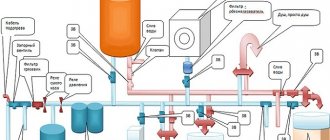
Any installation of water pipes begins with drawing up a project. The scheme must be well designed, otherwise the pipeline system will not be able to function properly. This does not mean that the project should become a miracle of engineering - the main thing is that you can easily navigate the finished circuit, so that if errors arise during the work, you can easily figure it out and quickly solve them.
The project must contain the following information:
- Soil properties - its type, whether it is loose, rocky or sandy.
- The area of land over which the pipe will be laid. It is necessary to calculate so that you can always consider the number of forks and entrances.
Remember that the laying of water supply pipes must pass along a pre-leveled area. Ignoring this nuance may lead to unexpected bad consequences in the near future.
How to choose the optimal pipe products for water supply in a private home?
There is a distinction between water supply networks based on the following criteria:
- Location. There are external networks that are exposed to the influence of external atmospheric factors and internal ones, on which such influences are minimized.
- Bandwidth. The water supply network is divided into main (general) and local. In the first case, large cross-section pipe products are used, designed to supply water to many consumers. In the second case, as a rule, pipe products with a cross section of 0.5 or ¾ inches are used.
Laying depth of water pipes
Of course, in order to correctly lay pipes underground, it is worth taking into account many conditions, because any deviation from the norms can lead to malfunctions in the operation of the entire water supply system. For example, when deciding how far a pipe can be buried in the ground, it is worth considering the material from which it is made.
In addition, it will be necessary to study the individual characteristics of each type of pipe in order to understand in which cases it is advisable to use one or another type of product.
As practice shows, the optimal pipe for water supply to a private house underground is of the “HDPE PN10” type, made of polyethylene.
Products of this type are distinguished by the following qualities:
- absolute resistance to corrosion, unlike metal analogues;
- the permissible operating pressure in the system is 10 atmospheres, in addition, such pipes can be easily bent to obtain the desired configuration;
- resistance to temperature changes during changing seasons.
Characteristics
The technical characteristics of the material determine the scope of its application. When making a gas pipeline, you can use different types of plastic pipes. Each of them has its own technical characteristics.
Metal-plastic parameters:
- High chemical resistance.
- The material is not subject to oxidation.
- The maximum coolant temperature is up to 95 degrees.
- The maximum permissible pressure is up to 25 bar. If the temperature is high, the permissible pressure is reduced to 10 bar.
- The thickness of the metal layer between the plastic is up to 0.3 mm.
Characteristics of polyethylene:
- outer diameter of tubes - 10–110 mm;
- maximum coolant temperature - up to 95 degrees;
- at high temperatures the maximum pressure is up to 10 bar.
Polypropylene parameters:
- maximum coolant temperature - 90 degrees;
- permissible pressure at maximum temperature - up to 10 bar.
Polypropylene pipes can withstand short-term overheating up to 110 degrees.
Diameter of plastic pipes
Subtleties of underground installation of water supply lines
When it comes to the above-ground part of the water supply system, you need to give preference to products that are strong and reliable enough to successfully withstand changes in temperature and pressure. In this case, the type of pipe described above is perfect, another advantage of which is ease of installation using fitting fasteners.
And to make it easier to decide which pipes for underground water supply are best suited in each specific case, it is worth paying attention to the existing ready-made water supply projects, proven by practice, and also take into account the requirements of technical standards. With this approach, you will get inexpensive and high-quality plumbing, and installed without much effort.
Video description
The secrets of installing PP pipes are revealed in this video:
Polyvinyl chloride
The main advantage of PVC is its small coefficient of thermal expansion and stability of linear dimensions when transporting hot water. But such pipes are very fragile, especially at low temperatures, and have high thermal conductivity. Due to the impossibility of threaded and welded connections, their assembly is carried out using glue, which is not always convenient and takes a lot of time.
For reference! PVC pipes are considered an ideal material for sewer systems.
Adhesive connection of PVC pipes Source strojdvor.ru
Technical standards for buried systems
You can find out information about how deep a water supply pipe should run in the ground from a special document - SNiP. All the subtleties and characteristics for pipes made of various materials are spelled out there, and it also describes at what depth one or another type of product can be laid. In essence, this document contains a lot of varied information, most of which will be, if not entirely interesting to you, then at least useful, because it will remove many related questions.
According to the regulations, the minimum depth for laying any pipe is a distance of 1.5 meters, since, often in winter, the soil freezes to about 1.4 meters. If you do not maintain such a depth, you may encounter damage to the water supply lines, which will significantly complicate, if not make it completely impossible, the further operation of the system.
It is worth noting that the depth of freezing largely depends on the type of soil in a particular region. To find out exactly this indicator, it is worth consulting with specialists who will tell you all the necessary information that you need to know. Armed with information, you can avoid many possible problems associated with temperature changes and soil freezing.
