Fastening sewer pipes is an important step in providing high-quality communications. In order for installation work to be carried out in proper compliance with all standards, you need not only experience, but also knowledge of certain rules and legal regulations.
In this article we will look at fastening sewer pipes: methods and points that should be paid attention to during installation.
The sewer network can be laid using a hidden (closed installation) or open installation method (attaching sewer pipes to the wall) in accordance with clause 17.9 of SNiP 2.04.01-85. But the installation of drainage networks is not possible at all facilities and types of premises: a specific list and existing exceptions are listed in subparagraph 10 of section No. 17 of the above-mentioned legal act.
The advantages of the closed type include the following:
- Saving usable space; Aesthetics; Low risk of damage.
In turn, the open laying of the communication network has the following advantages:
- Easy to install; Easy to repair; Versatility.
The closed type of installation requires obligatory gating of walls, which in many cases is simply impossible. For example, if you need to fasten a sewer pipe to a sandwich panel or you need to lay a sewer system in buildings with a weak frame foundation. Thus, open installation has become the most widespread, which we will pay attention to in this article.
Installation features. Fastening sewer pipes
Installation begins with the selection of pipelines and fittings. Fastenings of plastic sewer pipes, as well as fastenings of cast iron sewer pipes, must withstand operating and high pressure in accordance with SNiP 2.04.01-85, paragraph 10.1.
Correct fastening of sewer pipes ensures proper operation of the system, therefore, before performing installation work, you should familiarize yourself with the current standards of SNiP 2.04.01-85, in particular section 17, as well as the calculations given in paragraph 18. It should be noted that depending on the complexity of the project and its Features: Various types of brackets are used for fastening sewer pipes. For reliable fixation during the installation of an internal sewer system, fastening clamps are most often used, performing several functions at once: Preventing the structure from deforming under load; Compensating for the exhaust of a plastic pipeline under the influence of temperature; Absorbing noise; Regulating the distance of the pipe from the wall or, if sewer pipes are being attached to the ceiling, the height of their location. Before carrying out the actual installation work, it is recommended to draw a detailed communication diagram, as well as make precise markings.
This will simplify all the work and allow you to determine the design features. When laying a drainage system, you should determine the distance for fastening the sewer pipes, which depends on their diameter and the type of drainage. In domestic conditions, it is often enough to install a clamp in areas of at least 2 meters, as well as at a distance of up to 15 -ten centimeters at bends or connecting areas where sewer pipes are attached to each other. These standards are given in SNiP 2.04.01-85, clause 17.2. For proper operation of communications, its straight sections should be placed at an angle.
The magnitude of the slope directly depends on the diameter of the pipe. The minimum slope should not be less than 0.002, i.e.
2 cm per meter (according to SNiP 2.04.01-85, subparagraphs 11 of section 9). Choosing a lower coefficient is fraught with stagnation of the flow, and a larger slope will provoke an excessively rapid drainage of water, in which the dirt simply will not have time to be washed away. Thus, the installation of an internal sewer system is divided into the following stages: Selecting the pipe material and type of installation; Calculating the required slope; Determination of the fastening step; Selection of suitable fastening clamps; Preparation of a communication diagram and application of appropriate markings. At this point, the preliminary stage can be considered complete. Next, it’s worth moving on to a more detailed study of the issue of selecting fasteners, since it is key to achieving the correct operation of the entire system.
General system requirements
A single sewer riser must pass through all floors of the building. Pipes laid horizontally flow into it. They can be fixed to the wall at an angle that ensures adequate fluid flow in the channel. The magnitude of the slope is specified in SNIP and depends on the internal diameter of the sewer.
For a 50 mm channel, the minimum slope is 0.03. This means that for every meter of pipe a rise of 3 cm must be observed. For a 110 mm channel, the minimum slope is 0.02 (2 cm per meter).
From the vertical riser the drain is carried out into a drain of a larger diameter, which is located in the basement of the building. It drains water from the house to the external sewerage system. Pipes in the basement should be attached to the walls or ceiling.
