When equipping a well, special attention is paid to the selection of pipes for drilling (casing). Pipes are needed so that water from the aquifer gets into the wellbore through a filter, and a submersible pump pumps it to the surface. In addition, the columns serve to strengthen the wellbore and isolate it from the upper aquifers.
Before you start drilling, it is advisable to find out which pipes are best for the well.
Casing pipe: properties and purpose
A water well for a private house is a small-diameter vertical channel drilled in the ground using a special installation. Its depth often reaches several tens or even hundreds of meters. To prevent the destructive effects of natural factors on its walls and preserve the original quality of water extracted from deep layers, a special casing pipe is used for the well.
From the technical side, it performs the following number of functions:
- Prevents wall collapse and ensures the safety of water intake parameters throughout the entire period of operation.
- Eliminates the penetration of ground and surface flows into the watercourse due to the complete sealing of the tunnel.
- Prevents contamination and destruction of equipment from silt, soil particles, suspended particles, and aggressive substances.
- Maintains the original diameter of the well and protects it from ground displacements.
- Provides resistance to the pressure of soil masses.
Diagram of a well with casing Source housecomputer.ru
If drilling is carried out in hard rock or to a shallow depth with a guarantee of maintaining the original parameters of the channel, then a well without casing is allowed. However, most often a pipe string is still installed. Moreover, it can be either single or double.
In the first case, the casing simultaneously plays the role of both a protective contour and a working artery - through which water is directly drawn. The second option is when a separate pipe is installed inside the protective circuit. As a rule, such a need arises when quicksand is detected at the drilling site or there is a high probability of upper runoff entering the well, as well as wall collapse.
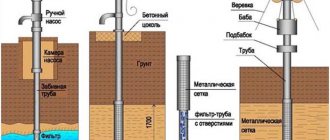
Well casing device
If you plan to do the installation yourself, you need to study the design of the structure:
- initial filter - made in the form of a mesh product, installed to retain large fractions;
- gravel cushion at the bottom of a hydraulic structure - prevents groundwater from penetrating into the well;
- cap - prevents precipitation and dirt from getting inside.
Installing a filter is not enough to equip a well. To do this, it is necessary to correctly assemble (if it is not solid) and fix the column.
Selection rules
There are two types of criteria, consideration of which allows you to accurately decide which pipe is best to use for a water well, these are:
- Technical.
- Operational.
Factors of the first category include:
- Diameter.
- Method of connecting pipe sections.
- Type of material.
Choosing the diameter of the casing pipe Source ytimg.com
The diameter of the casing pipe for a well is calculated using a special formula, taking into account a number of parameters. It is generally accepted that along the internal contour its value should be at least 110 mm. This is due to two reasons - optimal water intake conditions and the selection of submersible pumping equipment of suitable dimensions.
The well will have better performance characteristics when the pipe segments are fastened with a threaded connection. It will ensure maximum tightness, strength and durability of the casing. In most cases, the installation company decides what diameter the installed pipe string should be and what type of connection is required for it in a particular case.
Factors of the operational category of criteria for choosing a pipe for casing:
- Inertness of the material relative to aggressive environments.
- Resistance to external compression of soil masses.
- Endurance relative to mechanical loads - to ensure integrity during transportation and installation.
- Increased resistance to corrosion.
- Long service life.
- Optimal cost.
Three modern materials meet the requirements: steel, plastic and asbestos cement.
Note! Which pipes are best to use for a water well must be decided in advance - before searching for an installer. Typically, a company works with only one material and has in its arsenal special equipment and proven technology for a specific type of pipe.
Casing pipe with thread Source vostokpipe.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in water supply, sewerage and related work
Casing pipes
Casing pipes are high-strength pipes of large diameter - Ø 114 - 508 mm.
Purpose of casing pipes:
- fastening the well walls after drilling,
- overlap and isolation from each other of oil-bearing, gas-bearing, aquifer-bearing formations and interlayers.
Casing pipes and couplings for them are made from steel grades of strength groups C, D, K, E, M, P with normal extended thread.
Pipes are supplied in lengths of 9.5 - 13 m.
Each supplied set of pipes is supplied with a certificate certifying the quality of the pipes and the standard.
