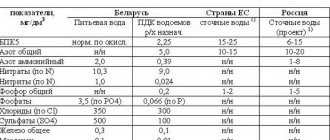
Acceptable indicators of waste impurities
The sewer system of a business or city system is checked for the amount of impurities in the liquid. Their maximum permissible rate in the drain is measured in millimeters per liter. So, the MPC indicators have the following values:
- Number of announced substances – 500;
- BOD – 500;
- COD – 800;
- Remaining dense matter – 2000;
- Essentially containing impurities – 20.
In addition, there are rules and regulations regarding the physical state of water. So, the temperature should not exceed 40 degrees, and the acid level should not exceed 8.5 pH. Control over the condition of wastewater discharges should monitor the amount of suspended elements and the maximum permissible concentration of hydrogen sulfide.
Factors affecting fish
The main factors influencing the life of fish are:
- oxygen;
- water temperature;
- salinity;
- pH;
- carbon dioxide;
- composition of salts.
Transparency is also an important factor for fish life . It depends on the amount of suspended particles, the color of the water and its temperature. The closer the color is to blue, the higher the transparency. If the color tends to yellow, then the water is cloudy and less transparent.
Natural waters should be tasteless and odorless. They appear from the presence of fish, the development of certain types of algae and lower fungi.
MPC of harmful substances
Maximum permissible concentrations of maximum permissible concentrations are a sanitary and hygienic standard established by law. Maximum permissible concentrations of maximum permissible concentrations of harmful substances and their compounds in water are certain concentrations, under the daily influence of which over a long period of time, pathological changes or diseases do not occur in the human body, controlled by modern research methods at any time in a person’s life and subsequent generations.
Table 1. Regional MPCs of wastewater in the Russian Federation and the European Union
| Water quality indicators, chemicals | Maximum permissible concentrations of maximum permissible concentrations of wastewater from industrial enterprises: | ||||||||
| EU | Moscow | Saint Petersburg | Yaroslavl | Tula | Kursk | Izhevsk | Ekaterinburg | MPC RH | |
| pH | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 |
| Iron (Fe), mg/l | 2-20 | 1 | 0,4 | 0,1 | |||||
| Copper (Cu, total), mg/l | 0,1-4 | 0,02 | 0,004 | 0,001 | |||||
| Zinc (Zn2+), mg/l | 0,5-7 | 0,1 | 0,03 | 0,01 | |||||
| Cadmium (Cd, total), mg/l | 0,01-0,6 | 0,005 | 0,003 | 0,005 | |||||
| Nickel (Ni2+), mg/l | 0,5-3 | 0,1 | 0,01 | ||||||
| Chromium (Cr6+), mg/l | 0,1-0,5 | 0,1 | 0,07 | 0,02 | |||||
| Chromium (Cr3+), mg/l | 0,5-5 | 0,1 | 0,4 | 0,07 | |||||
| Aluminum (Al3+), mg/l | 1-10 | 0,04 | |||||||
| Lead (Pb, total), mg/l | 0,2-1 | 0,06 | 0,006 | ||||||
| Silicon (SiO32-), mg/l | 1 | ||||||||
| Tin (Sn, total), mg/l | 2-10 | ||||||||
| Manganese (Mn), mg/l | 0,2 | ||||||||
| Calcium (Ca2+), mg/l | — | 150 | 180 | ||||||
| Hardness, mEq/l | — | ||||||||
| Sulfates (SO42-), mg/l | — | 250 | 100 | ||||||
| Chlorides (Cl-), mg/l | — | 170 | 300 | ||||||
| Nitrates (NO3-), mg/l | — | 23,5 | 40 | ||||||
| Phosphates (PO43-), mg/l | — | 1,5 | 1,6 | ||||||
| Ammonia and ammonium salts, mg/l | — | 23,1 | 3 | ||||||
| Petroleum products, mg/l | 0,1-5 | 0,5 | 0,3 | 0,05 | |||||
| Surfactant, mg/l | 2,5 | 0,9 | |||||||
| Superfloc A-100 Flocculant: anionic polyacrylamide amine - 95% active moisture - 4.5%, impurities - 0.5%, mg/l | 0,25 | ||||||||