Selecting fasteners for securing sewer pipes
To attach sewer pipes to a wall or ceiling, special clamps of various diameters are often used. For rigid fixation, a clamp is selected to match the diameter of the pipe, and in areas where it is only necessary to maintain the axial direction of the system, clamps of larger diameter are used, which, if necessary, can compensate for the thermal stretching of the plastic sewer system.
The distance between sewer pipe fastenings is selected based on technical parameters (diameter, flow volume, etc.), in accordance with current SNiP standards. Thus, cast iron pipes are secured using clamps - for every 3 meters of pipe, 2 clamps are used, secured with M8/M10 studs.
Plastic pipes are secured with clamps or brackets installed on horizontal surfaces every 1 m (if the pipe diameter is less than 63 mm), 1.5 m (if the pipe diameter is from 63 to 160 mm) and 2 m (if the pipe diameter is more than 160 mm), and on vertical surfaces, brackets or clamps are installed every 1.5 m (if the pipeline diameter is less than 63 mm) and 2 m (if the diameter is more than 63 mm). In this case, the length of the pipeline that does not rest on a solid base, that is, in places where pipes turn and are connected to plumbing equipment, should not exceed 0.5 m. The rubber gasket of the fastening clamps prevents the transmission of sound from the waste stream through the supporting structures.
Also in many cases, support consoles are used. To fix a riser bracket of standard diameter, a double profile is selected. This fastening method is widely used for installation in places where it is necessary to reduce the load on the load-bearing capacity of the wall structure, for example, if it is necessary to fasten a sewer pipe to a sandwich panel or its half-timbered crossbars, to provide even greater rigidity and fixation.
There are various types of brackets for attaching sewer pipes, which have an optimally low thermal expansion rate and fire resistance.
If earlier pipelines and sewerage were rare in private country houses, today these amenities are necessary conditions for a comfortable life even outside of big cities. In this regard, when building a private house, the question of the correct installation, fastening and removal of sewer lines becomes very relevant for the owners. An important part of the sewer installation work in a private house is the installation of pipe fasteners, during which certain simple but very important rules must be followed.
Their compliance also depends on what types of fasteners will be used when installing the drainage system. Types of materials for sewer pipe clamps. Types of clamp fasteners for sewer pipes Sewer pipes are secured using special fastening devices called clamps. From the name itself it becomes obvious that the pipe is fixed here using its girth. In addition to the wrapping element, the design of the clamp includes a screw, dowel or anchor device that secures the clamp to a wall or other load-bearing surface.
Taking this into account, for sewer installation you may need a drill or hammer drill, as well as a set of keys and screwdrivers for tightening nuts, bolts, self-tapping screws, etc. The clamps used to secure sewer pipes are made both metal and plastic. Both types are very simple and convenient during the installation process. Fastenings for plastic sewer pipes: a – for adjustment; b – for driving; c – for a screw connection. In addition, pipe manufacturers often, for the convenience of consumers, produce fasteners complete with pipes, couplings, angles and other basic elements of the sewer system.
Therefore, there is no question of choosing between different types of clamp fasteners. When choosing between plastic and metal clamps, you must also pay attention to the aesthetic component of the room where the sewage system will pass, especially if the latter is open, not hidden inside interior structures or walls. In this case, plastic clamps look more attractive and less noticeable. Although, of course, usually the sewerage system is not located in places accessible to public viewing, so fasteners for it are selected based on other factors.
For example, according to the principle of fastening, which can be fixed, blind or loose, not tightly tightened. Types of fastening sewer pipes: to the wall, to the screed. It is very important to understand that fastening with the same clamp can be done rigidly, tightly, with a strong by clamping the pipe, or can be done with some understretching. The last fastening is called floating and is performed to ensure the integrity of the pipes during thermal deformation. The same types of clamps are used for both fastenings.
However, there are also fasteners that can only be used for floating fastening. Typically, such clamps do not have clamping or tightening bolts. At the same time, such fasteners are very convenient, since they snap into place very simply and do not require the use of special equipment for their installation. An important component of the design of the clamps are special gaskets that are located between the female, clamping part of the fastener and the pipe.