On each pipe, at a distance of 0.4 - 0.6 m from its end, free from the coupling, a stamp is knocked out, which indicates:
- Nominal diameter, mm
- Steel strength group
- Thread length
- Wall thickness, mm
- Manufacturer's trademark
- Month and year of issue
Pipes of steel strength groups K, E, L, M, R are subjected to heat treatment.
The coupling threads must be galvanized. The tightness of pipe connections is ensured by conical sealing surfaces located at the end of the pipe. The connection is provided with a contact along the internal stop ends, which fixes the specified tension when securing the connection. Domestic industry produces casing pipes of the following designs:
- couplings with short and long conical threads of triangular profile (GOST 632-80);
- couplings with a conical thread of a triangular profile and strengthened ends due to reduction (TU 14-3-1076-82);
- couplings with a conical thread of a trapezoidal profile (type OTTM according to GOST 632-80);
- couplings with a conical thread of a trapezoidal profile and conical sealing bands at the ends behind the thread on the side of smaller diameters (type OTTG according to GOST 632-80);
- OTTM type with sealing anti-seize coating on coupling threads (TU 14-3-1417-86);
- according to GOST 632-80 with a sealing unit made of polymer material (TU 14-3-1667-89);
- couplings with a persistent conical thread of a trapezoidal profile “Buttress” (TU 14-3-1678-89);
- electric-welded couplings with persistent conical thread “Buttress” (TU 14-3-1599-88);
- electric-welded couplings with persistent conical thread “Buttress” with a sealing unit made of polymer material (TU 14-3-1732-90);
- coupling-free, thick-walled, high-strength OTTM type threads (TU 39-0147016-28-92);
- coupling type OTTM with increased resistance to crushing (TU 39-0147014-20-91).
Manufacturers:
- Taganrog Metallurgical Plant (TMZ)
347928 Taganrog, Rostov region, st. Zavodskaya, 1 tel. 5-03-02 teletype 298202, telegraph “Rent”
- Vyksa Metallurgical Plant (VMZ)
607030 Vyksa-7, Nizhny Novgorod region, tel. 9-30-97 teletype 151332, telegraph "Voskhod"
- Seversky Pipe Plant (SevTZ)
624090 Polevskaya Sverdlovsk region. tel. 21-01 teletype 348873, telegraph “Luch”
- Sinarsky Pipe Plant (SinTZ)
623401 Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk region. tel. 6-32-73 teletype 348416, telegraph “Morning”
- Chelyabinsk Pipe Rolling Plant (ChTPZ)
454129 Chelyabinsk, st. Mashinostroiteley, 27 tel. 55-74-32 teletype 124113, telegraph "Coat of Arms"
- Volzhsky Pipe Plant (VTZ)
404119 Volzhsky, Volgograd region. tel. 4-43-57 teletype 310122, telegraph "Volzhsky Pipe"
- Nizhnedneprovsky Pipe Rolling Plant (NDTZ)
320060 Dnepropetrovsk-60, st. Stoletova, 21 tel. 20-73-03 teletype 143217, telegraph “Dnepropetrovsk-81, Liebknecht”
- Nikopol South Pipe Plant (YUTZ)
322901 Ukraine, Nikopol, Lenin Ave., 56 tel. 28-33-08 teletype 349326, telegraph “Luna”
- Azerbaijan Pipe Rolling Plant (AZTZ)
373200 Sumgait, Azerbaijan tel. 3-99-11 teletype 142110, telegraph Aztrub
- Rustavi Metallurgical Plant (RMZ)
383040 Georgia, Rustavi, st.
Gagarina, 12 tel. 19-20-10 teletype 327275, telegraph “Steel” Casing pipes are made from steels of strength groups D, K, E, L and M, the mechanical properties of which are given in table. 88.
Pipes, casing couplings
(GOST 632-80) have a short and long conical thread of a triangular profile with a taper of 1:16 with a pitch of 3.175 mm and a profile angle of 60? (drawing).
The thread is seated on the sides of the profile. The tightness of the connection is created by compaction of thread compound in the gaps during mechanical screwing.
Connections with extended threads (U) have greater tightness and resistance to tensile loads.