| COD, mg/l | 150-400 | 270 | 176 | ||||||
| Suspended substances, mg/l | 50-60 | 150 | 103 | ||||||
| Dry residue, mg/l | — | 500 |
Article by specialists from the Russian Chemical Technical University named after D.I. Mendeleev: Validity and unreasonableness of using various lists of maximum permissible concentrations for wastewater from galvanic production
Table 2. Maximum permissible concentrations of wastewater MPC in the EU
| Belgium | France1 | Germany | England and Wales2 | Italy3 | Holland | Spain | Portugal | |
| Discharge into the city sewerage system (GK) or into a fishery reservoir (RF) | RHV | GK | RHV | |||||
| Silver (Ag), mg/l | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | ||||
| Luminium (Al), mg/l | 10 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1-2 | 5 | ||
| Cadmium (Cd), mg/l | 0,6 | 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,01 | 0,02 | 0,2 | 0,1-0,5 | 0,2 |
| Cyanide (CN free), mg/l | 0,1 | 0,2 | 0,2 | 0,5 | 0,2 | 0,5-1 | 0,1 | |
| Hexavalent chromium (Cr VI), mg/l | 0,5 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,2 | 0,1 | 0,2-0,5 | 0,1 |
| Total chromium (Cr), mg/l | 5 | 3 | 0,5 | 1 | 2 | 0,5 | Cr(III) 2-4 | Cr(III)3 |
| Copper (Cu), mg/l | 4 | 2 | 0,5 | 2 | 0,1 | 0,5 | 0,2-10 | 2 |
| Fluorine (F), mg/l | 10 | 15 | 50 | 6 | 6-12 | 15 | ||
| Iron (Fe), mg/l | 20 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2-10 | 5 | ||
| Mercury (Hg), mg/l | 0,1 | 0,005 | 0,05 | 0,05-0,1 | 0,05 | |||
| Nickel (Ni), mg/l | 3 | 5 | 0,5 | 1 | 2 | 0,5 | 2-10 | 5 |
| Nitrites (NO2), mg/l | 1 | 0,6 | 1 | |||||
| Phosphorus (P), mg/l | 2 | 10 | 2 | 10 | 15 | 10-20 | 10 | |
| Lead (Pb), mg/l | 1 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,2 | 0,2-0,5 | 1 | ||
| Tin (Sn), mg/l | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 10 | 2 | |
| Zinc (Zn), mg/l | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 3-20 | 5 | |
| COD | 300 | 150 | 400 | 160 | 150 | |||
| EDTA, mg/l | ||||||||
| Petroleum products, mg/l | 5 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 5 | 0,1 | 20-40 | ||
| Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) | 1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | |||||
| Suspended substances, mg/l | 50 | 60 | ||||||
| Total salt content, mg/l | no restrictions on sulfates | no limits | no limits | |||||
| Total content of heavy metal ions (IHM) | 15 | no limits | 50kg/year/general 20kg/year/metal | 3 | E metals 15–20 mg/l | |||
| 1. France: Water consumption: 8 liters per 1 m2 of treated surface for each washing stage. 2. Environment Agency of England and Wales. 3. Reduced maximum concentration limits for harmful substances have been adopted by law in some areas (for example, the catchment area of the Venice Lagoon). 4. Maximum permissible concentrations of maximum permissible concentrations of fishery reservoirs |
Who controls the composition and properties of wastewater?
On May 22, 2021, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 22, 2020 No. 728 was adopted, which amended the rules for cold water supply and wastewater disposal and approved new rules for monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 30.3 of the Federal Law of December 7, 2011 No. 416-FZ “On Water Supply and Wastewater Disposal”, the organization that carries out wastewater disposal is responsible for monitoring the composition and properties of wastewater. Or another organization authorized by it.