The main function of the gasket is to absorb noise that may arise due to vibration and internal loads on the sewer. Having examined the main types of clamps and their design features, let us turn to several basic rules for installing these fasteners. Installation diagram of a sewer outlet. Fastening of retaining elements is carried out in accordance with certain requirements and rules. The sewer system is a complex complex of various elements that will subsequently be subject to various influences: load, vibration, corrosion, clogging.
In this regard, it is necessary to adhere to certain recommendations and rules during installation of the system. Rule one: location of fasteners. It is very important to correctly calculate the location of all clamps. Fastenings are made where the sewerage system has bends, branches, reinforcement fastenings, and connections between pipes.
To correctly calculate the location of the clamps, you must first draw up a general layout of sewer pipes. This scheme can be marked with center lines directly on the walls. Rule two: pipe slope. It is necessary to fasten the clamp holders in such a way that the minimum slope of the sewer pipe is at least 20 mm per linear meter of pipeline.
In this case, frequent perpendicular turns should be avoided, which are the most dangerous from the point of view of clogging in places of the sewer. Rule three: alternating rigid, fixed clamps and floating fasteners. Each pipe must be secured with at least one rigid, non-slip fastener, usually located at the base of the pipe - the point of its connection with other sewer elements. At the same time, fastening rules require alternating different types of clamps: rigid and floating. Rule four: the distance between fasteners.
When installing plastic or metal-plastic sewer pipes, their fastening is carried out based on a 2-meter distance between the clamps. If heavier metal pipes are used, then it is advisable to fasten them more often, somewhere around 1-1.5 meters. Rule five: reliability of fastening. During operation, sewer pipes are subject to certain loads, vibrations, and temperature changes.
This means that they must be securely fastened to walls or other load-bearing surfaces. The dowels or anchors of the clamps must be firmly held in the supporting material, which must not crumble or crack. Sometimes, due to the inability to securely fasten the clamp, you even have to change the original pipe laying scheme. Thus, by following these basic but very important rules, you can simply install a sewer outlet yourself in your own private home.
Moreover, manufacturers of all structural elements and materials today take utmost care of convenience and ease of installation. All fasteners, clamps, connecting elements and gaskets are installed very simply. Their installation does not require the use of special tools or special professional skills. Share a useful article: Similar articles:
Content:
1. Fastening sewer pipes with clamps
2. Types of clamps for fastening to the wall3. Installation of sewerage pipes4. Laying pipes in the wall
In order for the sewerage system to work normally, and for various kinds of problems not to arise during its operation, it is necessary to properly fasten the sewerage pipes to the wall. When laying open, clamps are used, which make it possible to fix parts of the structure in accordance with the design.
It is important to maintain the alignment of different sections of pipes: if this rule is not followed, thermal expansion will not be balanced, and structural problems will not be long in coming. Sometimes the pipeline is installed using a closed method, and this arrangement of the structure also requires special attention. This article will discuss how to secure sewer pipes in different conditions.
Important points
There are several important recommendations that, if followed, will help you avoid mistakes:
- The deviation of pipes in a vertical position should not exceed 2 mm (per 1 m of length).
- The clamp must not be placed in the area where pipelines are connected to each other.
- When sealing fasteners, it is strictly forbidden to use wood plugs or welding.
- Riser pipes in industrial buildings are attached every 3 m (according to SNiP). SNiP is a set of regulations devoted to construction.
- Riser pipes in residential buildings are fixed if the height of one floor is over 3 m. This applies to steel pipelines.
- Plastic sewer pipes should be strengthened, not forgetting the slope.
Before finally installing the clamps, it is necessary to calculate the connections with the pipes, with the exception of soft types of fixation. For socket connections, rubber rings are used. Compensation type pipes are used only once.
Table of installed parameters
Fastening polypropylene pipes
The gap between the fastenings of polypropylene pipes is calculated during design. This step, coupled with rigid fixation, ensures longer operation. In this situation, fasteners that have a rubber gasket in their design will come in handy.
Fastening polypropylene pipes
The distance between the fastenings of polypropylene pipes according to SNIP directly depends on:
- temperature regime of the distilled substance;
- content of aluminum or fiberglass in the pipe wall;
- coefficient of linear expansion in a polypropylene pipeline;
- thickness, diameter and material of pipe manufacture;
- additional loads.