Manufacturers:
1. AzTZ - pipes with dimensions of 114, 127 and 146 mm;
2. SinTZ - 146 mm; 3. TMZ - 140, 146 and 168 mm; 4. YuTZ - 146...325 mm; 5. RMZ - 219 and 245 mm; 6. NDTZ - 245, 273, 299 and 324 mm; 7. ChTPZ - 351. 377 and 426 mm.
The geometric parameters of the pipes are given in table. 89.
Note. Pipe length L ==9500… 13000 mm; allowed in a batch of pipes with a length of 8000...9500 mm - up to 20% and with a length of 5000...8000 mm - up to 10%.
Coupled casing pipes with conical threads of triangular profile and strengthened ends due to reduction
TU 14-3-1076-82) (figure).
A distinctive feature of a threaded connection is that the threaded section from the end of the pipe to the main plane is conical with a constant wall thickness and a taper equal to the taper of the thread (see figure).
In this case, the wall thickness under the thread increases, which ensures an increase in the critical tensile force. In order to ensure the passage of rock cutting and other tools, a special chamfer is made at the ends of the pipes.
Manufacturer:
NDTZ - pipes of sizes 245, 273, 299 and 324 mm of strength groups D, E and K
The geometric parameters of the pipes are given in table. 89.
Casing pipes with conical threads of trapezoidal profile, type OTTM (GOST 632-80) (picture). A connection with a trapezoidal thread ensures good make-up without distortions or jamming, and the number of revolutions during make-up is reduced.
The connection provides high strength under tensile loads, minimal column dimensions, and high tightness. The OTTM thread has a taper of 1:16, a thread pitch of 5.08 mm, and fits along the inner and outer diameters of the thread. The tensile strength of OTTM pipes is 25...50% higher than that of casing pipes with triangular threads.
Manufacturers:
1. AzTZ - pipes measuring 146 mm;
2. YuTZ - 146 mm; 3. NDTZ - 146, 245, 299 and 324 mm; 4. SinTZ - 146 mm; 5. TMZ - 140, 146 and 168 mm; 6. VTZ - 168, 245 and 324 mm; 7. SevTZ - 219 and 245 mm.
The geometric parameters of the pipes are given in table. 90.
Note. Pipe length L = 9500… 13000 mm; allowed in a batch of pipes with a length of 8000...9500 mm up to 20% and with a length of 5000...8000 mm - up to 10%.
Casing pipes with conical threads of trapezoidal profile and conical sealing belts type OTTG
(GOST 632-80) (figure), provide high tightness of the connection and are intended for fastening wells with formation pressure of 60...100 MPa (see figure).
The threaded part of the OTTG pipe connection corresponds to the OTTM pipe connection.
The tightness of the connection is ensured by conical sealing bands located behind the thread on the side of smaller diameters.
The magnitudes of the destructive loads of OTTG pipes are equal to the destructive loads of OTTM pipes.
Manufacturers:
1. TMZ - pipes measuring 168 mm;
2. VTZ -168 and 245 mm; 3. SevTZ - 219 and 245 mm.
The geometric parameters of the pipes are given in table. 91.
Note. Pipe length L = 9500… 13000 mm; allowed in a batch of pipes with a length of 8000...9500 mm up to 20% and with a length of 5000...8000 mm - up to 10%.
Casing pipes type OTTM with sealing anti-seize coating of coupling threads
TU 14-3-1417-86) (figure). A distinctive feature of these pipes is the application of an anti-seize sealing coating with a thickness of 29...30 and 30...50 microns to the threads of the couplings.
The coating improves the make-up of a threaded connection, reduces the torque during assembly by 10...20%, and eliminates jamming in the thread when assembling pipes in the factory and in the well.
When the coating thickness is 30...50 microns, the structural and technological gaps in the threaded connection are filled with zinc, which ensures high tightness of the connection.
The presence of a coating of increased thickness on the threads of the couplings eliminates friction of the “steel on steel” pair, as a result of which make-up and unscrewing of the connection is possible at least 2 times without compromising its strength and tightness.