The subject of control is the composition and properties of wastewater, which are physical and legal. persons who have entered into a water supply and sanitation agreement are sent to the central sewerage system (CSV).
MPC of harmful substances
Maximum permissible concentrations of more than 960 chemical compounds have been established for water, which are grouped into three groups according to the following hazard indicators (LPH - limiting hazard indicator): sanitary-toxicological (s.-t.), general sanitary (general), organoleptic (org. ). Maximum concentration limits for some harmful substances in water bodies are presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Maximum concentrations of harmful substances in water bodies for domestic, drinking and cultural water use, mg/l
| Substance | LPV | MPC |
| Aluminum | S.-t. | 0,5 |
| Ammonia (by nitrogen) | Org. | 1,5 |
| Acetone | S.-t. | 2 |
| Benzpyrene | S.-t. | 0,000005 |
| Petrol | Org. | 0,1 |
| Bromine | S.-t. | 0,2 |
| Beryllium | S.-t. | 0,0002 |
| Bor | S.-t. | 0,5 |
| Bismuth | S.-t. | 0,1 |
| Benzene | S.-t. | 0,1 |
| Dimethylamine | Org. | 0,3 |
| Diethyl ether | Org. | 0,3 |
| Iron | Org. | 0,005 |
| Isoprene | General | 1,2 |
| Acetic acid | General | 0,1 |
| Synthetic fatty acids C5 - C20 | Org. | 0,1 |
| Manganese | Org. | 1 |
| Copper | S.-t. | 3 |
| Methanol | Org. | 0,1 |
| Oil | S.-t. | 0,0005 |
| Mercury | S.-t. | 0,03 |
| Lead | Org. | 1 |
| Carbon disulfide | General | absence |
| Sulfides | S.-t. | 0,05 |
| Formaldehyde | S.-t. | 0,0001 |
| Elemental phosphorus | General | 1 |
| Zinc | Org. | 0,5 |
| Ethylene | Org. | 0,5 |
| Molybdenum | S.-t. | 0,25 |
| Urea | General | 1 |
| Cadmium | S.-t. | 0,001 |
| Ethylene glycol | S.-t. | 1 |
Maximum permissible concentrations of harmful substances for fishery reservoirs and watercourses are established for 521 ingredients, grouped into groups according to the following LPs: toxicological, organoleptic, fishery and general sanitary. Water for drinking animals, according to standards, should not be inferior to the quality of drinking water, however, the requirements for organoleptic properties may be slightly reduced. Only in exceptional cases, in areas with a shortage of fresh water, in agreement with the sanitary-epidemiological service and veterinary supervision, is it allowed to use water of high mineralization for washing and watering animals, preparing feed and cleaning premises. The most stringent requirements must be placed on the condition of water used in livestock farming, since infection of animals through water and the development of epizootics cause enormous damage to the national economy.
It should be noted that the currently used methods for assessing water quality using the system of maximum permissible concentrations of pollutants do not provide a complete picture of the state of natural waters and are not a sufficient guarantee of their protection from pollution. The conditions under which the discharge of municipal and industrial wastewater into reservoirs and watercourses is possible are determined by the “Rules for the protection of surface waters from wastewater pollution” and the “Rules for the sanitary protection of coastal sea waters”, approved in 1974. But these rules are designed to ensure the purity of the reservoir only at the sites of drinking, cultural and household or fishery water use points. This approach has already led to the fact that many rivers in our country are polluted locally or continuously throughout almost their entire length. In stagnant and low-flowing reservoirs, self-purification processes proceed even more slowly and emergency situations often arise. Such phenomena occurred in Lake Ladoga, one of the sources of water supply for St. Petersburg, and in many large reservoirs. All modern treatment facilities are built using destructive treatment methods, which boil down to the destruction of water polluting substances through their oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, decomposition, etc., and the decomposition products are partially removed from the water in the form of gases or sediments, and partially remain in it in the form of soluble mineral salts. As a result, so-called non-toxic mineral salts enter natural waters in quantities corresponding to the maximum permissible concentrations, but many times higher than their natural concentrations in the aquatic environment. Therefore, the discharge of wastewater into rivers and reservoirs, which has undergone deep purification from organic compounds of nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur and other elements, nevertheless increases the content of soluble sulfates, phosphates, nitrates and other mineral salts in the water, causing eutrophication of reservoirs, their “blooming”. » due to the rapid development of blue-green algae; the latter, dying, absorb a lot of oxygen and deprive the water of its ability to self-purify.