Ignoring these factors will negatively affect the service life and throughput of the pipeline. If the distance between the fasteners is too large, the supports will become pinched and the polypropylene pipes will bend, which will lead to the destruction of the entire system.
It is quite difficult to independently calculate the distance between clamps for PVC pipes. To facilitate this task, manufacturers of building materials include instructions for use with their products (polypropylene pipes), which contain an explanatory table (calculation depending on the diameter of the pipe and the temperature of the liquid being passed through). Example in the photo.
If the company is reliable, then the technical catalog is publicly available. In the absence of information about the distance between the fasteners, professionals advise making small gaps between the clamps.
This method has two disadvantages:
- Installation of polypropylene pipes will take longer than previously expected.
- You will have to purchase a number of additional clamps.
Fastening sewer pipes
The design of a sewerage pipeline is carried out taking into account the relevant regulatory documents (SNiP). Fastenings will be necessary; without them, the sewer system will not function normally, since its alignment will be lost. In this case, not only a clamp is used, but also a plastic clip.
In the first case, the material from which the pipe is made does not matter (iron or PVC). In the second, in addition to the clip itself, you will need a dowel. If the sewer pipeline contains PVC, then its diameter will not be large. The reason for this is that plastic is not designed to bear too much stress. The size of the clip varies between 16-50 mm. It is not used for fixing the pipe to the floor.
Fastening sewer pipes
Steel or iron sewer pipes do not change under the influence of high temperature, which cannot be said about those made of PVC. This process is compensated by a clamp. In this case, both rigid and floating methods are used.
The distance between the fastenings of PVC sewer pipes is determined by the plan of the sewer system. Fastening is carried out using a minimum gap. The frequency is 40 cm with a diameter of 50 mm. Further indicators increase proportionally, for example, if the diameter is 100 mm, then the distance from one fastening to another is 80 cm.
Pipe marking
The installation of the pipeline on the ceiling is carried out in the same way; it is usually carried out in the basement. It is prohibited to use fasteners in the form of clamps on bends; there must be a distance of 1.5 inch. It is necessary to fix the connection between the fitting and the pipe.
Steel pipeline fastening
The distance between the fastenings of steel pipes according to SNiP depends on the diameter. If the nominal diameter reaches no more than 20 mm, then the gap between the clamps should not exceed 2.5 m. With a diameter of up to 32 mm - 3 m.
For a hole with a radius of 40 mm, a distance of 4 m is needed. When laying a steel pipeline openly, the master will need clamps and brackets. The use of welding (gas or electric) is strictly prohibited. Steel pipelines laid using a trenchless method are not considered operational.
Fastening sewer pipes with clamps
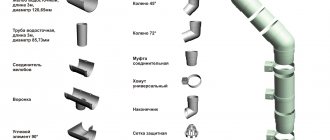
Pipeline installation should be based on some calculations shown in the system design. Thus, the pipeline should not have different voltages, and thermal expansion should be provided for. Fastenings for sewer pipes are most often special clamps. They have rubber seals that ensure reliable coverage of the pipe around the perimeter of its outer section. Some clamps are not equipped with rubber liners, so in this case, elements with a smooth working surface and rounded inner edges are used. Sewer pipes are secured to the wall using different types of clamps. Structurally, a standard clamp consists of two semicircular ties that allow you to completely grip the pipe. A distinctive feature and advantage of clamps is the ability to adjust them to the diameter of the pipe. All clamps are divided into several types.
One of the characteristics that allows us to classify plumbing clamps is the material used for manufacturing:
Metal. Metal clamps allow for the most rigid and powerful fastening.
Plastic. Plastic clamps can not only secure the pipe tightly, but also provide a movable connection. Such clamps are practical and low cost.
Another feature that divides clamps into types is the type of fastening.
There are two types of fastenings:
Hard. Such fasteners for sewer pipes completely block their movement. As a rule, a rigid connection is used in cases where the pipeline must be fixed motionless, for which clamps are attached below the socket at a point as close as possible to it.
The rigid support of the fastening in this case is the fitting and its group. Floating. For such fastening, you can use the same clamps, but they should not be tightened completely so that the pipe can move inside the connection. This design is possible if the internal cross-section of the clamp is slightly larger than the external diameter of the pipe being secured.