Manufacturers:
1. NDTZ - pipes with dimensions of 146, 245, 299 and 324 mm;
2. SevTZ - 219 and 245 mm.
The geometric parameters of the pipes are given in table. 90.
Casing pipes in accordance with GOST 631-80 with a sealing unit made of polymer material
(TU 14-3-1667-89) (drawing). A distinctive feature of the threaded connection is the presence of special grooves in the couplings to accommodate sealing rings made of polymer material.
The dimensions and location of the grooves ensure that the operational characteristics of the pipes remain unchanged with high tightness of the connection (Table 92).
The remaining geometric parameters of the pipes must correspond to those given in table. 89.
Manufacturers:
1. TMZ - pipes with dimensions of 140, 146 and 168 mm;
2. SinTZ - 146 mm;
3. SevTZ - 219 and 245 mm.
Pipes of all strength groups are manufactured in accordance with GOST 632-80.
Casing pipes with persistent conical threads of trapezoidal profile “Buttress”
TU 14-3-1678-89) (figure) provide high tightness of the connection and increased strength under tensile loads compared to triangular threads.
The performance characteristics of pipes with Buttress threads are similar to OTTM pipes in accordance with GOST 632-80.
Buttress and OTTM threads are not interchangeable due to different lengths.
Manufacturer:
SevTZ - pipes with dimensions of 219 and 245 mm.
The geometric parameters of casing pipes with Buttress threads are given in Table. 93.
The remaining geometric parameters of the pipes must correspond to those given in table. 90.
Electric-welded casing pipes with persistent conical thread “Buttress”
(TU 14-3-1599-88) (figure) are characterized by increased accuracy in outer diameter and wall thickness (see figure).
The strength of the threaded connection in relation to the strength of the main body of the pipe is 0.9 and is at the strength level of hot-rolled OTTM pipes. The welded joint is of equal strength to the pipe body.
Manufacturer:
VSW - pipes in sizes 146, 168 and 245 mm.
The geometric parameters of the pipes are given in table. 94.
Note. Pipe length L = 11000×200 mm.
Electric-welded casing pipes with Buttress threads and a sealing unit made of polymer material
TU 14-3-1732-90) (figure) are intended for fastening gas-lift and gas-condensate wells in the temperature range -60... +250? C (see figure, table 95).
The dimensions and location of the grooves for placing O-rings ensure high tightness of the connection.
The operational characteristics of the pipes are similar to pipes according to TU 14-3-1667-89.
Manufacturer:
VSW - pipes in sizes 146, 168 and 245 mm.
The remaining geometric parameters of the pipes must correspond to those given in table. 94.
Casing pipes type OTTM, couplingless, thick-walled, threaded, high-strength
TU 39-0147016-28-92) (figure) are designed for fastening wells with high external crushing pressure.
A distinctive feature of the connection is the introduction into the design of the OTTM thread of an additional seal “A” at the end of the nipple end and “B” at the end of the coupling end, which ensures high tightness of the pipes (see figure).
Manufacturer:
SevTZ - pipes measuring 245 mm of strength groups L, M and R.
The geometric parameters of coupling-free thick-walled casing pipes are given below.
The critical crushing pressure for pipes of strength groups L is 110 MPa, M is 125 MPa.
The calculated hydraulic pressure for pipes of strength groups L is 102.6 MPa, M is 118.7 MPa, P is 145.7 MPa.
Casing pipes with increased resistance to crushing
TU 39-0147014-20-91 (figure), which is achieved by reducing the ovality of pipes during their manufacture, have critical pressure characteristics higher by approximately 8% compared to pipes manufactured according to GOST 632-80 (see figure) .
Manufacturer:
SevTZ - pipes measuring 245 mm with a wall thickness of 7.9; 8.9;
10.0; 11.1; 12.0 mm and 219 mm wall thickness 7.7; 8.9; 10.2;
11.4; 12.7 mm strength groups D, E, L and M.
Pipes manufactured according to TU 39-0147014-23-91 have critical pressure characteristics that are 15...20% higher compared to pipes manufactured according to GOST 632-80.
Manufacturer:
VMZ - pipes measuring 146 mm with a wall thickness of 7.0; 7.7 mm;
168 mm wall thickness 7.3; 8.0; 8.9 mm; 245 mm thick
walls 7.9; 8.9 mm strength group Ds categories I and II.