Modern industry annually synthesizes many new substances; the establishment of their maximum permissible concentrations is inevitably delayed, especially since, when these substances enter water, they can create new, unexplored combinations of compounds with unknown properties.
Thus, the existing MPCs developed by the sanitary and hygienic service do not fully reflect the impact of alien substances on aquatic ecosystems.
Definition
Enterprise wastewater includes water that, after being used in the industrial cycle, is contaminated with production waste.
Almost every industry uses water in its production process, which contaminates it with waste and can change its physical characteristics, such as temperature. Nowadays, in modern enterprises, wastewater is divided into categories according to composition, according to the conditions of disposal and treatment, as well as further use in a closed water supply cycle.
MPC classification
Sampling of wastewater at the enterprise is carried out by special environmental organizations. The peculiarities of their analysis are to identify maximum permissible concentrations based on various indicators. If there is any excess of the norm, then GOST provides for punishment of the person who caused harm to the natural environment.
Hygienic MPCs combine substances that, if exceeded, can cause harm to human health or lead to deterioration in water quality. The standard regulates the amount of toxic elements in water bodies and water storage areas.
One of the most dangerous impurities can be the chemical type. There can be a large amount of substances of this nature, so their maximum permissible concentrations are divided into the following groups:
- Excessively dangerous concentrations;
- Impurities with a high level of danger;
- Hazardous elements;
- Substances of moderate degree of danger.
Conducting an analysis of enterprises includes special formulas and methods for calculating the presence of deviations from the norms. Diagnostics should be characterized by the frequency chosen by the organization conducting the inspection.
What is included in the range of services provided?
To eliminate excesses of the maximum permissible concentration of wastewater, it is necessary to carry out a set of works to restore the functionality of sewer networks and treatment facilities. Our company employees will carry out the following procedures:
- Sewer pipes, tanks and chambers of treatment facilities are washed. The hydrodynamic method will remove accumulated substances and normalize their concentration. Eliminating excesses of wastewater MPC requires working with the entire sewer network. We guarantee that we will quickly complete the task.
- In the course of localizing the reasons for exceeding the maximum permissible concentration of wastewater, it is necessary to conduct a complete comprehensive diagnosis and examination of the entire system. Telediagnostics allows you to determine the location of illegal tappings, blockages, damage to the walls of sewer pipes, malfunctions or destruction of wastewater treatment facilities that require elimination. After the diagnosis, a detailed report and plan are drawn up for the replacement of damaged defective sections of the network and/or reconstruction of existing treatment facilities and their individual structural elements.
- Reconstruction of existing or installation of new treatment facilities or individual modules is carried out. Old concrete structures often fail to cope with the task and are in deplorable condition, which is why maximum permissible concentrations are exceeded. We will be able to replace them with high-tech, efficient equipment. The buildings of NevaECO treatment facilities are made of fiberglass. Composite material is not destroyed by corrosion and aggressive chemical environments, so there is no doubt that the equipment will last a long time.
- Planned subscriber maintenance of networks and sewerage structures of the customer’s facility is carried out - thus achieving stable MPC indicators within the normal range throughout the entire operation of the enterprise.