To secure the pipes to the wall, you need the appropriate materials and tools:
- pipes and fittings; fastening clamps; supports; brackets; suitable tools.
The procedure for attaching pipes looks like this:
When laying the pipeline, it is necessary to take into account possible temperature changes.
For example, in a warm room they will be absent, so the sewer pipes are fixed to the ceiling or wall, because the pipes will not move along their axis. Fixation of pipes is carried out in places of bends, turns and fastening of fittings. Installation of movable supports is necessary if the pipes will expand under the influence of temperature.
In this case, the pipeline will be able to easily change its size, but it will not be able to deviate from the charted course. Before laying pipes, you need to mark on the wall the axes along which the pipeline will run. All supports are installed along the marked line so that the pipes stand in place.
To attach the supports, you can use self-tapping screws or dowels - the choice will depend on the material of the walls. When installing pipes at a distance from the wall, brackets are used. In any case, after installing the fasteners, you can proceed directly to laying the pipeline.
First, the pipe is mounted on a support. After this, the sewer pipes are secured to the wall using a fastening clamp. Most clamps are equipped with rubber cuffs, which not only compensate for thermal expansion, but also dampen vibration and noise.
The clamp is secured using a metal pin. The distance for fastening sewer pipes must be calculated in advance, knowing the material of the pipes: for plastic structures the distance is usually about 2 m, but heavier metal pipes need to be fastened more often. It is best to install pipes in grooves or channels.
As a result of this installation, the pipes will be fixed as securely as possible, and their insulation will be at the highest level. Both when calculating the project and when laying pipes, it is important to remember that it is necessary to observe a mandatory slope (minimum 2 cm per 1 meter), which ensures the movement of liquid inside the pipes. Also, when laying, it is advisable to minimize the number of right angles in order to prevent possible clogging of the system.
To lay pipes in masonry, it is necessary to prepare a channel to reduce the internal stress of the pipeline. Before placing the pipelines in their place, it is necessary to wrap all parts of the structure with soft material: mineral wool, glass wool or corrugated cardboard are suitable. If pipes in some area are exposed to high temperatures, it is worth reducing this effect by using insulation.
Horizontal laying of pipelines in collectors or connecting structures where there are several lines that require fastening to the wall must be carried out using supports in all areas of the system. When performing this work, it is important to remove all factors that impede the linear expansion of parts.
When laying pipes through ceilings, two aspects must be ensured: waterproofness and sound insulation. To achieve this effect, you will have to use high-quality cladding. When laying a sewer outlet through an asphalt covering, the pipeline is protected by ceiling cladding, protective pipes or a layer of thermal insulation. In addition, this design often involves the installation of fire safety equipment. Laying pipes in concrete requires that the attachment of sewer pipes to the wall be as reliable as possible, but it is also very important to provide free space for pipe expansion. In addition, the system is installed so that the pipes do not move during concreting. To protect the pipeline from the ingress of solution, it is necessary to properly seal all openings of the system.
Content:
The laying of sewer pipelines in private homes and cottages has recently become quite commonplace, since every person wants to live in comfortable conditions. In order for such a sewer system to last long enough and without failures, a number of rules must be taken into account during its installation, as well as the correct types of fasteners must be used. This article will tell you how to fasten sewer pipes, as well as what rules should be followed when performing installation work.
Types of fasteners
The standard fastening for sewer pipes to a wall or other support is a special clamp. This is a universal element capable of holding any round pipelines. There are different types of fasteners:
- crimp . Capable of simultaneously performing two functions - holding the pipeline and sealing the connection;
- guides _ Used only to indicate the position of the pipe relative to the supporting structure;
- support . They can fix pipes to vertical and horizontal planes - to walls, floors or ceiling slabs;
- safety . These elements are installed as additional support for complex system components.
To assemble PVC sewer systems, fasteners for sewer pipes of 110 or 50 mm are used. These are the most common sizes for vertical and horizontal pipelines.