However, if you do not have access to professional advice, then simply make the trench a little deeper. By laying pipes 1.6 meters from the surface, your water supply will be protected from any surprises associated with severe winter frosts.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Resistant to long-term gas exposure.
- The service life is about 100 years, if the pipeline is not overloaded.
- High level of flexibility. Thanks to this, it is possible to manufacture highways of complex configurations.
- Low weight of individual elements.
- No sediment accumulates on the smooth walls of the product.
- The material is not susceptible to rust.
Flaws:
- Not resistant to high temperatures.
- Plastic pipelines cannot be installed outdoors, as the material loses its technical characteristics in the cold.
- When heated strongly, the material expands. Because of this, to increase the strength of connections, individual sections of the pipeline need to install compensators.
- Low resistance to ultraviolet rays.
If you do not overload the pipeline, it will not break down and will withstand decades of active use.
The most common mistakes made when laying underground pipes
The underground installation of communications, of course, largely depends on the type of soil in a particular location. And, often, many difficulties arise with it during work, since the composition of the soil may simply not make it possible to deepen the pipes to the distance specified in SNiP. In particular, the soil may be very compact, rocky or boggy, so that you simply cannot get to the desired depth. In this case, many difficulties can arise in winter.
However, even in this case, there is a way out - insulating water supply pipes in a private house in various ways. In this case, a reasonable option would be to dig a trench as deep as possible and insulate the pipes well.
Steel pipelines
Classic steel products for water supply
Steel pipes are used for water supply, heating and sewerage systems. They are connected by welding or welded and threaded fittings. Service life - up to 25 years. This is where the advantages of steel pipes end. The disadvantages include: lack of corrosion protection, heavy weight, high thermal and electrical conductivity, decreased pipe permeability over time.
Another thing is galvanized pipes . Zinc protects pipeline surfaces from corrosion on both the internal and external sides. It also prevents the appearance of various deposits inside the pipe.
Microtunnelling method
Main article: Microtunnelling
Microtunneling is automated tunneling with pushing of the pipe lining structure, carried out without the presence of people in the excavation. This is a trenchless method of laying pipelines and communications using special jacking stations, when the pipe is “pushed” through the soil from one station to another using a special tunnel-boring shield, also called a drill (auger drilling) at a distance of 100-120 m, which mixes during operation rock with water and is transported by the cleaning system to the surface, where it is separated.
Microtunneling technology makes it possible to lay underground communications in densely built areas or areas crossed by transport and other communications. Work is carried out in water-saturated, non-rocky and rocky soils, including mixed mining, in coarse soils with the inclusion of gravel, pebbles, crushed stone in the form of an interlayer and boulders. The laying is carried out along a straight and curved route in profile and plan.
Behind the shield, pipes are pressed using jacks: steel, fiberglass, ceramic, concrete, reinforced concrete or polymer concrete with special fiberglass couplings that provide little resistance when pushing the pipes in the well. For the construction of sewer collectors, pipes with internal polyethylene insulation are usually used, which increases the service life of the structure by 3-5 times.
Laying is carried out using two pits: starting and receiving, the depth of which corresponds to the depth of laying. A powerful jacking station is installed in the starting pit, on which a tunneling shield is placed. Using jacks, the shield is driven into the ground to its length, after which a section of the pushing pipe of the same length is placed on the jacking station, and the process is repeated. After the pipes have been built up in separate sections, further penetration is carried out until the shield exits into the receiving pit. After this, the shield is dismantled, and the pipes remain in the ground.
By changing the standard size of the tunneling shield, it is possible to lay underground microtunnels of various internal diameters - from 250 mm to 3600 mm with a burial depth of up to 30 m. The minimum depth of the top of the pipeline relative to the ground surface should be at least 1.5-2 pipe diameters. The distance between the pipeline being laid and already located communications and structures must be at least 1 m. Shield penetration is used in semi-rocky and rocky soils, where it is impossible to use other methods, and concrete or reinforced concrete pipes are used.
The first part of the drill string can deviate by several degrees vertically and horizontally (up to 13 mm at 200 m), which requires constant adjustment of the drilling direction. Accuracy of penetration is achieved by a computer control complex using a laser shield guidance system. The drilling process is controlled from the surface by an operator using a navigation system.
Microtunneling technology makes it possible to lay communications and pipelines using small-diameter collectors in soil of any complexity - from unstable loams and aquiferous sands to rocks, including with a mixed face, in coarse soils with the inclusion of gravel, pebbles, crushed stone in the form of an interlayer and boulders.
An advanced control system for tunnel boring complexes ensures tunneling accuracy that meets the highest requirements and allows at every moment to control values that fully characterize the position of the tunneling shield, the parameters of its movement, as well as the operating parameters of its main components and mechanisms. The complexes are built on a modular principle, which makes it possible to relocate them from one facility to another and minimize the installation time for equipment.