Norms of maximum concentration limits for pollutants in wastewater discharged into sewers in cities.
| Ingradient | Units | Permissible concentration |
| Biochemical oxygen demand | ||
| Suspended solids | ||
| Ammonium salt nitrogen | ||
| Sulfates | ||
| Nitrate nitrogen | ||
| Petroleum products | ||
| Chrome general | ||
| General phosphorus |
Methods and methods for determining the content of pollutants in wastewater:
Biochemical oxygen consumption is measured by a BOD tester.
Suspended solids - determined by filtration through a membrane filter. Glass, quartz or porcelain, paper are not recommended due to hygroscopicity.
Nitrogen ammonium salts - the method is based on the interaction of ammonium ion with Nessler's reagent, resulting in the formation of mercury iodide - yellow ammonium:
NH 3 +2 (HgI 2 + 2 K) + 3 OH=3 HgI 2 + 7 KI + 3 H 2 O.
Sulfates - the method is based on the interaction of sulfate compounds with barium chloride, resulting in the formation of an insoluble precipitate, which is then weighed.
Nitrates - the method is based on the interaction of nitrates with sulfasalicylic acid to form a yellow complex compound at pH = 9.5-10.5. Measurements are carried out at 440 nm.
Petroleum products are determined by the gravimetric method, after pre-treating the test water with chloroform.
Chromium - the method is based on the interaction of chromate ions with diphenylcarbazide. As a result of the reaction, a purple compound is formed. Measurements are carried out at λ=540 nm.
Copper - the method is based on the interaction of Cu 2+ ions with sodium diethyldithiocarbonate in a weak ammonia solution with the formation of copper diethyldithiocarbonate, colored yellow-brown.
Nickel - the method is based on the formation of a complex compound of nickel ions with dimethylglyoxin, colored brownish-red. Measurements are carried out at λ=440 nm.
Zinc - the method is based (at pH = 7.0 - 7.3) on the compound of zinc with sulfarsazene, colored yellow-orange. Measurements are carried out at λ = 490 nm.
Lead - the method is based on the combination of lead with sulfarsazene, colored yellow-orange. Measurements are carried out at λ=490 nm.
Phosphorus - the method is based on the interaction of ammonium molybdate with phosphates. A solution of stannous chloride is used as an indicator. Measurements are carried out on KFK - 2 at λ = 690-720 nm.
Nitrites - the method is based on the interaction of nitrites with Griess reagent to form a yellow complex compound. Measurements are carried out at λ=440 nm.
Iron - the method is based on sulfasalicylic acid or its salts (sodium) form complex compounds with iron salts, and in a weakly acidic environment, sulfasalicylic acid reacts only with Fe +3 salts (red color), and in a weakly alkaline environment - with Fe +3 and Fe +2 salts ( yellow color).
Compound
In water, industrial waste forms complex multicomponent mixtures that are difficult to remove. The nature of pollution from discharges depends on the industry and the materials processed. For a clear example, here is a table of the composition of discharges from various enterprises.