Two types of installation are used:
- hard . The pipeline is tightly clamped with a clamp and fixed in a stationary state. This method is used for vertical pipelines (risers) that require complete immobility;
- movable _ The pipeline has the ability to move inside the clamp. This method is used for horizontal pipelines (beds), which do not need to be rigidly attached to supports. Mobility allows you to compensate for thermal expansion of the plastic.
In order to ensure free movement of the pipe, fasteners of a larger diameter are chosen. Any sewer clamp is manufactured in accordance with pipeline standards. Before starting assembly, you need to count the number of clamps. It is important to consider which areas will be rigidly fixed and which will be movable.
You may also like:
Plastic clamps
These are fasteners made of PVC of the same brand as the pipelines. There are clamps for all available diameters of system parts. The design of fasteners varies according to the assembly method:
- an element of two halves connected with screws. It is attached to the supporting planes using a pin screwed into a dowel. Provides a strong and rigid connection;
- clamp equipped with a movable latch. The pipe is inserted into the bracket, and the latch wraps around it from above and is fixed on a special protruding tooth.
The first type of clamps allows you to adjust the distance from the wall to the pipe. This is provided by a pin, which can be immersed deeper into the wall or slightly unscrewed from the fastener itself. The second type is convenient for assembly, as it does not require the use of additional tools. In this case, clamps with a latch are tightly attached to the support at a fixed distance from it.
Metal clamps
Metal fasteners are load-resistant. They usually consist of two halves that are connected with screws. Both parts have rubber gaskets that seal the connection and cut off the metal from the pipeline. Before fixing the sewer pipe to the wall, you only need to mark the axis and place the installation points for the clamps on it. It is important to remember the need to create a slope, for which the axis is immediately placed at an angle. For a diameter of 50 mm it is 30 mm for each meter of length.
Let's look at how to attach sewer pipes to the wall using metal clamps. The studs for such fasteners have two types of cutting. At one end there is a thread for attaching the lower half of the clamp, at the other there is a standard thread, like a screw. When installing, first drill a hole for the dowel. Then install the stud using a wrench or pliers. The gap between the two types of cutting is shaped like a hexagon. This section is used to install the element into the dowel. The last step is to screw the clamp half onto the stud. Then all that remains is to install part of the system and screw the upper part of the fastener.
Types of clamps for fastening sewer pipes
The sections of sewerage pipes are secured to each other using clamps, that is, the fixation is done by grasping the product. The entire structure of such fastening of sewer pipes, in addition to the clasping element, also consists of an anchor or dowel device with which the clamp is attached to a supporting structure, for example, to a wall. Therefore, for such work, you may need a drill or hammer drill, as well as wrenches and screwdrivers to tighten nuts, bolts and screws.
Workshop
So, you have a pipeline diagram ready and outlined. The necessary materials have been collected. You can start fastening.
Fixing the pipe to the wall requires a minimum distance. A similar requirement applies when attaching the duct to the ceiling. If you need to move away from the wall, you need to use a special metal bracket. Using a hammer drill, a hole is made in the supporting structure into which the dowel is driven. A clamp with a pipe is attached to it. After this, the side screws fix the desired position of the water supply.
At what distance are the fasteners installed? SNIP dictates the standard 10D, where D is the diameter of the channel. This means that pipe 50 is fixed every 50 cm, and pipe 100 is fixed every meter. Vertical risers are attached every 1-1.5 meters.
You should retreat 15 cm from curved sections. The joining of pipe parts and fittings is strengthened using crimp clamps. The minimum distance from the walls is 5 mm. If there is tight contact, the pipe may be damaged due to constant friction and vibration.
Metal and plastic clamps
A clamp for a sewer pipe can be made of either plastic or metal (for more details: “Which metal clamp to choose for fastening pipes and how to use it”). Both versions of these products are widely used in plumbing work, and their installation is not difficult.
Moreover, many manufacturers produce sewer pipes that are already equipped with all the necessary fasteners (couplings), angles, bends and other parts. This greatly simplifies the process of purchasing components for installing home sewage systems for consumers.
It is worth noting that when choosing what material the sewer pipe clamp will be made from, it is worth taking into account the location of such communications. In particular, this applies to those systems that will not be hidden behind wall panels or other interior elements. In this case, plastic products will look more inconspicuous, although the sewerage system itself is usually not on public display and is located in places where it will not be visible to anyone.