The remaining geometric parameters of the pipes must correspond to those given in table. 89 and 94.
Types of pipe material
Those who first encountered such a water supply to their home from deep sources often have the question of which pipe is better for a well - steel or plastic. However, in reality, there is also a third option - asbestos-cement. Let us analyze the features of application, their positive and negative properties in more detail.
Steel
Steel alloy is the most common casing material. Most companies offer rolled steel pipes for casing formation. The main reason is that its service life is similar to the period of operation of the well itself. However, due to the wide variety of ferrous metal products, some companies offer an alternative.
Casing steel pipes Source geolog.ru
To the natural question of the average consumer, what kind of steel pipes are used for a well, the answer is the following number of options:
- Cast iron.
- Enameled.
- Galvanized.
- Stainless.
- Metal-plastic.
The advantages of steel pipes include:
- Resistance to damage during installation and transportation.
- Not subject to soil compression.
- More than half a century of service life.
- Possibility of clearing a channel when clogged with silt using drilling technologies.
- Preservation of original parameters until the end of operation.
- Maximum well depth.
Among their disadvantages are:
- Susceptibility to corrosion.
- Penetration of rust into the water supply.
- High price.
Alternative options do not have some disadvantages - for example, they do not rust. However, the natural price for this is a significant increase in the cost of the project.
Casing metal-plastic pipes Source remoskop.ru
Steel casing pipe: time-tested!
Wells have been lined with steel profiles for a very long time—decades. Over the past time, they have passed all possible tests with honor in shallow and very deep wells, in soils of all types, confirming their reliability. Soil movements, external pressure of rock and individual stones are not a problem for the steel profile. The service life of a black steel column is 40-50 years. This period is determined by the rate of wall corrosion - 0.1 mm per year. At the same time, a small amount of rust getting into the water is not critical, especially if the water is used regularly.
classic casing pipe - steel 20, service life - 40-50 years
It is appropriate to remember here that the city water supply network also uses black steel casings. Iron comes into artesian water from limestone or other rock! If it were otherwise, then none of the wells lined with plastic or asbestos cement would have had an iron removal filter installed.
The strength of steel profiles allows you to carry out any repair work or well cleaning without fear. The high cost of steel allows shallow sand wells to be lined with durable thick-walled plastic. But for an artesian well there is no alternative to steel. The great depth of aquiferous limestone and long periods of well use require the use of the most reliable materials for casing.
Selection by diameter
The diameter of the casing pipe for a water well is the most important characteristic, without which the drilling procedure will not begin. Its value directly depends on water consumption at peak consumption - that is, when all possible consumers are involved in the facility:
- Kitchen faucet.
- Shower.
- Washing machine and dishwasher.
- Bathroom.
- Garden watering system, etc.
According to regulatory data, the minimum water supply from a domestic well is approximately 700 liters per hour. Further, if we assume that at peak load 5000 liters of water per hour are required, then in accordance with the manufacturers’ recommendations it is necessary to install pumping equipment with a working diameter of 10 cm.
To calculate the internal diameter of the casing pipe, it is necessary to add twice the distance from the casing walls to the working diameter of the pump. If we assume that it is equal to 5 mm (the diameter of the pump should be slightly less than the internal diameter of the casing), then it turns out = 100 + 5x2 = 110 mm. And this is only the internal value of the parameter. The outer diameter of the pipe for a water well will be obtained by adding to it twice the wall thickness of the pipe itself. If it is, for example, 6 mm, then it turns out = 110 + 6x2 = 122 mm. The hole of the channel being drilled is always slightly larger than the diameter of the casing.
Purpose and features of pipes
For drilling, pipes with standard diameters from the following size range are used: 32, 90, 114, 125 mm and above.
The greater the performance of the water supply system and pump, the higher the required pipe diameter. However, you should not take it with excess supply. If the cross-section is too high, the pressure drops and the price rises.
Applicability of pipes of different sizes:
- 32 mm - for supplying water to a height of up to 10 m using an external self-priming pump (hydrophore). A flexible hose is lowered through the pipe to the water;
- 90-125 mm - a submersible pump is lowered into the pipe when the well depth is more than 10 m.