| Classification of wastewater from various enterprises | |
| Metallurgical industry | Mineral impurities, dust, dirt, sand, scale, oils, heavy metals, acids |
| Pulp and paper industry | Fibers, selenium, chlorine, sulfur dioxide, turpentine |
| Mechanical engineering industry | Petroleum products, phenols, suspended substances |
| Oil refining industry | Petroleum products, sulfates, suspended solids, chlorides |
| Poultry and meat processing plants | Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, viruses and bacteria |
| Fishing industry | Fats, vegetable oils, proteins, minerals |
| Oil industry | Hydrogen sulfide, paraffins, ammonia, mercaptans, sulfides, phenols, petroleum products, mineral salts, ammonium nitrogen |
| Plastic production | Phenols, plasticizers |
| Mining and processing industry | Heavy metals, acids, organic solvents |
| Coal industry | Suspended substances (coal dust and particles of associated rocks), petroleum products in the form of mineral oils |
| Textile industry | Mineral and organic impurities, reagents, detergents, fibers and suspended solids |
| Canned food production | Suspended solids, ammonium nitrogen, chlorides, sulfates, ether-soluble substances, phosphorus |
| Sugar and starch production | Nitrogen, potassium, calcium and phosphorus |
| Dairy industry | Milk serum |
MPC
For surface water bodies, the following maximum permissible concentrations of pollutants in the waters of water bodies are used:
| No. | Analyzed indicators | Hazard class (Order of Rosrybolovstvo dated January 18, 2010 No. 20 and SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00) | MPC of water bodies of fishery importance (Order of the Federal Agency for Fisheries dated August 4, 2009 N 695 On approval of guidelines for the development of water quality standards in water bodies of fishery importance, including standards for MPC of harmful substances in waters of water bodies of fishery importance | MPC of water bodies of fishery importance (Order of Rosrybolovstvo dated January 18, 2010 No. 20) | Maximum permissible concentrations of water bodies for drinking, domestic and recreational water use (GN 2.1.5.1315-03 as amended by GN 2.1.5.2280-07 and SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00) |
| water use category | water use category | ||||
| highest and first | second | For drinking and domestic water use, as well as for water supply to food enterprises (first category) | For recreational water use, as well as within populated areas (second category) | ||
| 1 | Transparency, cm | not lower than 20 | |||
| 2 | Suspended substances, mg/dm3 | the content of suspended substances at the control site (point) should not increase compared to natural conditions by more than: | Within populated areas, when discharging wastewater, carrying out work on a water body and in the coastal zone, the content of suspended substances at the control site (point) should not increase compared to natural conditions by more than 0.75 mg/m3. dm | ||
| 0.25 mg/dm3 | 0.75 mg/dm3 | ||||
| 3 | Water mineralization, mg/l | no more than 1000 (at the control point) | |||
| 4 | Hydrogen value (pH) | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | 6,5-8,5 | |
| 5 | Total BOD, mg O2/l (at a temperature of 20 °C should not exceed in water of water bodies) | 3,0 | 3,0 | ||
| 6 | BOD5, mgO2/l (should not exceed at a temperature of 20 degrees C) | 2 (at the control point) | 4 (at the control point) | ||
| 7 | COD, mgO/l | 30 (at the control point) | |||
| 8 | Dissolved oxygen O2, mg/dm3 | During the winter (under the ice) period there should be at least | At least 4 | ||
| 6 | 4 | ||||
| In the summer (open) period, all water bodies must have at least 6 | |||||
| 9 | Chloride anion Cl-, mg/l | 300 | 350 | ||
| 10 | Sulfate anion, SO4, mg/l | 100 | 500 | ||
| 11 | Phosphates (polyphosphates) Men(PO3)n, Men+2PnO3n+1, MenH2PnO3n+1, mg/l | 0.05 (oligotrophic water bodies) for phosphorus 0.15 (mesotrophic water bodies) for phosphorus 0.2 (for eutrophic water bodies) for phosphorus | 3.5 (1.14 for phosphorus) | ||
| 12 | Ammonium ion NH4+, mg/l | 0.5 (0.4 nitrogen) m | 1.93 (1.5 for nitrogen) | ||
| 13 | Nitrite anion NO2-, mg/l | 0.08 (0.02 for nitrogen) | 3.3 (1 for nitrogen) | ||