However, in most cases, the process of selecting sewer pipe fastenings is still based on slightly different factors. In particular, the type of fixation may matter, that is, fixed (fixed) or free (floating).
What's better?
Clamps seem to be more universal means of fastening. They can implement both rigid and floating fastening technologies. To do this, it is enough to adjust the tightening force of the screw connections.
They can handle any pipe diameter and are suitable for installing sewer lines made of both metal and polymer. The use of products with dowel nails increases the speed of pipeline installation by an order of magnitude, without in any way reducing the quality of fastening.
Ceiling and wall fixing options
Rigid or floating fixation
Please note that there can be two ways to secure a sewer pipe with a clamp: screw the fastener tightly and make it absolutely motionless; leave the screws slightly undertightened to compensate for the thermal expansion of the pipes - this type of fastening is called floating. In this case, you can use the same clamps.
At the same time, there are types of fasteners on sale that are only suitable for free, floating type of installation. As a rule, such products do not have tightening bolts. However, they are attached much easier - with latches, so no special devices are needed for their installation.
The design of the clamps must have special gaskets. They are placed between the pipe and the clamping part of the clamp. The main task of such a gasket is to absorb noise resulting from the load on the sewer pipe and vibration from the movement of wastewater.
Having understood the types of fasteners and the main materials for clamps, we present several main rules that are relevant when installing fasteners on sewer pipes.
Distance between fasteners
In order for the floor heating system to work efficiently and without unnecessary costs, you need to calculate the optimal pitch between the pipes in the floor. The standard distance is from 10 to 20 cm. The step can be either constant or variable:
- a constant contour step of 20 cm wide is used for systems with a heating load of up to 50 W per 1 sq. m;
- a distance of 15 cm is made with a heating system load of 80 W per 1 sq.m.
Variable pitch is used in other cases. If the installation of a water circuit near external walls is done with a distance of 10 cm, then, moving towards the center, this distance is gradually increased to 20 cm. For economical floor heating, it is recommended to make a distance of 15 cm.
Rules
When designing and installation work, it is necessary to use the rules and requirements set out in the following documents:
- SNiP 2.04.01–85: Sanitary Norms and Rules “Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings”;
- SNiP 2.04.03–85: Sanitary Norms and Rules “Sewerage. External networks and structures."
For internal sewerage:
- The productivity of the spillway system, on average, should be calculated based on consumption rates per person of 100–200 liters per day.
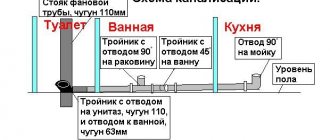
- The toilet is installed separately. The entrance to the main riser is a self-connection. There should be no other plumbing fixtures between it. When there is a massive release of water, a local hydraulic shock occurs. The result is the suction of liquid from the siphons, which acts as a water seal. It follows that the toilet must close the chain in the general drainage system.
- The diameter of the outlet pipes is the same size or increases as it approaches the main riser.
- The distance of the toilet from the riser should not exceed 1 meter. Other sources of waste – no more than 3 meters.
Approximate data for the installation of plumbing fixtures and slope:
| Plumbing device | Standard slope indicator | Distance from the main riser (drain) and the device, no more, cm | Diameter of drain pipes, not less, mm |
| Bath | 1 : 30 | 100–130 | 40 |
| Toilet | 1 : 48 | 150–170 | 40 |
| Shower cabin | 1 : 20 | up to 100 | 40 |
| Wash basin | 1 : 12 | up to 80 | 40 |
| Bidet | 1 : 20 | 70–100 | 30–40 |
| Kitchen sink | 1 : 36 | 130–150 | 30–40 |
| Combined drain (bathtub, sink, shower) | 1 : 48 | 170–230 | 50 |
| Central riser | 100 | ||
| Branches from the riser | 50–70 |
Ventilation must be provided. This could be the main riser facing the roof. Or a separate fan pipe.
Note. You cannot combine a general ventilation system and a vent riser. In this case, unpleasant odors will be able to enter the living quarters.