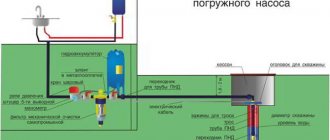
Casing technology
Well casing is carried out using a drilling rig using the following technology:
- At the initial stage, a channel is drilled that is larger than the diameter required - to a depth of at least 5 meters.
- Next, a smaller drill is installed, and drilling continues until the aquifer is reached.
- When water appears in the tunnel, hermetically connected pipe segments are installed.
- Once the required depth is reached, the pumping equipment is immersed.
- The well is being adjusted and tested.
Important! The drilling procedure should proceed evenly, and the casing should descend unhindered. Otherwise, the well pipe will be subject to overstress during installation, which will subsequently lead to rupture of the material and clogging of the well.
Which material is better?
The market is filled with a variety of pipes made from steel and plastic. The following is their comparative characteristics.
Steel: pros and cons
Steel pipes are made from ordinary steel, less often from stainless steel, with galvanized or enamel coating. They have the following advantages:
- mechanical strength - a product with a 6-mm wall can easily withstand any soil displacement and allows you to clean the well without fear of possible damage;
- tightness - individual pipes are welded together, which prevents the penetration of water from the upper layers;
- good maintainability;
- resistance to rust with proper sealing
of the pipe outlet with the head - “there is not enough oxygen in the water for the pipe inside to rust”; - durability - service life is at least 50 years, which is confirmed by real facts.
The disadvantage of stainless steel products is their high cost. Enameled pipes chip during installation, which can lead to rapid corrosion in the future. Galvanized pipes are cheaper, but when interacting with water, zinc oxide is formed - it is believed that it is hazardous to health.
The disadvantages of iron pipes, according to organizations that use PVC pipes, include: the susceptibility of iron to chemical reactions, corrosion instability, short service life (supposedly no more than 10 years), high weight, less hygiene compared to PVC.
Briefly about the main thing
The casing pipe in a well performs the following number of tasks:
- Keeps walls from collapsing.
- Protects against external water flowing into the well.
- Prevents it from clogging.
- Protects the well from destruction and compression by soil masses.
When deciding which casing pipes are better for a well - plastic, asbestos-cement or steel, it is necessary to proceed from the drilling depth, operating conditions and cost of work. When choosing a casing pipe, you should take into account not only the type of material and its properties, but also the way its segments are connected and the diameter, calculated according to the peak flow rate of water consumption. The casing procedure is carried out by specialized companies using special equipment according to the developed technology plan.
Ratings 0
Optimal diameter for casing
Drilling specialists are well aware that the optimal diameter of the well production casing must provide certain needs for high-quality water (subject to competent drilling operations and well construction).
The water supply source must cover the need:
In providing water for domestic needs - the functioning of plumbing, dishwasher and washing machine, etc.;
To provide for special needs - filling swimming pools, operating fountains, and, if necessary, servicing small washing equipment in the garage;
In water consumption for watering lawns, vegetable gardens, flower beds, gardens, and for maintaining greenhouses and greenhouses.
In other words, the choice of the optimal diameter of the well column determines the full water supply of the estate with a residential building and auxiliary buildings, as well as the entire private territory.
Types of materials and their characteristics
Borehole pipes are made of metal, asbestos cement or plastic. Very rarely, when organizing water intake, wooden products are used - they are absolutely environmentally friendly, but, despite the protective treatment, they are susceptible to soil moisture and are prone to deformation.
Type #1 - strength and durability of metal
Metal supply pipes are available in two versions:
- cast iron;
- steel, which can be enameled, galvanized, made of stainless steel.
Very rarely cast iron analogues are used for casing. Among their metal counterparts, these pipes are the most affordable, but the material is very fragile and heavy.
Many companies refuse to work with cast iron due to installation difficulties. In addition, it is impossible to guarantee the safety and tightness of the pipe - when the soil layer moves, the metal can crack
Steel is a traditional, decades-tested material for casing. The steel almost 100% meets the requirements for well pipes.
Products made of ferrous metal adequately withstand testing in wells of different depths, regardless of the type of soil.