| 14 | Nitrate anion NO3-, mg/l | 40 (9 for nitrogen) | 45 (10.16 for nitrogen) | ||
| 15 | Iron Fe, mg/l | 0,1 | 0,3 | ||
| 16 | Divalent manganese Mn2+, mg/l | 0,01 | 0,1 | ||
| 17 | Copper Cu, mg/l | 3 | 0,001 | 1 | |
| 18 | Zinc Zn, mg/l | 3 | 0,01 | 1 | |
| 19 | Lead Pb, mg/l | 2 | 0,006 | 0,01 | |
| 20 | Chromium3+ Cr, mg/l | 3 | 0,07 | ||
| 21 | Chromium6+ Cr, mg/l | 3 | 0,02 | 0,05 | |
| 22 | Chromium total Cr, mg/l | 0,05 | |||
| 23 | Aluminum Al, mg/l | 4 | 0,04 | 0,2 | |
| 24 | Nickel Ni, mg/l | 3 | 0,01 | 0,02 | |
| 25 | Cadmium Cd, mg/l | 2 | 0,005 | 0,001 | |
| 26 | Cobalt Co, mg/l | 3 | 0,01 | 0,1 | |
| 27 | Sulfides, mg/l | 0.005 For oligotrophic reservoirs 0.0005 | 0,05 | ||
| 28 | Surfactant (sodium dodecyl sulfate), mg/l | 4 | 0,5 | ||
| 29 | Petroleum products, mg/l | 3 | 0,05 | 0,3 | |
| 30 | Phenol (another name is hydroxybenzene or carbolic acid) C6H5OH, mg/l | 3 | 0,001 | 0,001* | |
| 31 | Formaldehyde, mg/l | 4 | 0,1 | 0,05 | |
| 32 | Arsenic | 0,05 | 0,01 | ||
| 33 | Calcium | 4 | 180 | ||
| 34 | Magnesium | 4 | 40 | 50 | |
| 35 | Potassium | 4 | 50 (10 for reservoirs with mineralization up to 100 mg/l) | ||
| 36 | Selenium | 2 | 0,002 | 0,01 | |
| 37 | Fluoride anion | 3 | 0.05 (in addition to the background fluoride content, but not higher than their total content of 0.75 mg/l) | ||
| 38 | Sodium | 4 | 120 | 200 | |
| 39 | Molybdenum | 2 | 0,001 | 0,07 | |
| *from GN 2.1.5.1315-03: MPC of phenol - 0.001 mg/l - is indicated for the amount of volatile phenols that give water a chlorophenolic odor during chlorination (test chlorination method). This maximum permissible concentration applies to water bodies for domestic and drinking water use, subject to the use of chlorine for water disinfection during its purification at water supply facilities or when determining the conditions for the discharge of wastewater subjected to disinfection with chlorine. In other cases, the content of the amount of volatile phenols in the water of water bodies is allowed in concentrations of 0.1 mg/l. |
Daily water consumption standards
Water consumption standards SNiP according to the documentation are used for drinking and domestic needs. This includes cooking, daily hygiene, and much more. And for a private house, we also add washing the vehicle, watering the house area and flower beds, filling the pool, etc. Let's consider the daily water consumption standards of SNiP:
- Cooking – 3 liters;
- Drinking water – up to 2 liters;
- Hand washing (without stopping the water) – up to 8 liters;
- Oral hygiene (without stopping the water) – up to 7 liters;
- Toilet flushing – up to 12 liters at a time;
- Taking a shower – 20 liters/minute;
- Taking a bath – 150 liters;
- Washing – up to 100 liters;
- Washing dishes – up to 10 liters at a time.
In total, we get from 300 to 570 liters per day. From the calculation it is clear that water consumption by SNiP differs significantly from actual indicators. Therefore, it is logical to think about saving water consumption.
Permitting documents for the discharge of industrial wastewater
If the enterprise being opened will cause harm to the environment as a result of its activities, it must obtain permitting documentation. To obtain a water use permit, an enterprise must have its wastewater analyzed in an accredited laboratory, where competent employees will take water samples for research. Sampling should be done after wastewater has passed through treatment facilities. Based on the results of the study, a protocol is formed, which indicates the content of harmful impurities. To obtain permission from Rosprirodnadzor, harmful substances in the protocol must not exceed the maximum permissible concentration. Also, a MAP norm is developed for each individual water user enterprise.
In addition to chemical analysis, the enterprise must:
- make an assessment of the amount of wastewater that must be removed from the enterprise in a certain unit of time;
- develop an action plan to reduce concentrations of harmful substances that negatively affect the environment;
- agree on the optimal discharge point for industrial waters;
- collect a complete package of permitting documents.
Determination of explosive concentration
Measurement techniques
The main method of analysis is gravimetric. The essence of the approach is to purify water samples through filters and then dry them to a constant weight at a certain temperature. More details about this in RD 52.24.468-2005 “Suspended substances and the total content of impurities in waters. Methodology for measuring mass concentration using the gravimetric method" and PND F 14.1:2:4:254-2009 "Methodology for measuring mass concentrations of suspended solids and calcined suspended solids in samples of drinking, natural and waste water using the gravimetric method."
Overview of instruments and measuring instruments
To measure the amount of suspended solids in a water sample, use:
- Laboratory scales (GOST R 53228)
- Graduated cylinders (GOST 1770)
- Mechanical watches (GOST 3145)
- Laboratory funnels (GOST 25336)
- Glasses and cups (GOST 25336)
- Biological dishes (Petri dishes) (GOST 25336)
- Desiccator (GOST 25336)
- Tweezers, spatula (GOST 21241 and GOST 9147)
- Drying cabinet and/or crucible (TU 64-1-909-80)
- Electric stove with adjustable heating power (GOST 14919)
- Vacuum filtration device (TU 3616-001-32953279).
As with other types of laboratory measurements, all instruments and measuring instruments must be tested and comply with the conditions of the relevant GOSTs.
Measurement conditions
To perform measurements in the laboratory, conditions must be observed that meet the requirements of regulatory and technical documentation (for example, PND F 14.1:2:4.254-09), namely:
- Ambient temperature from 16 to 28℃
- Atmospheric pressure from 84 to 106 kPa
- Relative humidity no more than 80% at 25℃
- AC frequency 50±1Hz
- Mains voltage 220±22 V
Operator qualification
Like many other chemical methods. water analysis, analysis for the content of suspended substances should be carried out by persons with the qualification of a chemical technician or chemical laboratory assistant, familiar with the technique of gravimetric analysis.
Fines for water users
View fines for water users
The size of fines for water users depends on the nature of the violation. Water pollution can even threaten the water user with criminal liability. Fines will not affect you only if you comply with environmental legislation and have all the permits required by the enterprise. EcoPromCenter specialists will help you with any issue of water use!
At the time of writing, changes are still being made. For subscribers with wastewater disposal of less than 30 cubic meters per day, the fee is 20,000 rubles/month. In addition, it is planned to introduce a new service regarding payment for environmental damage to wastewater networks. It should be taken into account that it is necessary to wait for the final results of the changes to fully understand how water users will have to report.
Types of surfactants
Depending on the properties of the synthetic surfactant when dissolved in water and its characteristics, the following types of surfactants are distinguished [3]:
- anionic;
- cationic;
- ampholytic;
- nonionic.
Anionic - form negatively charged ions in water. These include salts of sulfuric acid esters and salts of sulfonic acids (sulfonates). The radical can be alkyl, alkyl acrylic, alkyl naphthyl. Compounds may contain double bonds and functional groups.
Cationic - ionizes in an aqueous solution to form positive organic ions. These are quaternary ammonium salts, usually consisting of a straight chain hydrocarbon radical (number of carbon atoms - from 12 to 18); methyl, ethyl, or benzyl radical; a bromine, chlorine, iodine atom or an ethyl or methyl sulfite residue.
Ampholytic - exhibit different properties depending on the pH of the environment. In an acidic solution they exhibit cationic properties, and in an alkaline solution they exhibit anionic properties.
Nonionic - do not dissociate into ions in an aqueous solution.
Based on the degree of biochemical stability and molecular structure, synthetic surfactants are divided into soft, intermediate and hard. Primary and secondary alkyl sulfates of normal structure are most easily oxidized. In compounds with more branched chains, the oxidation rate decreases. Refractory surfactants include alkylbenzenesulfonates based on propylene tetramers.