The standard wall thickness is 5-6 mm, the service life is about 50 years. Durability is determined by the corrosion rate of the steel sheet - 0.1 mm per year
Arguments in favor of rolled steel pipes:
- structural rigidity - the material is equally good for small wells (50 m) and for deep drilling (up to 300 m);
- precise axial alignment of the assembly and reliability of inter-pipe joints;
- stability of the material – when in contact with water, steel does not emit harmful substances;
- possibility of maintenance - due to the mechanical strength and resistance to vibration in the installed casing, cleaning of the well channel and additional drilling in case of silting or clogging is permissible.
The main disadvantage of steel mains is the high cost of the material. Manufacturers of cheaper analogues, extolling their products, appeal to another disadvantage of steel - the formation of rust.
There is an opinion that the resulting pollution worsens the quality of water and increases the iron content in it. However, tests of well water show that this is a myth.
Rust is insoluble in water. Even a household filter can retain oxidized metal particles. A possible problem due to rust is the breakdown of pumping equipment designed to pump clean water
Rolled metal with corrosion protection is more expensive than conventional steel pipes, but the technical and operational features of the materials cast doubt on the advisability of overpaying.
Enameled pipes . The coating prevents corrosion, but it is very fragile and it is unlikely to be able to avoid damage during casing. Places of chips and microcracks in enamel are points where rust appears.
During the destruction process, through corrosion may form in the damaged area, since thinner metal is used in the production of enameled pipes.
The enameled pipeline meets all sanitary and hygienic standards and does not change the taste of the water. The disadvantage of the material is the impossibility of fully cleaning the line due to the fragility of the enamel
Galvanized pipeline . With regular contact with water, zinc oxide is formed on the walls of the pipe - a substance hazardous to health. The use of galvanizing is permissible only when constructing a technical well.
The standard thickness of a galvanized pipe is 2-2.5 mm - this is not always enough to ensure structural rigidity. Such a highway is subject to deformation due to soil movements
Stainless steel . The material has all the advantages of rolled steel and an even higher cost. Stainless steel is characterized by its anti-corrosion resistance, which has a positive effect on its service life.
Is it worth buying stainless steel if the service life of a high-yield well is equal to the service life of a steel pipe? We must start from the financial capabilities and purpose of the well.
The installation of a metal main is economically justified when constructing a deep artesian well designed for regular use.
It is advisable to make “surface” sand channels for seasonal use from more affordable materials.
Type #2 - corrosion resistance of asbestos cement
Asbestos cement pipes, which have been used in the organization of water disposal for more than 70 years, have also been tested for years.
The material has some positive qualities:
- asbestos cement is absolutely not subject to corrosion;
- neutral composition of the material - the components do not enter into chemical reactions;
- unlimited service life - more than 60-70 years;
- low cost.
Despite their significant advantages, asbestos-cement elements are rarely used today in the development of a “water source”.
The main disadvantage of asbestos cement is fragility. In order to strengthen the pipe wall, they make it thicker, which increases the weight of the product and forces them to dig a hole of a larger diameter.
The negative aspects of asbestos cement include:
- Installation difficulties . Installation of a fragile main requires highly qualified performers. The work is carried out using lifting equipment.
- No thread . The sections of the main line are connected end-to-end - achieving complete tightness of the fixation points without threads is problematic.
- Questionable security . There is a theory that asbestos fibers contain chrysotile, a source of carcinogenic substances that have a detrimental effect on health. However, in practice this statement has not been proven.
- Difficult to clean . Concrete is a porous material in which dirt accumulates in microcracks. To perform high-quality cleaning of the casing walls, the well will have to be completely drained.
After installing the asbestos-cement casing, subsequent drilling operations in the well are excluded.
The technical characteristics of the material do not allow the use of asbestos cement pipes for a “sandy” source. This casing is applicable for artesian wells with a depth of no more than 100 m
Type #3 - wear-resistant and affordable plastic
Relatively recently, the market for casing products has been replenished with plastic pipes. Modern technologies have provided worthy competition to traditional steel pipes.
Comparative advantages of polymer elements:
- immunity to water - even with constant contact with a humid environment, corrosion does not form on the plastic;
- retain their structure for a long time and do not collapse;
- do not affect the composition of drinking water;
- the material does not provoke the development of pathogenic microorganisms;
- ease of installation and transportation due to low weight;
- it is possible to use a threaded connection to assemble the column, ensuring absolute tightness of the joints;
- cost-effectiveness - a well with plastic pipes will cost an order of magnitude cheaper than metal or asbestos-cement casing.
The expected service life of a polymer water main is about 50 years. This theory is based on the corrosive inertness of the material.
The main disadvantage of plastic is low strength. Therefore, polymer pipes can only be installed in single-pipe wells not exceeding a depth of 50 m, or in double-pipe wells as internal casing
An additional argument against the use of plastic elements is sensitivity to temperature changes and mechanical stress. The plastic casing will not withstand soil movements and will deform in severe frosts.
Polymer water intake pipes are made from different types of raw materials: unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (UPVC), frost-resistant polypropylene (MPP) and low-density polyethylene (HDPE).
The choice of supply pipe for a well pump is based on the technical characteristics of the polymers.
PVC-U pipes are the most durable - the elastic modulus is 3000 MPa. A product with a diameter of 12.5 cm, when immersed in the ground 30 m, can withstand a load of 5 tons or more. Well casing with a uPVC column can be done on almost all types of soil
The weak point of elements made of unplasticized polyvinyl chloride is sensitivity to frost. This problem is solved by installing a heating cable in the well.
Polymer MPP and HDPE pipes have good frost resistance. However, their density is often insufficient for use as a stand-alone casing. Most often, such plastic is used as a production pipe for double-column well construction.
The plastic elements of the highway are joined in different ways. Special welding is used to connect PP pipes. When creating a highway from other polymers, a socket or threaded method of fixation is used
Type #4 - combined pipeline
In order to reduce corrosion processes and improve the quality of the supply water, some drilling companies propose casing the well according to the “pipe-in-pipe” .
A plastic channel made of food-grade HDPE polymer is inserted into the steel line.
Advantages of the combined method:
- Protection against pollution . The plastic pipe acts as a kind of barrier between the water and the steel walls of the casing - less rust gets into the line, which is dangerous for the pumping unit.
- Maintainability . If the production polymer pipe is damaged, it can be replaced with a new one, maintaining the integrity of the casing;
- Possibility of subsequent deepening of the well . If necessary, the plastic “sleeve” is pulled out, the hole is drilled out, and the polymer line is installed back with emphasis on the new horizon.
The “pipe-in-pipe” technology allows for high-quality well maintenance - regular cleaning and prompt filter changes.
Typically, a plastic production pipe passes through the limestone and goes deep into the aquifers. Thus, the steel does not come into contact with the drinking water supply. The disadvantage of a “double” highway is an increase in the cost of the project
Any doubts left?
Are you still in doubt about what diameter of well pipe will be optimal for your site? Feel free to choose a 160 mm food grade polyethylene pipe. To find out more about casing pipes and order well drilling, contact a consultant by calling 8 3452 930-317.
From us you can order drilling, arrangement and repair of wells, as well as water treatment. We work in any area all year round, even with great depths of water carriers, and thanks to modern powerful equipment and a professional approach, we drill reliable, efficient wells with a long service life. Our clients gain access to high-quality, uncontaminated drinking water in the required volume, and can forget for a long time about the need to repair or restore a well, since its average service life is 50 years.
Still have questions? Call +7 3452 930-317
Selection of pipes for well construction
To understand which pipe to choose for a well, you need to plan the upcoming work. Of course, this should be done by specialists. The main planning factors include:
- geological conditions at the drilling site (soil types, etc.);
- depth and types of aquifers;
- estimated demand for water volumes.
When carrying out work on problematic soils, you will need at least an increased thickness of the pipe for the well. There are situations when the casing string has to be made up of two or even three pipes of different sections, inserted one into the other.
When drilling in normal soils up to 100 m deep, pipes with minimal wall thickness are sufficient. For greater depths, you will need thick-walled products. Simply put, the choice of pipes for well construction is determined by objective circumstances. However, to meet the demand for water volumes, a different approach is used.